Abstract
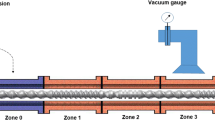
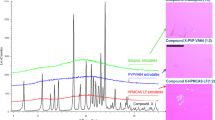
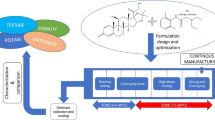
In this study, a quality-by-design (QbD) approach was used to optimize the development of paracetamol (PMOL) sustained-release formulations manufactured by hot-melt extrusion (HME). For the purpose of the study, in-line near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy as a process analytical technology (PAT) was explored while a design of experiment (DoE) was implemented to assess the effect of the process critical parameters and to identify the critical quality attributes (CQA) of the extrusion processing. Blends of paracetamol, ethyl cellulose (EC) and Compritol® 888 ATO (C888) were processed using a twin screw extruder to investigate the effect of screw speed, feed rate and drug loading on the dissolution rates and particle size distribution. The principal component analysis (PCA) of the NIR collected signal revealed the optimum extrusion processing parameters. Furthermore, the integration of the DoE experiments demonstrated that drug loading has a significant effect on the only quality attribute, which was the PMOL dissolution rate. This QbD approach was employed as a paradigm for the development of pharmaceutical formulations via HME processing











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gavin PA, David SJ, Osama AD, Daniel NM, Mark SMc. Hot-melt extrusion: an emerging drug delivery technology. Pharm Technol Eur. 2009;2(1)
Maniruzzaman M, Boateng JS, Snowden MJ, Douroumis D. A review of hot-melt extrusion: process technology to pharmaceutical products. IRRN Pharm. 2012;2012:436763.
Maniruzzaman M, Boateng JS, Bonnefille M, Aranyos A, Mitchell JC, Douroumis D. Taste masking of paracetamol by hot-melt extrusion: an in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012;80(2):433–42.
Cilurzo F, Cupone IE, Minghetti P, Selmin F, Montanari L. Fast dissolving film made of maltodextrins. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;70(3):895–900.
Kalivoda A, Fischbach M, Kleinebudde P. Application of mixtures of polymeric carriers for dissolution enhancement of fenofibrate using hot-melt extrusion. Int J Pharm. 2012;429(1–2):58–68.
De Brabander C, Vervaet C, Remon JP. Development and evaluation of sustained release mini-matrices prepared via hot melt extrusion. J Control Release. 2003;89:235–47.
Roblegg E, Jäger E, Hodzic A, Koscher G, Mohr S, Zimmer A, et al. Development of sustained-release lipophilic calcium stearate pellets via hot melt extrusion. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011;79:635–45.
Almeida A, Possemiers S, Boone MN, De Beer T, Quinten T, Van Hoorebeke L. Ethylene vinyl acetate as matrix for oral sustained release dosage forms produced via hot-melt extrusion. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011;77(2):297–305.
ICH. International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use, Topic Q8 (R2): Pharmaceutical development, Geneva, 2009.
ICH. International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use, Topic Q9: Pharmaceutical quality system, Geneva, 2005.
International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use, Topic Q10: Pharmaceutical quality system, Geneva, 2008.
Yu LX. Pharmaceutical quality by design: product and process development, understanding, and control. Pharm Res. 2008;25(4):781–91.
Fonteyne M, Soares S, Vercruysse J, Peeters E, Burggraeve A, Vervaet C, et al. Prediction of quality attributes of continuously produced granules using complementary PAT tools. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012;82(2):429–36.
Wu H, White M, Khan MA. Quality-by-design (QbD): an integrated process analytical technology (PAT) approach for a dynamic pharmaceutical co-precipitation process characterization and process design space development. Int J Pharm. 2011;405(1–2):63–78.
Adam S, Suzzi D, Radeke C, Khinast JG. An integrated quality by design (QbD) approach towards design space definition of a blending unit operation by discrete element method (DEM) simulation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2011;42(1–2):106–15.
Xie L, Wu H, Shen M, Augsburger LL, Lyon RC, Khan MA, et al. Quality-by-design (QbD): effects of testing parameters and formulation variables on the segregation tendency of pharmaceutical powder measured by the ASTM D 6940-04 segregation tester. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97(10):4485–97.
Food and Drug Administration CDER. Guidance for industry, PAT—a framework for innovative pharmaceutical development, manufacturing, and quality assurance. 2006
Saerens L, Dierickx L, Lenain B, Vervaet C, Remon JP, De Beer T. Raman spectroscopy for the in-line polymer–drug quantification and solid state characterization during a pharmaceutical hot-melt extrusion process. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011;77(1):158–63.
Saerens L, Dierickx L, Quinten T, Adriaensens P, Carleer R, Vervaet C. In-line NIR spectroscopy for the understanding of polymer–drug interaction during pharmaceutical hot-melt extrusion. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012;81(1):230–7.
De Beer T, Burggraeve A, Fonteyne M, Saerens L, Remon JP, Vervaet C. Near infrared and raman spectroscopy for the in-process monitoring of pharmaceutical production processes. Int J Pharm. 2011;417(1–2):32–47.
Kelly AL, Gough T, Dhumal RS, Halsey SA, Paradkar A. Monitoring ibuprofen–nicotinamide cocrystal formation during solvent free continuous cocrystallization (SFCC) using near infrared spectroscopy as a PAT tool. Int J Pharm. 2012;426(1–2):15–20.
Almeida A, Saerens L, De Beer T, Remon JP, Vervaet C. Up scaling and in-line process monitoring via spectroscopic techniques of ethylene vinyl acetate hot-melt extruded formulations. Int J Pharm. 2012;439(1–2):223–9.
Windbergs M, Strachan CJ, Kleinebudde P. Understanding the solid-state behaviour of triglyceride solid lipid extrudates and its influence on dissolution. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;71(1):80–7.
Windbergs M, Strachan CJ, Kleinebudde P. Influence of structural variations on drug release from lipid/polyethylene glycol matrices. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;37(5):555–62.
Rossi A, Savioli A, Bini M, Capsoni D, Massarotti V, Bettini R, et al. Solid-state characterization of paracetamol metastable polymorphs formed in binary mixtures with hydroxypropylmethylcellulose. Thermochim Acta. 2001;406:55–67.
Qi S, Gryczke A, Belton P, Craig DQM. Characterisation of solid dispersions of paracetamol and EUDRAGIT® E prepared by hot-melt extrusion using thermal, microthermal and spectroscopic analysis. Int J Pharm. 2008;354:158–67.
Qi S, Avalle P, Saklatvala R, Craig DQM. An investigation into the effects of thermal history on the crystallisation behaviour of amorphous paracetamol. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;69:364–71.
Sweeney G. (thesis) Queen’s Belfast University 2012.
Vithani K, Maniruzzaman M, Slipper IJ, Mostafa S, Miolane C, Cuppok Y, et al. Sustained release solid lipid matrices processed by hot-melt extrusion (HME). Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2013;110:403–10.
Haupt M, Thommes M, Heidenreich A, Breitkreutz J. Lipid-based intravesical drug delivery systems with controlled release of trospium chloride for the urinary bladder. J Control Rel. 2013;170:161–6.
Conflict of interest
Authors Islam, Maniruzzaman, Hasley, Chowdhry and Douroumis declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M.T., Maniruzzaman, M., Halsey, S.A. et al. Development of sustained-release formulations processed by hot-melt extrusion by using a quality-by-design approach. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 4, 377–387 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-014-0197-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-014-0197-8