Summary
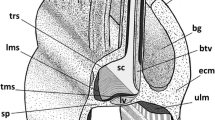
The cytological features and membrane specialisations of neuroepithelial cells (apical cells) in direct contact with the lumen of the lung were studied with transmission and scanning electron microscopy. The luminal surface of the apical cell is characterised by microvilli, a cilium with an 8+1 microtubular pattern and numerous coated vesicles. The cytoplasmic region immediately beneath the luminal plasma membrane contains numerous smooth-walled vesicles, tubules and microtubules, a few microfilaments and dense granules (15–20 nm in diameter). The luminal pole of the cell is marked off from the basal or vascular pole by a well-defined terminal web associated with junctional complexes. Protrusion of the luminal pole occurs as a transient phenomenon and is accompanied by a pinching in of the cell at the terminal web. It is proposed that the distinctive features of the luminal pole of the apical cell are comparable to those of recognised chemoreceptor cells. It is also proposed that in view of the common features of apical and basal cells the apical cell functions as a receptor/transducer and the basal cells serve as an accessory source of peptides/5-hydroxytryptamine to be released on stimulation of the apical cell. Furthermore, we have drawn attention to the structural heterogeneity of the neuroepithelial bodies in various vertebrate classes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew A (1976) APUD cells, apudomas and the neural crest. S Afr Med J 50:890–898
Cutz E, Chan W, Wong V, Conen PE (1974) Endocrine cells in rat fetal lungs. Ultrastructural and histochemical study. Lab Invest 30:458–464
Cutz E, Chan W, Sonstegard KS (1978) Identification of neuro-epithelial bodies in rabbit fetal lungs by scanning electron microscopy: A correlative light, transmission and scanning electron microscope study. Anat Rec 192:459–466
Fujita T, Kobayashi S (1973) The cells and hormones of the GEP endocrine system. The current of studies. In: Fujita T (ed) Gastro-entero-pancreatic endocrine system — a cell-biological approach. Igaku Shoin, Tokyo, pp 1–16
Graziadei PPC (1971) The olfactory mucosa of vertebrates. In: Beidler L (ed) Handbook of Sensory Physiology, IV. Chemical Senses 1, Olfaction. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 27–58
Hung KS, Hertweck H, Hardy J, Loosli C (1973) Ultrastructure of nerves and associated cells in bronchiolar epithelium of the mouse lung. J Ultrastruct Res 43:426–437
Hung KS, Chapman A, Mestemacher M (1979) Scanning electron microscopy of bronchiolar neuroepithelial bodies in neonatal mouse lungs. Anat Rec 193:913–916
Lauweryns JM, Cokelaere M (1973) Hypoxia-sensitive neuro-epithelial bodies. Intrapulmonary secretory neuroreceptory modulated by the CNS. Z Zellforsch 145:521–520
Lauweryns JM, Liebens M (1977) Microspectrography of formaldehyde and fluorescamine-induced fluorescence in rabbit pulmonary neuroepithelial bodies: Demonstration of a new, probably polypeptide intracytoplasmic substance. Experientia 33:1510–1511
Lauweryns JM, Peuskens J, Cokelaere M (1970) Argyrophil, fluorescent and granulated (peptide and amine producing?) AGC cells in human bronchial epithelium; light and electron microscopic studies. Life Sci 9:1417–1429
Lauweryns JM, Cokelaere M, Theunynck P (1972) Neuroepithelial bodies in the respiratory mucosa of various mammals. Z Zellforsch 135:569–592
Lauweryns JM, Cokelaere M, Theunynck M, Deleersnyder M (1974) Neuroepithelial bodies in mammalian respiratory mucosa: light optical, histochemical and ultrastructural studies. Chest 65:22S-29S
Lauweryns JM, Cokelaere M, Deleersynder M, Liebens M (1977) Intrapulmonary neuroepithelial bodies in newborn rabbits. Cell Tissue Res 182:523–540
Rodewald R, Newman S, Karnovsky MJ (1976) Contraction of isolated brush borders from the intestinal epithelium. J Cell Biol 70:541–554
Rogers DC, Haller CJ (1978) Innervation and cytochemistry of the neuroepithelial bodies in the ciliated epithelium of the toad lung (Bufo marinus). Cell Tissue Res 195:395–410
Sorokin SP (1968) Reconstruction of centriole formation and ciliogenesis in mammalian lungs. J Cell Sci 3:207–230
Tilney LG, Cardell RR (1970) Factors controlling the reassembly of the microvillous border of the small intestine of the salamander. J Cell Biol 47:400–422
Tranzer JP, Richards JG (1976) Ultrastructural cytochemistry of biogenic amines in nervous tissue: Methodologie improvements. J Histochem Cytochem 24:1178–1193
Wasano K, Yamamoto T (1978) Monoamine-containing granulated cells in the frog lung. Cell Tissue Res 193:201–209
Wright TN, Ross R (1975) Proteoglycans in primate arteries. I. Ultrastructural localisation and distribution in the intima. J Cell Biol 67:660–674
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rogers, D.C., Haller, C.J. The ultrastructural characteristics of the apical cell in the neuroepithelial bodies of the toad lung (Bufo marinus). Cell Tissue Res. 209, 485–498 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234760
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234760