Summary
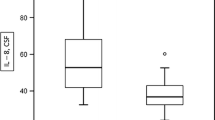
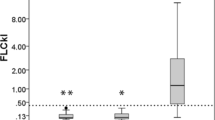
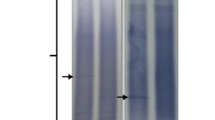
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was examined in 90 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients and in 50 age-matched normal controls. Total protein concentration was significantly higher in ALS patients than in normal controls. CSF IgG and albumin, quantitatively determined by single radial immunodiffusion, were significantly increased in ALS. No difference in serum concentrations was observed between ALS patients and normal controls. On isoelectric focusing a clear-cut “fingerprint” pattern was observed in 11 of 12 cases. These findings support the hypothesis that blood-brain barrier damage occurs in ALS. The finding of a higher mononuclear cell count in young ALS patients is briefly discussed in the light of the hypothesis that an exogenous agent might be of some relevance in pathogenesis. An alteration of at least one of the CSF parameters considered was found in 45.5% of ALS cases.
Zusammenfassung
In 90 Fällen von amyotrophischer Lateralsklerose und bei 50 auch im Alter entsprechenden Kontrollen wurde der Liquor untersucht. Der Eiweißgehalt war bei den Patienten mit ALS signifikant höher als bei den Kontrollen. Die Albuminfraktion und das IgG, die mit Immunodiffusionsmethoden quantitativ bestimmt wurden, waren bei der ALS im Liquor signifikant erhöht, während sie sich im Serum gleich wie bei den Kontrollfällen verhielten. Bei der isoelektrischen Fokusierung ließ sich ein eindeutiges „Finger-print-pattern“ in elf von zwölf Fällen beobachten. Diese Befunde sprechen dafür, daß bei der ALS eine Störung der Blut-Hirnschranke vorliegt. Es wird kurz auf die Beobachtung einer vermehrten Zahl mononukleärer Zellen bei jungen Patienten mit ALS eingegangen und im besonderen die Frage diskutiert, in wieweit ein exogenes Agents in der Pathogenese eine Rolle spielen könnte. Mindestens eines der obern erwähnten Parameter war bei 45% aller ALS Fälle im Liquor verändert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aimard G, Bady B, Baisson D, Trouillas P, Devic M (1976) Sclérose laterale amyotrophique survenue avant 40 ans. Remarques à propos de 25 observations. Rev Neurol (Paris) 132:563–566
Castaigne P, Lhermitte F, Schuller E, Rouques C (1971) Les proteines du liquide céphalo-rachidien au cours de la sclérose latérale amyotrophique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 125:393–400
Fishman RA (1980) Cerebrospinal fluid in diseases of the nervous system. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
Gårde A, Kjellin KG (1971) Diagnostic significance of cerebrospinal fluid examination in myelopathy. Acta Neurol Scand 47:555–568
Guiloff RJ, McGregor B, Thompson E, Blackwood W, Paul E (1980) Motor neuron disease with elevated cerebrospinal fluid protein. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:390–396
Kjellin KG, Stibler H (1976) Isoelectric focusing and electrophoresis of cerebrospinal fluid proteins in muscular dystrophies and spinal muscular atrophies. J Neurol Sci 27:45–57
Kjellin KG, Vesterberg O (1974) Isoelectric focusing of CSF proteins in neurological diseases. J Neurol Sci 23:199–213
Kostulas VK, Link H (1982) Agarose isoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid and serum evaluated on 998 neurological patients. Acta Neurol Scand [Suppl 90] 65:266–267
Laterre EC (1975) Cerebrospinal fluid. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol. 19. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 125–138
Laterre EC, Callewaert A, Heremans JF, Sfaello Z (1970) Electrophoretic morphology of gammaglobulins in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the nervous system. Neurology (Minneap) 20:982–990
Lowenthal A (1964) Agar gel electrophoresis in neurology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Mancini G, Carbonara AD, Heremans JF (1965) Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry 2:235–254
Pena CE (1977) Virus-like particles in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; electron microscopical study of a case. Ann Neurol 1:290–297
Poloni M, Rocchelli B, Mezzarello P, Pinelli P (1982) Cerebrospinal fluid in motor neuron disease: the value of isoelectric focusing (IEF). Acta Neurol (Napoli) 4:271–272
Reiber H (1980) The discrimination between different blood-CSF barrier dysfunctions and inflammatory reaction of the CNS by a recent evaluation graph for the protein profile of cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol 224:89–99
Rosen AD (1978) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clinical features and prognosis. Arch Neurol 35:638–642
Siegel S (1956) Nonparametric statistics for the behavioural sciences. McGraw-Hill, New York
Tibbling G, Link H, Ohman S (1977) Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 37:385–390
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw-Hill, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leonardi, A., Abbruzzese, G., Arata, L. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) findings in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol 231, 75–78 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313720
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313720