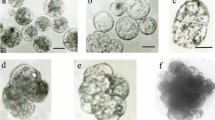
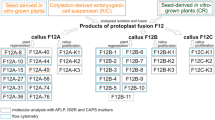
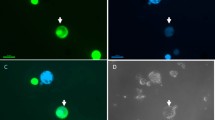
Summary
Somatic hybrids between the Japanese radish and cauliflower (Brassica oleracea) were produced by protoplast electrofusion in order to introduce clubroot disease resistance in the Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus) into Brassica crops. After electrofusion of iodoacetamide-treated cauliflower protoplasts with untreated radish ones, culture was performed under conditions, that allowed only cauliflower protoplasts to regenerate. Out of 40 regenerated plants, 37 were morphologically of a hybrid type and 3 of a cauliflower type. On the basis of isozyme and RFLP analysis, all of the hybrid-type plants tested proved to be true hybrids. Of the 10 true hybrids tested, 9 were found to contain chloroplasts similar to those found in the Japanese radish, while only 1 contained those of the cauliflower. Using two mitochondrial genes as probes, we were able to show that 3 hybrids contained mitochondria of the Japanese radish, with some modification, while 7 hybrids had either parental or new patterns. All of the hybrid-type plants showed resistance to clubroot disease as high as that found in the Japanese radish. Some hybrids were self-fertile. All of the self-fertile hybrids were found to contain 36 chromosomes, indicating that they were amphidiploids. In addition, a few seeds were obtained from a backcross of the self-fertile hybrids to both parents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels R, Moran LB (1984) Molecular analysis of alien chromatin introduced into wheat. Stadlex Genet Symp 16:529–557
Chetrit P, Mathieu C, Vedel F, Pelletier G, Primard C (1985) Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism induced by protoplast fusion in Cruciferae. Theor Appl Genet 69:361–366
Ellerstrom S, Zagorcheva L (1977) Sterility and apomictic embryo-sac formation in Raphanobrassica. Hereditas 87:107–120
Hanson MR, Rothenberg M, Boeshore ML, Nivison HT (1985) Organelle segregation and recombination following protoplast fusion: analysis of sterile cytoplasms. In: Zaitlin M, Day P, Hollaender A (eds) Biotechnology in plant science: relevance to agriculture in the eighties. Academic Press, New York, pp 129–144
Hirai M, Kajiura I (1987) Genetic analysis of leaf isozymes in Citrus. Jpn J Breed 37:377–388
Landgren M, Glimelius K (1990) Analysis of chloroplast and mitochondrial segregation in three different combinations of somatic hybrids produced within Brassicaceae. Theor Appl Genet 80:776–784
Levings III CS (1983) The plant mitochondrial genome and its mutants. Cell 32:659–661
McNaughton IH (1973) Synthesis and sterility of Raphanobrassica. Euphytica 22:70–88
Maliga P, Menczel L (1986) Chloroplast transfer and recombination through protoplast fusion. In: Vasil IK (ed) Cell culture and somatic cell genetics, vol III. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 601–612
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Morikami A, Nakamura K (1987) Structure and expression of pea mitochondrial F1 ATPase alpha subunit gene and its pseudogene involved in homologous recombination. J Biochem 101:967–976
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio-assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nagata T, Takebe I (1971) Plating of isolated tobacco mesophyll protoplasts on agar medium. Planta 99:12–20
Namai H, Sarashima M, Hosoda T (1980) Interspecific and intergeneric hybridization breeding in Japan. In: Tsunoda S, Hinata K, Gomez-Campo C (eds) Brassica crops and wild allies: biology and breeding. Jpn Sci Soc Press, Tokyo, pp 191–203
Sugiura M, Shinozaki K, Zaita N, Kusuda M, Kumano M (1986) Clone bank of the tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) chloroplast genome as a set of overlapping restriction endonuclease fragments: mapping of eleven ribosomal protein genes. Plant Sci 44:211–216
Takaiwa F, Oono K, Sugiura M (1984) The complete nucleotide sequence of a rice 17S rRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res 12:5441–5448
Vallejos CE (1983) Enzyme activity staining. In: Tanksley SD, Orton TJ (eds) Isozymes in plant genetics and breeding: part A. Elsevier Sci Publ, Amsterdam, pp 469–516
Yoshikawa H (1981) Breeding for club-root resistance in Chinese cabbage. In: Telekar NS, Griggs TD (eds) Chinese cabbage. Proc 1st Int Symp. Asian Vegetable Research and Development Center, Tainan, pp 405–413
Yoshikawa H, Ashizawa M, Hida K (1979) Studies on breeding for clubroot resistance in Brassicaceae vegetables. II: Clubroot resistance of Japanese radish. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 48 [Suppl 1]:144–145
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by I. Potrykus
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagimori, M., Nagaoka, M., Kato, N. et al. Production and characterization of somatic hybrids between the Japanese radish and cauliflower. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 84, 819–824 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227390
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227390