Abstract
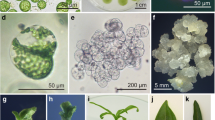
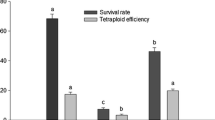
Highly asymmetric somatic hybrid plants were obtained by PEG/DMSO fusion of gamma-irradiated mesophyll protoplasts of the kanamycin-resistant (KmR+) interspecific hybrid Lycopersicon esculentum x L. pennellii (EP) with mesophyll protoplasts of Solanum melongena (eggplant, E). Elimination of the EP chromosomes was obtained by irradiating the donor genome with different doses of gamma rays (100, 250, 500, 750 and 1000 Gy). The selection of somatic hybrid calli was based on kanamycin resistance; EP and E protoplasts did not divide due to the irradiation treatment and sensitivity to kanamycin, respectively. KmR+ calli were recovered following all irradiation doses of donor EP protoplasts. The hybrid nature of the recovered calli was confirmed by PCR amplification of the NptII gene, RAPD patterns and Southern hybridizations using potato ribosomal DNA and pTHG2 probes. Ploidy levels of calli confirmed as hybrid were further analyzed by flow cytometry. Such analyses revealed that the vast majority of hybrid calli that did not regenerate shoots were 5–9n polyploids. The three asymmetric somatic hybrid plants obtained were regenerated only from callus with a ploidy level close to 4n, and such calli occurred only when the donor EP had been exposed to 100 Gy. The amount of DNA in somatic hybrid calli, from 100-Gy exposure, was found by dot blot hybridization with the species-specific probe, pTHG2, to be equivalent with 3.1–25.8% of the tomato genome. Thus, DNA contained in 3.8–13.2 average-size tomato chromosomes was present in these hybrid calli. The asymmetric somatic hybrid plants had the eggplant morphology and were regenerated from one hybrid callus that contained an amount of tomato DNA equivalent to 6.29 average-size tomato chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991a) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991b) Estimation of nuclear DNA content of plants by flow cytometry. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:221–231
Babiychuk E, Kushnir S, Gleba YY (1992) Spontaneous extensive chromosome elimination in somatic hybrids between somatically congruent species Nicotiana tabacum L. and Atropa belladonna L. Theor Appl Genet 84:87–91
Beck E, Ludwig G, Auerswald EA, Reiss B, Schaller H (1982) Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene 19:327–336
Chyi Y, Jorgensen RA, Goldstein D, Tanksley SD, Loaiza-Figueroa F (1986) Locations and stability of Agrobacterium-mediated T-DNA insertions in the Lycopersicon genome. Mol Gen Genet 204:64–69
Daunay MC, Lester RN, Laterrot H (1991) The use of wild species for the genetic improvement of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). In: Hawkes L, Lester RN, Nee M, Estrada N (eds) Solanaceae III: taxonomy, chemistry, evolution. Royal Botanic Gardens of Kew and Linnean Society of London, London, pp 389–412
Daunay MC, Chaput MH, Sihachakr D, Allot M, Vedel F, Ducreux G (1993) Production and characterization of fertile somatic hybrids of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) with Solanum aethiopicum L. Theor Appl Genet 85:841–850
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Dudits D, Maroy E, Praznovszky T, Olah Z, Gyorgyey J, Cella R (1987) Transfer of resistance traits from carrot into tobacco by asymmetric somatic hybridization: regeneration of fertile plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8434–8438
Famelaer I, Gleba YY, Sidorov VA, Kaleda VA, Parokonny AS, Boryshuk NV, Cherep NN, Negrutiu I, Jacobs M (1989) Intrageneric asymmetric hybrids between Nicotiana plunbaginifolia and Nicotiana sylvestris obtaind by gamma-fusion. Plant Sci 61:105–117
Galbraith DW, Harkins KR, Maddox JM, Ayres NM, Sharma DP, Firoozabady E (1983) Rapid flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle in intact plant tissues. Science 220:1049–1051
Gleba YY, Sytnik KM (1984) Protoplast fusion. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York
Gleba YY, Hinnisdaels S, Sidorov VA, Kaleda VA, Parokonny AS, Boryshuk NV, Cherep NN, Negrutiu I, Jacobs M (1988) Intergeneric asymmetric hybrids between Nicotiana plumbaginifolia and Atropa belladonna obtained by „gamma-fusion”. Theor Appl Genet 76:760–766
Gleddie S, Keller WA, Setterfield G (1986) Production and characterization of somatic hybrids between Solanum melongena L. and S. sisymbriifolium Lam. Theor Appl Genet 71:613–621
Guri A, Izhar S (1984) Improved efficiency of plant regeneration from protoplasts of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Plant Cell Rep 3:247–249
Guri A, Sink KC (1988a) Organelle composition in somatic hybrids between an atrazine-resistant biotype of Solanum nigrum and Solanum melongena. Plant Sci 58:51–58
Guri A, Sink KC (1988b) Interspecific somatic hybrid plants between eggplant (Solanum melongena) and Solanum torvum. Theor Appl Genet 76:490–496
Guri A, Dunbar LJ, Sink KC (1991) Somatic hybridization between selected Lycopersicon and Solanum species. Plant Cell Rep 10:76–80
Imamura J, Saul MW, Potrykus I (1987) X-ray irradiation promoted asymmetric somatic hybridization and molecular analysis of the products. Theor Appl Genet 74:445–450
Kao KN (1977) Chromosomal behavior in somatic hybrids of Soybean-Nicotiana glauca. Mol Gen Genet 150:225–230
Kovtun YV, Korostash MA, Butsko YV, Gleba YY (1993) Amplification of repetitive DNA from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia in asymmetric somatic hybrids between Nicotiana sylvestris and Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Theor Appl Genet 86:221–228
Lipp Joao KL, Brown TA (1993) Enhanced transformation of tomato co-cultivated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58C1Rifr:: pGSFR1161 in the presence of acetosyringone. Plant Cell Rep 12:422–425
Liu KB, Li YM, Sink KC (1995) Asymmetric somatic hybrid plants between an interspecific Lycopersicon hybrid and Solanum melongena. Plant Cell Rep (in press)
McCabe PF, Dunbar LJ, Guri A, Sink KC (1993) T-DNA-tagged chromosome 12 in donor Lycopersicon esculentum x L. pennellii is retained in asymmetric somatic hybrids with recipient Solanum lycopersicoides. Theor Appl Genet 86:377–382
Medgyesy P, Menczel L, Maliga P (1980) The use of cytoplasmic streptomycin resistance: chloroplast transfer from Nicotiana tabacum into Nicotiana sylvestris, and isolation of their somatic hybrids. Mol Gen Genet 179:693–698
Melzer JM, O'Connell MA (1992) Effect of radiation dose on the production of and the extent of asymmetry in tomato asymmetric somatic hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 83:337–344
Menczel L, Nady F, Kiss ZR, Maliga P (1981) Streptomycin-resistant and -sensitive somatic hybrids of Nicotiana tabacum x Nicotiana knightiana: correlation of resistance to N. tabacum plastids. Theor Appl Genet 59:191–195
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Piastuch WC, Bates GW (1990) Chromosomal analysis of Nicotiana asymmetric somatic hybrids by dot blotting and in situ hybridization. Mol Gen Genet 222:97–103
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Schoenmakers HCH, Wolters AMA, Nobel EM, de Klein CMJ, Koornneef M (1993) Allotriploid somatic hybrids of diploid tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) and monoploid potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Theor Appl Genet 87:328–336
Shepard JF (1982) Cultivar dependent cultural refinements in potato protoplast regeneration. Plant Sci Lett 26:127–132
Sihachakr D, Haicour R, Serraf I, Barrientos E, Herbreteau C, Ducreux G, Rossignol L, Souvannavong V (1988) Electrofusion for the production of somatic hybrid plants of Solanum melongena L. and Solanum khasianum C.B.Clark. Plant Sci 57:215–223
Tan M.-LC, Rietveld EM, van Marrewijk GAM, Kool AJ (1987) Regeneration of leaf protoplasts of tomato cultivars (L. esculentum): factors important for efficient protoplast culture and plant regeneration. Plant Cell Rep 6:172–175
Trick H, Zelcer A, Bates GW (1994) Chromosome elimination in asymmetric somatic hybrids: effect of gamma dose and time in culture. Theor Appl Genet 88:965–972
Wijbrandi J, Posthuma A, Kok JM, Rijken R, Vos JGM, Koornneef M (1990) Asymmetric somatic hybrids between Lycopersicon esculentum and irradiated Lycopersicom peruvianum. Theor Appl Genet 80:305–312
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski AJ, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Wolters AMA, Schoenmakers HCH, van der Meulen-Muisers JJM, van der Knaap E, Derks FHM, Koornneef M, Zelcer A (1991) Limited DNA elimination from the irradiated potato parent in fusion products of albino Lycopersicon esculentum and Solanum tuberosum. Theor Appl Genet 83:225–232
Zabel P, Meyer D, van de Stolpe O, van der Zaal B, Ramanna MS, Koornneef M, Krens F, Hille J (1985) Towards the construction of artificial chromosomes for tomato. In: van Vloten-Doting L, Groot GSP, Hall TC (eds) Molecular form and function of the plant genome. (NATO ASI, series A). Life Sci 83:609–624
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by P. Maliga
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samoylov, V.M., Sink, K.C. The role of irradiation dose and DNA content of somatic hybrid calli in producing asymmetric plants between an interspecific tomato hybrid and eggplant. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 92, 850–857 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221897
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221897