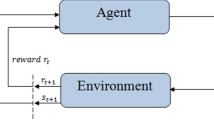
To schedule a job shop, the first task is to select an appropriate scheduling algorithm or rule. Because of the complexity of scheduling problems, no general algorithm sufficient for solving all scheduling problems has yet been developed. Most job-shop scheduling systems offer alternative algorithms for different situations, and experienced human schedulers are needed to select the best dispatching rule in these systems. This paper proposes a new algorithm for job-shop scheduling problems. This algorithm consists of three stages. First, computer simulation techniques are used to evaluate the efficiency of heuristic rules in different scheduling situations. Second, the simulation results are used to train a neural network in order to capture the knowledge which can be used to select the most efficient heuristic rule for each scheduling situation. Finally, the trained neural network is used as a dispatching rule selector in the real-time scheduling process. Research results have shown great potential in using a neural network to replace human schedulers in selecting an appropriate approach for real-time scheduling. This research is part of an ongoing project of developing a real-time planning and scheduling system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, K. R. (1974) Introduction to Sequencing and Scheduling, John Wiley, New York.
Croall, I. F. and Mason, J. P. (1992) Industrial Applications of Neural Networks, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Dong, J. (1995) Organization structure, concurrent engineering and computerized enterprise integration. International Journal of Concurrent Engineering: Research and Applications, 3, 167–176.
Dong, J. and Parsaei, H. R. (1992) Dynamic feature-based process planning and scheduling. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 23, 141–144.
Dong, J. and Parsaei, H. (1994) Design and implementation of a feature-based process planning system. International Journal of Computers and Industrial Engineering, 27, 1–4.
Fox, W. S. (1987) Constraint-Directed Search: A Case Study of Job Shop Scheduling. Research Notes in AI, Morgan Kaufman, Los Altos, CA.
Gere, W. S. (1966) Heuristic in job shop scheduling. Management Science, 13(3), 167–190.
Gurnani, H. and Johri, P. K. (1991) A study of performance objectives in the scheduling of manufacturing lines. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 10(5), 422–429.
Karsiti, M. N., Cruz, J. B. Jr and Mulligan, J. H. Jr (1992a) Simulation studies of multilevel dynamic job shop scheduling using heuristic dispatching rules. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 11(5), 346–358.
Karsiti, M. N., Cruz, J. B. Jr and Mulligan, J. H. Jr (1992b) Performance forecasts as feedback for schedule generation. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 11(5), 326–333.
Luh, P. B. and Hoitomt, D. J. (1993) Scheduling of manufacturing systems using the Lagrangian relaxation technique. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 38(7), 1066–1079.
Nasr, N. and Elsayed, E. A. (1990) Job shop scheduling with alternative machines. International Journal of Production Research, 28(9), 1595–1609.
Panwalkar, S. S. and Iskander, W. (1977) A survey of scheduling rules. Operations Research, 25(1), 45–61.
Pritsker, A. A. B. (1986) Introduction to Simulation and Slam II, Systems Publishing, West Lafayette, IN/John Wiley, New York.
Rabelo, L. C. and Yih, Y. (1994) Development of a two-level scheduling prototype using artificial intelligence techniques for a ‘systems’ company, in Flexible Automation and Integrated Manufacturing, pp. 232–242. Proceedings of the 4th International FAIM Conference. Begell House Publishers, New York.
Sauer, J. (1993) Dynamic scheduling knowledge for metascheduling. Industrial and Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems.
Shmilovici, A. and Maimon, M. A. (1992) Heuristics for dynamic selection and routing of parts in an FMS. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 11(4), 285–296.
Vancheeswaran, R. and Townsend, M. A. (1993) Two-stage heuristic procedure for scheduling job shops. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 12(4), 315–325.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Dong, J.(. Dispatching rule selection using artificial neural networks for dynamic planning and scheduling. J Intell Manuf 7, 243–250 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00118083
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00118083