Summary
The carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin have been identified as the macular pigments of the human retina. Nutritional epidemiological reports indicate that high consumption of fruits and vegetables rich in these carotenoids is correlated with reduced risk of some illnesses, e.g. agerelated macular degeneration (AMD).
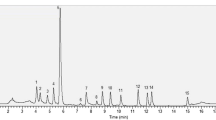
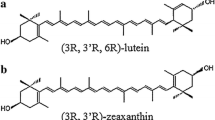
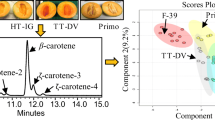
Because carotenoids are extremely sensitive to UV light and oxygen, they occur in nature as several Z/E stereoisomers which can differ considerably in their biological effectiveness. With particular regard to dietary supplementation we have focussed on identification and quantification of all the carotenoid stereoisomers occurring in a variety of raw and processed homegrown and commercial spinach samples, a natural source of carotenoids. Isolation of the unstable carotenoid stereoisomers from biological tissues without sample-preparation artifacts requires a mild, rapid, complete, and reproducible extraction technique such as matrix solid-phase dispersion (MSPD). Separation and unequivocal structural elucidation of the main carotenoid stereoisomers was achieved by use of hyphenated analytical techniques and exclusion of light and oxygen. HPLC analysis with highly selective C30 columns was used for quantitative determination of the main Z/E carotenoid stereoisomers and HPLC-APCI-MS and HPLC-NMR on-line coupling was used for unequivocal structural elucidation. Whereas HPLC-APCI-MS can distinguish between the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin, HPLC-NMR enables identification of all the main Z/E stereoisomers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krinsky, N.I.; Russett, M.D.; Handelman, G.J.; Snodderly, D.M.J. Nutr. 1990,120, 1654–1662.
Sommerburg, O.; Keunen, J.E.E.; Bird, A.C.; van Kuijk, F.J.G.M.Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1998,82, 907–910.
Biesalski, H.K.; Schrezenmeir, J.; Weber, P.; Weiß, H.E.Vitamine, Georg Thieme, Stuttgart,1997.
Van Het Hof, K.H.; West, C.E.; Weststrate, J.A.; Hautvast, J.G.J. Nutr. 2000,130, 503–506.
Castenmiller, J.J.; West, C.E.; Linssen, J.P.; van Het Hof, K.H.; Voragen, A.G.J. Nutr. 1999,129, 349–355.
Boileau, A.C.; Merchen, N.R.; Wasson, K.; Atkinson, C.A.; Erdman Jr, J.W.J. Nutr. 1999,129, 1176–1181.
Brown, L.; Rimm, E.B.; Seddon, J.M.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chaban-Taber, L.; Spiegelman, D.; Willett, W.C.; Hankinson, S.E.Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999,70, 517–524.
Bub, A.; Watzl, B.; Abrahamse, L.; Delincée, H.; Adam, S.; Weber, J.; Müller, H.; Rechkemmer, G.J. Nutr. 2000,130, 2200–2206.
Cooper, D.A.; Eldridge, A.L.; Peters, J.C.Nutr. Rev. 1999,57, 201–214.
Schalch, W.; Dayhaw-Barker, P.; Barker, F.M. In Nutritional and Environmental Influences on the Eye: Taylor, A., Ed., CRC Press LLC,1999, 215–249.
Handelman, G.J.; Snodderly, D.M.; Adler, A.J.; Russett, M.D.; Dratz, E.A.Methods Enzymol. 1992,213, 220–230.
Bone, R.A.; Landrum, J.T.; Friedes, L.M.; Gomez, C.M.; Kilburn, M.D.; Menendez, E.; Vidal, I.; Wang, W.Exp. Eye Res. 1997,64, 211–218.
Snodderly, D.M.Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995,62, 1448–1461.
Khachik, F.; Bernstein, P.S.; Garland, D.L.Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997,38, 1802–1811.
Dachtler, M.; Glaser, T.; Kohler, K.; Albert, K.Anal. Chem. 2001,73, 667–674.
Hammond, B.R.; Johnson, Jr, E.J.; Russell, R.M.; Krinsky, N.I.; Yeum, K.-J.; Edwards, R.B.; Snodderly, D.M.Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997,38, 1795–1801.
Eye Disease Case-Control Study GroupArch. Ophthalmol. 1993,111, 104–109.
Seddon, J.M.; Ajani, U.A.; Sperduto, R.D.; Hiller, R.; Blair, N.; Burton, T.C.; Farber, M.D.; Gragoudas, E.S.; Haller, J.; Miller, D.T.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Willett, W.J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1994,272, 1413–1420.
Barker, S.A.J. Chromatogr. A 2000,885, 115–127.
Barker, S.A.J. Chromatogr. A 2000,880, 63–68.
Sander, L.C.; Sharpless, K.E.; Craft, N.E.; Wise, S.A.Anal. Chem. 1994,66, 1667–1674.
Albert, K.Trends Anal. Chem. 1998,17, 648–658.
Albert, K.J. Chromatogr. A 1999,856, 199–211.
Raitza, M.; Wegmann, J.; Bachmann, S.; Albert, K.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000,39, 3486–3489.
Van Breemen, R.B.; Huang, C.R.; Tan, Y.; Sander, L.C.; Schilling, A.B.J. Mass Spectrom. 1996,31, 975–981.
Tang, G.; Andrien, B.A.; Dolnikowski, G.G.; Russell, R.M.Methods Enzymol. 1997,282, 140–154.
Lacker, T.; Strohschein, S.; Albert, K.J. Chromatogr. A 1999,854, 37–44.
Dachtler, M.; Glaser, T.; Händel, H.; Lacker, T.; Tseng, L.-H.; Albert, K. In Encyclopedia of Separation Science, Level II: Wilson, I.D.; Adlard, E.R.; Cooke, M.; Poole, C.F., Eds, Academic Press, London,2000, 747–760.
Strohschein, S.; Pursch, M.; Albert, K.J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999,21, 669–677.
Albert, K.; Dachtler, M.; Glaser, T.; Händel, H.; Lacker, T.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Strohschein, S.; Tseng, L.-H.J. High Resol. Chromatogr. 1999,22, 135–143.
Vilegas, W.; Vilegas, J.H.Y.; Dachtler, M.; Glaser, T.; Albert, K.Phytochem. Anal. 2000,11, 317–321.
Zechmeister, L.cis-trans Isomeric Carotenoids; Vitamin A and Arylpolyenes, Academic Press, New York,1962.
Lesellier, E.; Tchapla, A.; Marty, C.; Lebert, A.J. Chromatogr. 1993,633, 9–23.
Glaser, T.; Dachtler, M.; Albert, K.GIT Labor-Fachz. 1999,43, 904–909.
US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, USDA-NCC Carotenoid Database for Foods,1998.
http://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp/ Data/car98/car98.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In memoriam professor ernst bayer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glaser, T., Lienau, A., Zeeb, D. et al. Qualitative and quantitative determination of carotenoid stereoisomers in a variety of spinach samples by use of MSPD before HPLC-UV, HPLC-APCI-MS, and HPLC-NMR on-line coupling. Chromatographia 57 (Suppl 1), S19–S25 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02492079
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02492079