Abstract
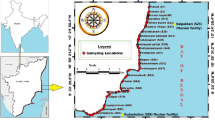
Primordial radionuclides in sand sediments that are often used as constructing materials are one of the sources of radiation hazard in dwellings. Activity concentrations of the primordial radionuclides of 40K, 226Ra and 232Th have been measured in sand sediments collected from streams and streamlets lying within and around the uranium mineralization deposit blocks of Kylleng-Pyndensohiong, Mawthabah Areas of West Khasi Hills District, Meghalaya, India. The technique of gamma-ray spectroscopy using a NaI(Tl) detector with a PC-based multi channel analyser was applied for determination of the activity concentrations. The activity of the sand sediments obtained in this study ranges from 95.3 to 1,088.8 Bq kg−1 for 40K; 38.3 to 784.1 Bq kg−1 for 226Ra and 78.0 to 316.1 Bq kg−1 for 232Th. Sand sediments from two sampling locations lying within the mineralization zone show highest concentrations of these radionuclides. The radiological hazards of the sand sediments were calculated using various models given in the literature. The radium equivalent activity was found to be higher than the accepted standard criterion value of 370 Bq kg−1 and the values of external and internal hazard indices were also found to be higher than unity in these two sampling locations. Besides these two sampling locations, a sampling location lying at a nearby distance from the mineralization zone also exhibits hazard indices values greater than unity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrani D, Tahtat M (2001) Natural radioactivity in Algerian building materials. Appl Radiat Isot 54:687–689
Beretka J, Mathew PJ (1985) Natural radioactivity of Australian building materials, industrial wastes and by-products. Health Phys 48(1):87–95
El-Arabi AM, Abbady Adel GE, Khalifa IH (2007) Radioactive and geochemistry characteristics of the garnetiferous granite of Um Sleimat Area, Egypt. Online J Earth Sci 1(1):9–20
Fleischer RL (1997) Radon: overview of properties, origin and transport. In: Durrani SA, Ilic R (eds) Radon measurements by etched track detectors, application in radiation protection earth sciences and environment. World Scientific, Singapore, pp 1–20
Gupta KR (1997) Uranium mineralization in Domiasiat Area, West Khasi Hills District, Meghalaya a case study. Exploration for Atomic Minerals, Part III, AMD—Training Course Handbook 3:55–66
HASL-300 (1990) Environmental Measurement Laboratory (HASL) Procedures Manual. 27th edn, In: Chieco Nancy A, Bogen DC, Knutson EO (eds) US Department of Energy 1, New York
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) (1977) Recommendation of ICRP Publication 26. Pergama Press, Oxford
Krieger R (1981) Radioactivity of construction materials. Betonwek Fertigteil Technik 47:468
Krisiuk EM, Tarasov SI, Shamov VP, Shlak NI, Lisachenko EP, Gomelsky LG (1971) A study of radioactivity in building materials. Research Institute for Radiation Hygiene, Leningrad
Labidi S, Essafi F, Mahjoubi H (2006) Estimation of the radiological risk related to the presence of radon 222 in a hydrotherapy centre in Tunisia. J Radiol Prot 26:309–316
Miles JCH, Appleton JD (2005) Mapping variation in radon potential both between and within geological units. J Radiol Prot 25:257–276
Mirza NM, Ali B, Mirza SM, Tufail M, Ahmad N (1991) A shape and mesh adaptive computational methodology for gamma ray dose from volumetric sources. Radiat Prot Dosim 38:307–314
Narayana Y, Rajashekara KM, Siddappa K (2005) Radioactivity in a major river of Coastal Karnataka. Environ Geochem 8(1, 2):186–189
Obed RI, Farai JP, Jibiri NN (2005) Population dose distribution due to soil radioactivity concentration levels in 18 cities across Nigeria. J Radiol Prot 25:305–312
OECD (Organization of Economic Co-operation and Development) (1979) Exposure to radiation from natural radioactivity in building materials. Report by a Group of Experts of the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency, Paris
Organo C, Murphy P (2007) The Castle island radon survey-follow-up to the discovery of a house with extremely high radon concentrations in County Kerry (SW Ireland). J Radiol Prot 27:275–285
Porstendorfer J (1994) Properties and behaviour of radon and thoron and their decay products in the air. J Aerosol Sci 25(2):219–263
Ramachandran TV, Eappen KP, Nair RN, Mayya YS, Sadasivan S (2003) Radon–Thoron levels and inhalation dose distribution patterns in Indian dwellings. BARC Report, BARC/2003/E/026
Ramkumar S, Rajaram S, Kannan V, Hegde AG (2007) Natural radioactivity in building materials at Kalapkkam. Mitig Pollut Clean Environ, 414–419
Sadasivan S (1989) Asian Regional Workshop on Methods of Analysis of radionuclides Contaminants of United Nations, pp 195
Shukla VK, Sartandel SJ, Ramachandran TV (2001) Natural Radioactivity Levels in soil samples from high radiation background areas of Kerala. Radiation Protection and Environment 24(1/2):437–439
Sinha RM (2005) Exploration for atomic minerals in India—an overview. IANCAS Bull 4(3):159–173
Tufail M, Akhtar N, Javied S, Hamid T (2007) Natural radioactivity hazards of building bricks from saline soil of two districts of Pakistan. J Radiol Prot 27:481–492
Tzortzis M, Tsertos H, Christopher S, Christodoulides G (2003) Gamma-ray measurements of naturally occurring radioactive samples from Cyprus characteristic geological rocks. Radiat Meas 37:221–229
United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effect of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) (1993) Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation. Report to the General Assembly, United Nations, New York
United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effect of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) (2000) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly, United Nations, New York
Acknowledgments
The author(s) duly acknowledge Shri H.S. Kushwaha, Dir., HS&EG, BARC, Mumbai and Shri V.D. Puranik, Head, EAD, BARC, Mumbai, Dr. R.M. Tripathi, EAD, BARC, Mumbai, Dr. S.K. Jha, EAD, BARC, Mumbai, Prof. B. Kharbuli, Department of Zoology, NEHU, Shillong and Dr. A.K. Das, Department of Basic Sciences, NEHU, Shillong for their constant encouragement, valuable suggestions and guidance provided throughout the period of work. Thanks also go to Shri N. Nongrem and Shri M. Kurbah for their help which they have rendered in carrying out the sample collection from the study area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
War, S.A., Nongkynrih, P., Khathing, D.T. et al. Assessment of the radiological hazards of sand sediments collected from streams and streamlets of the uranium deposit areas in West Khasi Hills District, Meghalaya, India. Environ Earth Sci 65, 1695–1703 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1147-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1147-0