Abstract
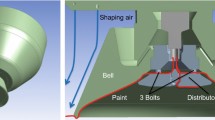
The current trend in automotive finishing industry is to use more electrostatic rotating bell (ESRB) need space to their higher transfer efficiency. The flow physics related with the transfer efficiency is strongly influenced by operating parameters. In order to improve their high transfer efficiency without compromising the coating quality, a better understanding is necessary to the ESRB application of metallic basecoat painting for the automobile exterior. This paper presents the results from experimental investigation of the ESRB spray to apply water-borne painting. The visualization, the droplet size, and velocity measurements of the spray flow were conducted under the operating conditions such as liquid flow rate, shaping airflow rate, bell rotational speed, and electrostatic voltage setting. The optical techniques used in here were a microscopic and light sheet visualization by a copper vapor laser, and a phase Doppler particle analyzer (PDPA) system. Water was used as paint surrogate for simplicity. The results show that the bell rotating speed is the most important influencing parameter for atomization processes. Liquid flow rate and shaping airflow rate significantly influence the spray structure. Based on the microscopic visualization, the atomization process occurs in ligament breakup mode, which is one of three atomization modes in rotating atomizer. In the spray transport zone, droplets tend to distribute according to size with the larger drops on the outer periphery of spray. In addition, the results of present study provide detailed information on the paint spray structure and transfer processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Bauckhage, K., Scholz, T. and Schulte, G., 1994, “Atomization of Water-based Metallic Paints by Means of Electrostatic Rotary Atomizers,”Proceedings of ICLASS-94. pp. 1010-1019. July 18-22, 1994, Rouen, France.
Bauckhage, K., Scholz, T. and Schulte, G., 1995, “The Influence of Applied High-Voltage on the Atomization Characteristic of a Commercial High-Speed Rotary Atomizer,”4th International Congress Optical Particle Sting, Nurnberg, Germany, 21-23 March 1995, pp. 337-346.
Bell, G.C. and Hochburg. J., 1981, “Mechanisims of Electrostatic Atomization, Transport, and Deposition of Coating,”Proceddings of Seventh International Conference in Organic Science and Technology, Athens, Greece.
Corbeels, P. L., Senser, D. W. and Lefebvre. A. H., 1992. “Atomization Characteristics of a High Speed Rotary Bell Paint Applicator.”Atomization and Sprays, Vol. 2, pp. 87–99.
Dombrowski, N. and Lloyd. T. L., 1974, “Atomization of Liquids by Spinning Cups,”Chemical Engineering Journal, Vol. 8, pp. 63–81.
Domnick, J., Lindenthal, A.. Mundo. C, Ruger, M. and Sommerfeld, M., 1994, “Combined Experimental and Numerical Investigations of the Spray Coating Process,”7th Int. Coating Process Science and Techn. Symp. Atlanta. April 18-21.
Elmoursi, A. A. and Lee, H. Y., 1989, “Droplet and Flake Size Distribution in the Electrostatic Spraying of Metallic Paint,”SAE paper 890354.
Fukuta. K.. Murate, M., Ohhashi, Y. and Toda. K., 1993, “New Electrostic Rotary Bell for Metallic Paint,”Metal Finishing, October, 1993, pp. 39-42.
Hines, R. L., 1996, “Electrostatic Atomization and Spray Painting,”J. Applied Phys., Vol. 37, pp. 2730–2736.
Hinze. J. O. and Milborn, H., 1950, “Atomization of Liquids by Means of a Rotating Cup,”Journal of Applied Mechanics, Vol. 17, pp. 145–153.
Inkpen, S. and Melcher, J. R., 1987, “Dominant Mechanisms for Color Differences in the Mechanical and the Electrostatic Spraying of Metallic Paints,”Industrial Engineering Chemistry Research, Vol. 26, pp. 1645–1653.
Kelly, A. J., 1994, “On the Statistical Quantum and Practical Mechanics of Electrostatic Atomization.”Journal of Aerosol Science, Vol. 25(6), pp. 1159–1177.
Kwok, K. C. and Liu, B. Y. H., 1991, “New Research Approach to Air Spray Painting.”Proceedings of ICLASS-91, Gaithersburg, MD, pp. 105-112.
Lefebvre, A. H., 1989,Atomization and Sprays. pp. 189–193, 222–228, Taylor and Francis, Bristol, PA.
Marshall. W. R., 1954. “Performance Characteristics of Spinning-Disk Atomizers,”in Chapter 3 of Atomization and Spray Drying, Republished by Johansen Crosby & Assoc, Inc., Madison, Wl. 1986.
Matsumoto, S., Belcher, D. W. and Crosby, E. J., 1985, “Rotary Atomizers : Performance Under- standingandPrediction,” Proceedings of ICLASS85, Madison. WI, pp. lA/l/l-21.
Okuda. H. and Kelly, A. J., 1996. “Electrostatic Atomization-Experiment, Theory and Industrial Applications,”Physics of Plasmas. Vol. 3(5), pp. 2191–2196.
Tachi, K., 1985, “Effect on Rotating Cup Shapes and Spray Conditions on Spray Atomization.”J. of the Japan Soc. of Colour Material, Vol. 58(7), 1985.
Tachi, K. and Okuda. C., 1992. “Color Variation of Automotive Metallic Finishes,”Journal of Coatings Technology,Vol. 64(81l),pp. 64–77.
Tong, E., Chmielewski, G. and Nivi. H.. 1995. “Paint Spray Airflow Management.”Proceedings of International Body Engineering Conference & Exposition (IBEC 95), pp. 39-49, Oct. 31-Nov. 2. 1995, Detroit. MI, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Im, KS., Lai, MC. & Yoon, SJ. Spray characteristics on the electrostatic rotating bell applicator. KSME International Journal 17, 2053–2065 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982446
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982446