Abstract
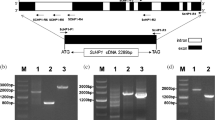
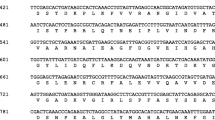
The vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase (V-PPase) is an electrogenic H+ pump, which was found in the plant vacuolar membrane. Two cDNA clones (OVP1 and OVP2) encoding the V-PPase were isolated from cultured rice (Oryza sativa L.) cells and subsequently sequenced. The sequence analysis has revealed thatOVP1 contains 2316 nucleotides of open reading frame (ORF) and 362 nucleotides of the 3′-untranslated region, whereasOVP2 comprises 2304 nucleotides of ORF and 312 nucleotides of the 3′-untranslated region. The nucleotide sequences of ORF ofOVP1 andOVP2 are 80.7% identical, and their 5′- and 3′-untranslated regions have 39.4% and 48.4% identity, respectively. The polypeptides encoded by the ORF ofOVP1 andOVP2 contain 771 and 767 amino acids, respectively, and the sequences of the OVP proteins are very similar to those of other V-PPases, which are shown to have 85–91% homology. Chromosomal mapping by RFLP techniques demonstrates that OVP1 and OVP2 are isoforms encoded by different genes. BothOVP1 andOVP2 are mapped on the same chromosome (chromosome 6) to a distance of ca. 90 cM. Northern analysis indicates that theOVP1 andOVP2 are also expressed in intact rice plants andOVP2 shows higher expression in the calli than the roots and shoots, compared toOVP1. These results show that at least two genes encoding the V-PPases are present in rice genome and their expressions are probably regulated in a different manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn S, Tanksley SD: Comparative linkage maps of the rice and maize genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 7980–7984 (1993).
Ausubel FM, Bret R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Struhl K: Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, Wiley, New York (1987).
Bowman EJ: Comparison of the vacuolar membrane ATPase ofNeurospora crassa with the mitochondrial and plasma membrane ATPases. J Biol Chem 258: 15238–15244 (1983).
Carystinos GD, MacDonald HR, Monroy AF, Dhindsa RS, Poole RJ: Vacuolar H+-translocating pyrophosphatase is induced by anoxia or chilling in seedlings of rice. Plant Physiol 108: 641–649 (1995).
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N: Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162: 156–159 (1987).
Cidon S, Nelson N: A novel ATPase in the chromaffin granule membrane. J Biol Chem 258: 2892–2898 (1983).
DeWitt ND, Harper JF, Sussman MR: Evidence for a plasma membrane proton pump in phloem cells of higher plants. Plant J 1: 121–128 (1991).
Ewing NN, Bennett AB: Assessment of the number and expression of P-type H+-ATPase genes in tomato. Plant Physiol 106: 547–557 (1994).
Ewing NN, Wimmers LE, Meyer DJ, Chetelat RT, Bennett AB: Molecular cloning of tomato plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Plant Physiol 94: 1874–1881 (1990).
Harms K, Wöhner RV, Schulz B, Formmer WB: Isolation and characterization of P-type H+-ATPase genes from potato. Plant Mol Biol 26: 979–988 (1994).
Houlne G, Boutry M: Identification of anArabidopsis thaliana gene encoding a plasma membrane H+-ATPase whose expression is restricted to anther tissues. Plant J 5: 311–317 (1994).
Ikeda M, Satoh S, Maeshima M, Mukohata Y, Moritani C: A vacuolar ATPase and pyrophosphatase inAcetabularia acetabulum. Biochim Biophys Acta 1070: 77–82 (1991).
Kakinuma Y, Ohsumi Y, Anraku Y: Properties of H+-translocating adenosine triphosphatase in vacuolar membranes ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 256: 10859–10863 (1981).
Kasamo K: Response of tonoplast and plasma membrane ATPases in chilling-sensitive and-insensitive rice (Oryza sativa L.) culture cells to low temperature. Plant Cell Physiol 29: 1085–1094 (1988).
Kim EJ, Zhen R-G, Rea PA: Site-directed mutagenesis of vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase. J Biol Chem 270: 2630–2635 (1995).
Kim Y, Kim EJ, Rea PA: Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding the vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase ofBeta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 106: 375–382 (1994).
Klein P, Kanehisa M, DeLisi C: The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 815: 468–476 (1985).
Kurata N: A high degree of conservation of genome structure between rice and wheat. Biotechnology 12: 276–278 (1994).
Kurata N, Nagamura Y, Yamamoto K, Harushima Y, Sue N, Wu J, Antonio BA, Shomura A, Shimizu T, Lin S-Y, Inoue T, Fukuda A, Shimano T, Kuboki Y, Toyama T, Miyamoto Y, Kirihara T, Hayasaka K, Miyano A, Monna L, Zhong HS, Tamura Y, Wang Z-X, Momma T, Umehara Y, Yano M, Sasaki T, Minobe Y: A 300 kilobase interval genetic map of rice including 883 expressed sequences. Nature Genet 8: 365–372 (1994).
Lerchl J, König S, Zrenner R, Sonnewald U: Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of isoforms encoding tonoplast-bound proton-translocating inorganic pyrophosphatase in tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 29: 833–840 (1995).
Lütcke HA, Chow KC, Mickel FS, Moss KA, Kern HF, Scheele GA: Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J 6: 43–48 (1987).
Maeshima M, Mimura T, Sato T: Distribution of vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase and a membrane integral protein in a variety of green plants. Plant Cell Physiol 35: 323–328 (1994).
Maeshima M, Yoshida S: Purification and properties of vacuolar membrane proton-translocating inorganic pyrophosphatase from mung bean. J Biol Chem 264: 20068–20073 (1989).
Mandara S, Taiz L: Partial purification of a tonoplast ATPase from corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol 78: 327–333 (1985).
Nakai K, Kanehisa M: A knowledge base for predicting protein localization sites in eucaryotic cells. Genomics 14: 897–911 (1992).
Nakamura Y, Kasamo K, Shimosato N, Sakata M, Ohta E: Stimulation of the extrusion of protons and proton ATPase activities with the decline in pyrophosphatase activity of the tonoplast in intact mung bean roots under high-sodium chloride stress and its relation to external levels of calcium ions. Plant Cell Physiol 33: 139–149 (1992).
Nelson N, Taiz L: The evolution of H+-ATPases. Trends Biochem Sci 14: 113–116 (1989).
Nyren P, Sakai-Nore Y, Strid A: Amino acid sequence similarities between the vacuolar proton-pumping inorganic pyrophosphatase and the c-subunit of F0F1-ATPases. Plant Cell Physiol 34: 375–378 (1993).
Ookura T, Wada M, Sakakibara Y, Kim HJ, Maruta I, Kawamura Y, Kasamo K: Identification and characterization of a family of genes for the plasma membrane H+-ATPase ofOryza sativa L.. Plant Cell Physiol 35: 1251–1256 (1994).
Oukuma S, Moriyama Y, Takano T: Identification and characterization of a proton pump on lysosomes by fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran fluorescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 2758–2762 (1982).
Palmgren MG, Christensen C: Functional comparison between plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase isoforms expressed in yeast. J Biol Chem 269: 3027–3033 (1994).
Rea PA, Kim Y, Sarafian V, Poole RJ, Davies JM, Sanders D: Vacuolar H+-translocating pyrophosphatases: a new category of ion translocase. Trends Biochem Sci 17: 348–353 (1992).
Rea PA, Poole RJ: Proton-translocating inorganic pyrophosphatase in red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) tonoplast vesicles. Plant Physiol 77: 46–52 (1985).
Rea PA, Poole RJ: Vacuolar H+-translocating pyrophosphatase. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 44: 157–180 (1993).
Rea PA, Sanders D: Tonoplast energization: Two H+ pumps, one membrane. Physiol Plant 71: 131–141 (1987).
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467 (1977).
Sarafian V, Kim Y, Poole RJ, Rea PA: Molecular cloning and sequence of cDNA encoding the pyrophosphate-energized vacuolar membrane proton pump ofArabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 1775–1779 (1992).
Shimmen T, MacRobbie EAC: Demonstration of two proton translocating systems in tonoplast of permiabilizedNitella cells. Protoplasma 136: 205–207 (1987).
Sussman MR: Molecular analysis of proteins in the plant plasma membrane. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 45: 211–234 (1994).
Suzuki K, Kasamo K: Effects of aging on the ATP and pyrophosphate-dependent pumpingof protons across the tonoplast isolated from pumpkin cotyledons. Plant Cell Physiol 34: 613–619 (1993).
Sze H: H+-translocating ATPases: Advances using membrane vesicles. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 36: 175–208 (1985).
Sze H, Ward JM, Lai S: Vacuolar H+-translocating ATPases from plants: structure, function, and isoforms. J Bioenerg Biomembr 24: 371–381 (1992).
Tanaka Y, Chiba K, Maeda M, Maeshima M: Molecular cloning of cDNA for vacuolar membrane proton-translocating inorganic pyrophosphatase inHordeum vulgare. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 190: 1110–1114 (1993).
Wada M, Takano M, Kasamo K: Nuclotide sequence of a complementary DNA encoding plasma membrane H+-ATPase from rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol 99: 794–795 (1992).
Zhen R-G, Baykov AA, Bakuleva NP, Rea PA: Aminomethylenediphosphonate: A potent type-specific inhibitor of both plant and phototrophic bacterial H+-pyrophosphatases. Plant Physiol 104: 153–159 (1994).
Zhen R-G, Kim EJ, Rea PA: Localization of cytosolically oriented maleimide-reactive domain of vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase. J Biol Chem 269: 23342–23350 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakakibara, Y., Kobayashi, H. & Kasamo, K. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase isoforms from rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 31, 1029–1038 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040721
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040721