Abstract
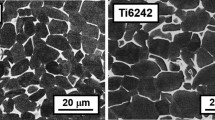
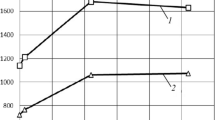
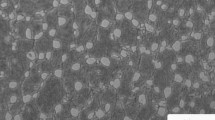
Cylindrical specimens of commercial pure titanium have been compressed at strain rates in the range of 0.1 to 100 s-1 and temperatures in the range of 25 °C to 400 °C. At strain rates of 10 and 100 s-1, the specimens exhibited adiabatic shear bands. At lower strain rates, the material deformed in an inhomogeneous fashion. These material-related instabilities are examined in the light of the “phenomenological model” and the “dynamic materials mode.” It is found that the regime of adiabatic shear band formation is predicted by the phenomenological model, while the dynamic materials model is able to predict the inhomogeneous deformation zone. The cri- terion based on power partitioning is compctent to predict the variations within the inhomo- geneous deformation zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Refences
H.L. Gegel, J.C. Malas, S.M. Doraivelu, and V.A. Shende:Metals Handbook, 9th ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1988, vol. 14, pp. 417–38.
S.L. Semiatin, M.R. Staker, and JJ. Jonas:Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32(9), pp. 1347–54.
H.L. Gegel: inSymposium on Experimental Verification of Process Models, C.C. Chen, ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1983, p. 23.
H. Zeigler:Some Extremum Principles in Irreversible Thermodynamics with Applications to Continuum Mechanics, Progress in Solid Mechanics, 1963, vol. IV, pp. 93–193.
A.K.S. Kalyan Kumar: MSc. Thesis, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, Oct. 1987.
Y.V.R.K. Prasad:Ind. J. Technol., 1990, vol. 28, pp. 435–51.
George E. Dieter:Mechanical Metallurgy, 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill Publishing Company, New York, NY, 1986.
J.J. Jonas, R.A. Holt, and C.E. Coleman:Acta Metall., 1976, vol. 24, pp. 911–18.
S.L. Semiatin, G.D. Lahoti, and S.I. Oh: inMaterial Behavior under High Stress and Ultra High Strain Rates, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1983, p. 119.
S.L. Semiatin and J.J. Jonas:Formability and Workability of Metals: Plastic Instability and Flow Localization, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1984.
J.K. Chakravarthy, Y.V.R.K. Prasad, and M.K. Asundi:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 829–36.
D. Padmavardhani and Y.V.R.K. Prasad:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2985–92.
D. Padmavardhani and Y.V.R.K. Prasad:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2993–3001.
N. Ravichandran and Y.V.R.K. Prasad:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2339–48.
N. Ravichandran and Y.V.R.K. Prasad:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1992, vol. A156, pp. 195–204.
M.C. Somani, E.S.B. Rao, N.C. Birla, M.L. Bhatia, V. Singh, and Y.V.R.K. Prasad:Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 2849–57.
B.V. Radhakrishna Bhat, Y.R. Mahajan, H.Md. Roshan, and Y.V.R.K. Prasad:Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 2223–30.
E.D. Levin:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 256, pp. 1558–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kailas, S.V., Prasad, Y.V.R.K. & Biswas, S.K. Microstructural Features of Flow Instability in α-Titanium Cylinders under High Strain Rate Compression at 25°C to 400 °C. Metall Trans A 24, 2513–2520 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02646530
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02646530