Abstract
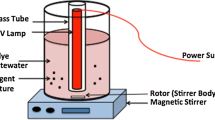
The electrochemical decolorization of the Reactive Violet 5 azo dye on a boron-doped diamond anode was used as a model process to test a novel definitive screening design (DSD). This method allows a dramatic reduction in the number of experiments needed to investigate those systems characterized by a large number of variables. In this study, the effect of nine quantitative parameters was investigated: initial dye concentration (60–120 mg L−1), current density (100–500 A m−2), NaCl concentration (5–20 mM), Na2SO4 concentration (35–65 mM), pH (3–11), temperature (20–45 °C), inter-electrode distance (0.5–3.5 cm), stirring rate (250–750 rpm) and electrolysis time (2–8 min). Analysis of DSD data showed that four out of the nine factors (initial dye concentration, current density, pH and electrolysis time) were statistically significant. These factors were retained for process characterization using a subsequent central composite design. Overall, the number of experiments was reduced from over 500 to only 41, thus confirming the validity of the proposed approach as a time-saving and efficient method.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anipsitakis GP, Dionysiou DD, Gonzalez MA (2006) Cobalt-mediated activation of peroxymonosulfate and sulfate radical attack on phenolic compounds. Implications of chloride ions. Environ Sci Technol 40:1000–1007
Aquino JM, Rocha-Filho RC, Rodrigo MA, Sáez C, Cañizares P (2013) Electrochemical degradation of the Reactive Red 141 dye using a boron-doped diamond anode. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:n1397
Bensalah N, Abdel-Wahab A (2013) Electrochemical inactivation of P. Aeruginosa, A. hydrophila, L. pneumophila using boron doped diamond anodes. J Adv Oxid Technol 16:9–15
Bheemaraddi MC, Patil S, Shivannavar CT, Gaddad SM (2014) Isolation and characterization of Paracoccus sp. GSM2 capable of degrading textile azo dye reactive violet 5. Sci World J 2014:410704. doi:10.1155/2014/410704
Brinzila CI, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Ciobanu RC, Lopes A (2012) Electrodegradation of tetracycline on BDD anode. Chem Eng J 209:54–61
Cañizares P, Sáez C, Sánchez-Carretero A, Rodrigo MA (2009) Synthesis of novel oxidants by electrochemical technology. J Appl Electrochem 39:2143–2149
Chung Y-C, Chen C-Y (2009) Degradation of azo dye reactive violet 5 by TiO2 photocatalysis. Environ Chem Lett 7:347–352
Deng Y, Ezyske CM (2011) Sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for simultaneous removal of refractory organic contaminants and ammonia in landfill leachate. Water Res 45:6189–6194
Erler A, de Mas N, Ramsey P, Henderson G (2013) Efficient biological process characterization by definitive-screening designs: the formaldehyde treatment of a therapeutic protein as a case study. Biotechnol Lett 35:323–329
Fetyan NAH, Ali MMS, Break LM (2013) Biodegradation of a textile mono azo dye: Reactive Violet 5 by a novel isolated bacterial strain. Life Sci J 10:397–403
Georgiou SD, Stylianou S, Aggarwal M (2014) Efficient three-level screening designs using weighing matrices. Statistics 48:48815–48833
Griesbach U, Malkowsky IM, Waldvogel SR (2010) Green electroorganic synthesis using BDD electrodes. In: Comninellis C, Chen G (eds) Electrochemistry for the environment. Springer, New York, pp 125–141
Hunger K (2003) Industrial dyes: chemistry, properties, applications. Wiley, Weinheim
Jain K, Shah V, Chapla D, Madamwar D (2012) Decolorization and degradation of azo dye—Reactive Violet 5R by an acclimatized indigenous bacterial mixed cultures-SB4 isolated from anthropogenic dye contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 213–214:378–386
Jones B, Nachtsheim CJ (2011) A class of three-level designs for definitive screening in the presence of second-order effects. J Qual Technol 43:1–15
Khare UK, Bose P, Vankar PS (2007) Impact of ozonation on subsequent treatment of azo dye solutions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 82:1012–1022
Libbrecht W, Deruyck F, Poelman H, Verberckmoes A, Thybaut J, De Clercq J, Van Der Voort P (2015) Optimization of soft templated mesoporous carbon synthesis using definitive screening design. Chem Eng J 259:126–134
Mascia M, Vacca A, Palmas S (2013) Electrochemical treatment as a pre-oxidative step for algae removal using Chlorella vulgaris as a model organism and BDD anodes. Chem Eng J 219:512–519
Michaud PA, Mahé E, Haenni W, Perret A, Comninellis Ch (2000) Preparation of peroxodisulfuric acid using boron-doped diamond thin film electrodes. Electrochem Solid State Lett 3:77–79
Montanaro D, Petrucci E (2009) Electrochemical treatment of Remazol Brilliant Blue on a boron-doped diamond electrode. Chem Eng J 153:138–144
Nandi BK, Patel S (2014) Removal of Brilliant Green from aqueous solution by electrocoagulation using aluminum electrodes: experimental, kinetics and modeling. Sep Sci Technol 49:601–612
Oturan N, Brillas E, Oturan MA (2012) Unprecedented total mineralization of atrazine and cyanuric acid by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton with a boron-doped diamond anode. Environ Chem Lett 10:65–170
Perret A, Haenni W, Skinner N, Tang XM, Gandini D, Comninellis C, Correa B, Foti G (1999) Electrochemical behavior of synthetic diamond thin film electrodes. Diam Relat Mater 8:820–823
Petrucci E, Di Palma L, Lavecchia R, Zuorro A (2015a) Modeling and optimization of Reactive Green 19 oxidation on a BDD thin-film electrode. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 51:152–158
Petrucci E, Di Palma L, Lavecchia R, Zuorro A (2015b) Treatment of diazo dye Reactive Green 19 by anodic oxidation on a boron-doped diamond electrode. J Ind Eng Chem 26:116–121
Scialdone O, Guarisco C, Galia A (2011) Oxidation of organics in water in microfluidic electrochemical reactors: theoretical model and experiments. Electrochim Acta 58:463–473
Sotgiu G, Foderà M, Marra F, Petrucci E (2014) Production and characterization of manganese oxide-based electrodes for anodic oxidation of organic compounds. Chem Eng Trans 41:115–120
Steter JR, Rocha RS, Dionísio D, Lanza MRV, Motheo AJ (2014) Electrochemical oxidation route of methyl paraben on a boron-doped diamond anode. Electrochim Acta 117:127–133
Wang C, Chang S, Ye M, Ren Q (2013) Current efficiency and energy consumption of electrochemical oxidation for ammonia removal from coking wastewater using boron-doped diamond electrode. Appl Mech Mater 295–298:1327–1332
Xiao L, Lin DKJ, Bai F (2012) Constructing definitive screening designs using conference matrices. J Qual Technol 44:1–7
Zhou Y, Zhi J (2009) The application of boron-doped diamond electrodes in amperometric biosensors. Talanta 7:1189–1196
Zuorro A, Lavecchia R (2014) Evaluation of UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process (AOP) for the degradation of diazo dye Reactive Green 19 in aqueous solution. Desalin Water Treat 52:1571–1577
Zuorro A, Santarelli ML, Lavecchia R (2013) Tea waste: a new adsorbent for the removal of reactive dyes from textile wastewater. Adv Mater Res 803:26–29
Zuorro A, Petrucci E, Di Palma L, Lavecchia R (2014) Kinetic modelling of electrochemical decolorization of diazo dyes on boron-doped diamond electrodes. Chem Eng Trans 41:121–126
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank Gammacolor Srl (Seveso, Italy) for providing the azo dye RV5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fidaleo, M., Lavecchia, R., Petrucci, E. et al. Application of a novel definitive screening design to decolorization of an azo dye on boron-doped diamond electrodes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 835–842 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-0933-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-0933-3