Abstract.
Objective
Flurbiprofen and nitroflurbiprofen were evaluated in a caecal ligation puncture (CLP) model of septic shock in the rat.
Methods and Results
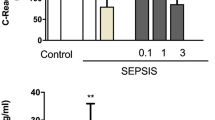
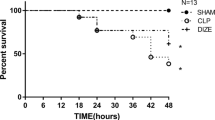
CLP (12 h) reduced blood pressure (72.5 ± 1.0 mm Hg c. f. 101.0 ± 3.6 mm Hg, P < 0.05), and increased plasma NOx (153.0 ± 11.5 μM c. f. 36.2 ± 3.2 μM, P < 0.05), IL-1β (534.0 ± 93.1 pg/mL c. f.; 9.6 ± 9.6 pg/mL, P < 0.05), TNF-α (88.0 ± 13.6 pg/mL, P < 0.05), inflammatory damage in lung and liver, and mortality. Both flurbiprofen (21 mg/kg, p. o.) and nitroflurbiprofen (30 mg/kg, p. o.) prevented the fall in blood pressure (e. g. 80.4 ± 2.1 mm Hg and 79.8 ± 1.2 mm Hg respectively, 12 h, P < 0.05), reduced organ damage and prolonged survival. Nitroflurbiprofen (but not flurbiprofen) increased plasma NOx and reduced plasma TNF-α concentration at all time points (except 1 h). Neither drug affected plasma IL-1β-levels.
Conclusions
These results suggest a protective effect of flurbiprofen and nitroflurbiprofen in septic shock.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- Nox:
-
nitrite/nitrate
- FLURB:
-
flurbiprofen
- NOF:
-
nitroflurbiprofen
- VEH:
-
vehicle
- NO-NSAID:
-
NO-releasing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- CLP:
-
Caecal ligation puncture
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- MODS:
-
multiple organ dysfunctions
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 28 September 2005; returned for revision 13 January 2006; returned for final revision 31 May 2006; accepted by K. Visvanathan 28 June 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anuar, F., Whiteman, M., Bhatia, M. et al. Flurbiprofen and its nitric oxide-releasing derivative protect against septic shock in rats. Inflamm. res. 55, 498–503 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-006-5150-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-006-5150-y