Summary
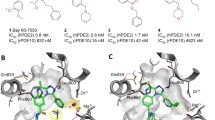
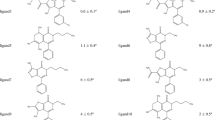
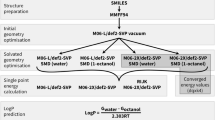
VX-478 belongs to a novel class of HIV-1 protease inhibitors that are based on N,N-disubstituted benzene sulfonamides. Force field parameters for the N,N-dialkyl benzene sulfonamide moiety have been assembled from the literature and from our own ab initio calculations. These parameters were employed to calculate solvation and binding free energy differences between VX-478 and two analogs. The free energy perturbation method has been used to determine these differences using two approaches. In the first approach, intergroup interaction terms only were included in the calculation of free energies (as in most reports of free energy calculations using AMBER). In the second approach, both the inter- and intragroup interaction terms were included. The results obtained with the two approaches are in excellent agreement with each other and are also in close agreement with the experimental results. The solvation free energies of N,N-dimethyl benzene sulfonamide derivatives (truncated models of the inhibitors), calculated using continuum solvation (AMSOL) methods, are found to be in qualitative agreement with the experimental and free energy perturbation results. The binding and solvation free energy results are discussed in the context of structure-based drug design to show how physicochemical properties (for example aqueous solubilities and bioavailabilities) of these HIV-1 protease inhibitors were improved, while maintaining their inhibitory potency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, E.E., Baker, C.T., Dwyer, M.D., Murcko, M.A., Rao, B.G., Tung, R.D. and Navia, M.A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 117 (1995) 1181.
Tung, R.D., Livingston, D.J., Rao, B.G., Kim, E.E., Baker, C.T., Boger, J.S., Chambers, S.P., Deininger, D.D., Dwyer, M.D., Elsayed, L., Funlghum, J., Li, B., Murcko, M.A., Navia, M.A., Novak, P., Pazhanisamy, S., Stuver, C. and Thomson, J.A., manuscript in preparation.
Vazquez, M.L., Bryant, M.L., Clare, M., DeCrescenzo, G.A., Doherty, E.M., Freskos, J.N., Getman, D.P., Houseman, K.A., Julien, J.A., Kocan, G.P., Mueller, R.A., Shieh, H.-S., Stallings, W.C., Stegeman, R.A. and Talley, J.J., J. Med. Chem., 38 (1995) 581.
Navia, M.A. and Murcko, M.A., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2 (1992) 202.
Lyle, T.A., Wiscount, C.M., Guare, J.P., Thompson, W.J., Anderson, P.S., Darke, P.L., Zugay, Z.A., Emini, E.A., Schleif, W.A., Qunitero, J.C., Emini, E.A. and Huff, J.R., J. Med. Chem., 34 (1991) 1228.
Kollman, P.A., Chem. Rev., 93 (1993) 2395.
Straatsma, T.P. and McCammon, J.A., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 43 (1992) 407.
Cramer, C.J. and Truhlar, D.G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 113 (1991) 8305.
Cramer, C.J. and Truhlar, D.G., J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Design, 6 (1992) 629.
McCarrick, M.A. and Kollman, P.A., Methods Enzymol., 241 (1994) 370.
Rao, B.G. and Murcko, M.A., J. Comput. Chem., 15 (1994) 1241.
Cieplak, P. and Kollman, P.A., J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Design, 7 (1993) 291.
Rao, B.G., Tilton, R.F. and Singh, U.C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 114 (1992) 4447.
Reddy, M.R., Varney, M.D., Kalish, V., Viswanadhan, V.N. and Appelt, K., J. Med. Chem., 37 (1994) 1145.
Van, Gunsteren, W.F., Protein Eng., 2 (1988) 5.
AMBER (v. 3.3) is a fully vectorized version of AMBER (v. 3.0) by Singh, U.C., Weiner, P.K., Caldwell, J.W. and Kollman, P.A., University of California, San Francisco, CA, 1986.
Weiner, S.J., Kollman, P.A., Case, D.A., Singh, U.C., Ghio, C., Alagona, G., Profeta, S. and Weiner, P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 196 (1984) 765.
Jorgensen, W.L., Chandrasekhar, J. and Madura, J.D., J. Chem. Phys., 79 (1983) 926.
QUANTA (v. 3.3) Parameter Handbook, Molecular Simulations, Waltham, MA, 1992.
Bindal, R.D., Golab, J.T. and Katzenellenbogen, J.A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 112 (1990) 7861.
AMSOL (v. 4.1), Cramer, C.J., Hawkins, G.D., Lynch, G.C., Truhlar, D.G. and Liotard, D.A., 1994.
Jorgensen, W.L. and Nguyen, T.B., J. Comput. Chem., 14 (1993) 195.
Dewar, M.J.S., Jei, C. and Yu, J., Tetrahedron, 49 (1993) 5003.
Stewart, J.J.P., J. Comput. Chem., 10 (1989) 209.
Hine, J. and Mookerjee, P.K., J. Org. Chem., 40 (1975) 292.
Rao, B.G. and Singh, U.C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 111 (1989) 3125.
Pearlman, D.A. and Connelly, P.R., J. Mol. Biol., 248 (1995) 696.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, B.G., Kim, E.E. & Murcko, M.A. Calculation of solvation and binding free energy differences between VX-478 and its analogs by free energy perturbation and AMSOL methods. J Computer-Aided Mol Des 10, 23–30 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00124462
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00124462