Summary
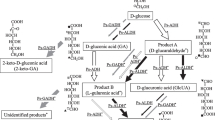
Gluconobacter oxydans subsp. suboxydans ATCC 621 oxidizes d-xylose to xylonic acid very efficiently, although it cannot grow on xylose as sole carbon source. The oxidation of xylose was found to be catalyzed by a membrane-bound xylose dehydrogenase. The xylono-γ-lactone formed in the oxidation reaction is subsequently hydrolyzed to xylonic acid by a γ-lactonase. The complete oxidation pathway of d-xylose in G. oxydans is evidently located in the periplasmic space.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Adachi O (1979) Studies on enzymes in carbohydrate metabolism of acetic acid bacteria. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 53:R77-R86
Adachi O, Ameyama M (1982) d-Glucose dehydrogenase from Gluconobacter suboxydans. In: Wood WA (ed) Methods in enzymology Vol 89, Academic Press, New York, pp 159–163
Ameyama M, Shinagawa E, Matsushita K, Adachi O (1981) d-Glucose dehydrogenase of Gluconobacter suboxydans: solubilization, purification and characterization. Agric Biol Chem 45(4):851–861
Bernhauer K, Riedl-Tumova E (1950) Oxydationen mittels Essigbakterien. Biochem Z 321:26–30
Brodie AF, Lipmann F (1955) Identification of a gluconolactonase. J Biol Chem 212:677–685
buchert J, Viikari L, Linko M, Markkanen P (1986) Production of xylonic acid by Pseudomonas fragi. Biotechnol Lett 8:541–546
Buchert J, Viikari L (1988) The role of xylonolactone in xylonic acid production by Pseudomonas fragi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:333–336
Buchert J, Puls J, Poutanen K (1988) Comparison of Pseudomonas fragi and Gluconobacter oxydans for production of xylonic acid from hemicellulose hydrolyzates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:367–372
Dahms S, Russo J (1982) d-Xylose dehydrogenase. In: Wood WA (ed) Methods in enzymology Vol 89, Academic Press, New York, pp 226–228
Dokter P, Frank Jzn J, Duine JA (1986) Purification and characterization of quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus L.M.D. 79.41. Biochem J 239:163–167
Hucho F, Wallenfels K (1972) Glucono-δ-lactonase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 276:176–179
Jermyn MA (1960) Studies on the glucono-δ-lactonase of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Biochim Biophys Acta 37:78–92
Leroux M, Tarr HLA (1963) Glucose and ribose oxidation by Pseudomonas fragi. Can J Biochem Physiol 41:1023–1034
de Ley J (1961) Comparative carbohydrate metabolism and a proposal for phylogenetic relationship of the acetic acid bacteria. J Gen Microbiol 24:31–50
Lien OG (1959) Determination of gluconolactone, galactonolactone and their free acids by the hydroxamate method. Anal Chem 31:1363–1366
Lockwod LB, Nelson GEN (1946) The oxidation of pentoses by Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol 52:581–586
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NH, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Matsushita K, Ameyama M (1982) d-Glucose dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens, membrane-bound. In: Wood WA (ed), Methods in enzymology Vol 89, Academic Press, New York, London, pp 149–159
van Ness JH (1981) Hydroxycarboxylic acids. In: Grayson M, Eckroth D (eds) Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology Vol 13, John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 99–103
van Schie B (1987) The physiological function of gluconic acid production in Acinetobacter species and other gram-negative bacteria. Implications for energy conservation. PhD thesis, Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands
van Schie BJ, Rouwenhorst RJ, de Bont JAM, van Dijken JP, Kuenen JG (1987) An in vivo analysis of the energetics of aldose oxidation by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26:560–567
Weimberg R (1961) Pentose oxidation by Pseudomonas fragi. J Biol Chem 236:629–635
Yamanaka K, Gino M, Kaneda R (1977) A specific NAD-d-xylose dehydrogenase from Arthrobacter sp. Agric Biol Chem 41(8):1493–1499
Yamanaka K, Gino M (1979) Purification and properties of d-xylose dehydrogenase in bacteria. Hakkokogaku Kaishi 57(5):322–331
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchert, J., Viikari, L. Oxidative d-xylose metabolism of Gluconobacter oxydans . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 29, 375–379 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265822
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265822