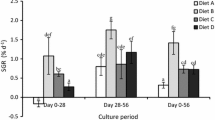
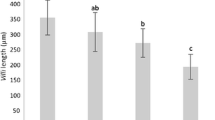
Vitamins were analysed in food (microalgae) and larvae of great scallop, Pecten maximus, during larval development. Microalgae used to feed larvae in hatcheries show great variability in their vitamin composition depending on both the species and culture condition (phase of growth). The microalgae used to feed Pecten maximus larvae were rich in vitamins; their content compared with diets used in fish culture appeared sufficient, with the possible exceptions of pyridoxine, biotin and pantothenic acid. Vitamins in bacteria, isolated from the larval rearing tank were also analysed, as they can also contribute to the diet. Vitamin B12, α-tocopherol and Β-carotene were detected in very low concentration in bacteria; however, some bacterial strains were rich in pantothenic acid, and the pattern of other vitamins was similar to that from microalgae. The presence of bacteria can complement the diet in panthothenic acid, as it has been demonstrated that bacteria are ingested by larvae. The vitamin content of Pecten maximus larvae was analysed from the second day after hatching to just before metamorphosis. The content of some vitamins, ascorbic acid (C), α-tocopherol and Β-carotene, increased during larval development, suggesting that their requirement was satisfied. However, thiamin and riboflavin decreased during larval development and further studies, possibly using microencapsulated vitamins supplements, are needed to determine whether these vitamins are limiting during larval development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackman, R.G. (1989) Marine Biogenic Lipids, Fats and Oils. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, Vol. 1, pp. 1–314.
Bjerkeng, B., Hertzberg, S. and Liaaen-Jensen, S. (1993) Carotenoids in food chain studies — V. Carotenoids of the bivalves Modiolus modiolus and Pecten maximus. Structural, metabolic and food chain aspects. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology 106B(2), 243–250.
Bourgeois, C.F., Chartois, H.R., Coustans, M.F. and George, P.R. (1989) Dosage automatisé de la vitamine C dans les aliments et les milieux biologiques. Analusis 17, 519–525.
Brown, M.R. and Miller, K.A. (1992) The ascorbic acid content of eleven species of microalgae used in mariculture. Journal of Applied Phycology 4, 205–215.
De Roeck-Holtzhauer, Y., Quere, C. and Claire, C. (1991) Vitamin analysis of five planktonic microalgae and one macroalga. Journal of Applied Phycology 3, 259–264.
Devauchelle, N., and Mingant, C. (1991) Review of the reproductive physiology of the scallop Pecten maximus, applicable to intensive aquaculture. Aquatic Living Resources 4, 41–51.
Fabregas, J. and Herrero, C. (1986) Vitamin content of four marine microalgae, potential use as source of vitamins nutrition. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 5, 259–264.
Gaby, S.K., Bendich, A., Singh, V.N. and Machlin, L.J. (1991) Vitamin Intake and Health. Marcel Dekker: New York.
Leclercq, M. and Bourgeay-Causse, M. (1981) Une methode simple, fiable et rapide: dosage simultane du rétinol et de tocopherol seriques par chromatographie liquide haute performence. Revue de l'Institut Pasteur de Lyon 14, 17–37.
Matsuno, T., Hiraoka, K. and Maoka, T. (1981) Carotenoids in the gonads of scallops. Bulletin of the Japanese society of Scientific Fisheries 47, 385–390.
Moal, J., Samain, J.F., Corre, S., Nicolas, J.L, and Glynn, A. (1996) Bacterial nutrition of great scallop larvae. Aquaculture International 4.
Morito, C.L.H. (1984) Factors affecting the thiamin requirement of rainbow trout (Salmo gardneri). MS thesis, Department of Nutritional Sciences, University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario.
NRC (National Research Council) (1983) Nutrient Requirement of Warmwater Fishes and Shellfishes. National Academy Press: Washington, DC.
Samian, J.F., Seguineau, C., Cochard, J.C., Delaunay, F., Nicolas, J.L., Marty, Y., Galois, R., Mathieu, M. and Moal, J. (1992) What about variability for Pecten maximus production? Oceanis 18, 49–66.
Soudant, P., Marty, Y., Moal, J. and Samain, J.F. (1996) Fatty acids and egg quality in the great scallop. Aquaculture International 4.
Walne, P.R. (1970) Studies on the food value of nineteen genera of algae to juvenile bivalves of the genera Ostrea, Crassostrea, Merceneria and Mytilus. Fish Investigation 26, 1–61.
Whyte, J.N.C., Bourne, N. and Hodgson, C.A. (1990) Nutritional condition of rock scallop, Crassadoma gigantea (Gray), larvae fed mixed algal diets. Aquaculture 86, 25–40.
Woodward, B. (1994) Dietary vitamin requirement of cultured young fish, with emphasis on quantitative estimates for salmonids. Aquaculture 124, 133–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seguineau, C., Laschi-Loquerie, A., Moal, J. et al. Vitamin requirements in great scallop larvae. Aquacult Int 4, 315–324 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120948
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120948