Abstract.
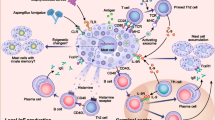
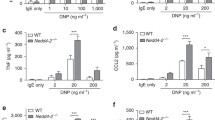
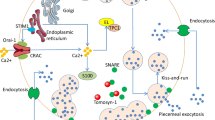
Mast cells (MCs) are both central effectors and signaling cells in allergic reactions. Their key role in the immunopathology of asthma and other allergic diseases has been well documented. Molecular events leading to MC activation have not been yet fully established, however. Recent studies emphasize the key role of the protein tyrosine kinases Lyn and Fyn in MC signal transduction. The finding that Lyn kinase negatively regulates MC degranulation and that Fyn kinase enhances this effector response is of great importance. This creates new possibilities for therapeutic intervention in asthma and other allergic diseases. This review summarizes current knowledge on MC intracellular signaling and discusses the most recent strategies for the treatment of allergic diseases based on MC signaling pathway inhibition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MC:
-
mast cell
- BMMCs:
-
bone marrow-derived MC
- Cbp:
-
Csk-binding protein
- CRH:
-
corticotropin-releasing hormone
- Csk:
-
carboxy-terminal Src kinase
- DAG:
-
diacylglycerol
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- IgE:
-
immunoglobulin E
- FcɛRI:
-
high-affinity receptor for IgE
- FcγRI:
-
high-affinity receptor for IgG
- Grb2:
-
growth factor receptor-bound 2
- Gab2:
-
Grb2-associated binder protein 2
- IP3:
-
inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate
- ITAMs:
-
immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs
- LAT:
-
linker for T cell activation
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MEK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
- PAR:
-
protease-activated receptor
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase
- PDK1:
-
PI3K-dependent protein kinase-1
- PIP2:
-
phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate
- PIP3:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- PLA2:
-
phospholipase A2
- PLCγ1/2:
-
phospholipase Cγ1/2
- PTK:
-
protein-tyrosine kinase
- SLP-76:
-
SH2-containing leukocyte-specific protein of 76 kDa
- Syk:
-
spleen tyrosine kinase
- Vav1:
-
hematopoietic-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kopeć, A., Panaszek, B. & Fal, A.M. Intracellular signaling pathways in IgE-dependent mast cell activation. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 54, 393–401 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-006-0049-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-006-0049-4