Abstract
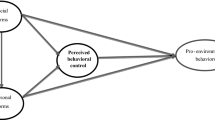
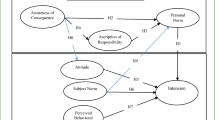
The effects of population growth in the world have prompted farmers to excessively use agricultural land to produce the required food. Hence, human activities have been endangering and destroying the environment. Accordingly, the present study was designed based on identifying and introducing the determinants of the application of pro-environmental behaviors among Iranian farmers. The present study was conducted using a questionnaire survey with structural equation modeling and technology acceptance model as the theoretical framework elements of the research. The study population consisted of all wheat farmers living in Khuzestan province (southwest of Iran). The results revealed that about 59.8% of the variance of the farmers’ pro-environmental behavior was estimated using the technology acceptance model. The results of structural equation modeling also revealed that variables of attitude and intention, perceived ease of use, and perceived usefulness had significant effects on farmers’ pro-environmental behaviors. In general, the results of the present study can be considered as scientific and logical evidence for utilizing the technology acceptance model in applying pro-environmental behaviors. In addition, the results of this study can help national and local policymakers as well as decision -makers to encourage farmers toward using pro-environmental behaviors.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
Integrated science data management
References
Abdollahzadeh, G., Sharifzadeh, M. S., & Damalas, C. A. (2016). Motivations for adopting biological control among Iranian rice farmers. Crop Protection, 80, 42–50.
Abdul Rashid, N., & Mohammad, N. (2012). A discussion of underlying theories explaining the spillover of environmentally friendly behavior phenomenon. Procardia-Social and Behavioral Sciences., 50, 1061–1072.
Adnan, N., Nordin, S. M., Bahruddin, M. A., & Tareq, A. H. (2019). A state-of-the-art review on facilitating sustainable agriculture through green fertilizer technology adoption: Assessing farmers behavior. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 86, 439–452.
Adnan, N., Nordin, S. M., & Anwar, A. (2020). Transition pathways for Malaysian paddy farmers to sustainable agricultural practices: An integrated exhibiting tactics to adopt green fertilizer. Land Use Policy, 90, 104255.
Aggelidis, V. P., & Chatzoglou, P. D. (2009). Using a modified technology acceptance model in hospitals. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 78(2), 115–126.
Agriculture Organization of Khuzestan. (2017). Agricultural status report in the last.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Orgnizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50, 179–211.
Akintunde, E. A. (2017). Theories and concepts for human behavior in environmental preservation. J Environ Sci Public Health, 1(2), 20e133. https://doi.org/10.26502/JESPH.012.
Akter, M., Fan, L., Rahman, M. M., Geissen, V., & Ritsema, C. J. (2018). Vegetable farmers’ behaviour and knowledge related to pesticide use and related health problems: A case study from Bangladesh. Journal of Cleaner Production, 200, 122–133.
Alambaigi, A., & Ahangari, I. (2016). Technology acceptance model (TAM) as a predictor model for explaining agricultural experts behavior in acceptance of ICT. International Journal of Agricultural Management and Development (IJAMAD), 6(1047–2017-1663), 235–247.
Bagheri, A., Bondori, A., Allahyari, M. S., & Surujlal, J. (2021). Use of biologic inputs among cereal farmers: application of technology acceptance model. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23(4), 5165-5181.
Blessing, I. A. (2012). Environmental literacy assessment: Exploring the potential for the assessment of environmental education/programs in Ontario schools. International Journal for Cross- Disciplinary Subjects in Education (IJCDSE), 3(1), 648–656.
Bleys, B., Defloor, B., Van Ootegem, L., & Verhofstadt, E. (2017). The environmental impact of individual behavior: Self-assessment versus the ecological footprint. Environment and Behavior, 50(2), 187–212.
Blok, V., Wesselink, R., Studynka, O., & Kemp, R. (2015). Encouraging sustainability in the workplace: A survey on the proenvironmental behavior of university employees. Journal of Cleaner Production, 106, 55–67.
Borkhani, F. R., & Mohammadi, Y. (2019). Perceived outcomes of Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs) technologies adoption in citrus farms of Iran (reflection of environment-friendly technologies). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(7), 6829–6838.
Cacciamani, S., Villani, D., Bonanomi, A., Carissoli, C., Olivari, M. G., Morganti, L., & Confalonieri, E. (2018). Factors affecting students’ acceptance of tablet PCs: A study in Italian high schools. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 50(2), 120–133.
Casaló, L. V., & Escario, J. J. (2018). Heterogeneity in the association between environmental attitudes and pro-environmental behavior: A multilevel regression approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 175, 155–163.
Castiblanco Jimenez, I. A., Cepeda García, L. C., Violante, M. G., Marcolin, F., & Vezzetti, E. (2021). Commonly used external TAM variables in e-learning, agriculture and virtual reality applications. Future Internet, 13(1), 7.
Chatfield, M., & Mander, A. (2009). The Skillings–Mack test (Friedman test when there are missing data). The Stata Journal, 9(2), 299–305.
Cheung, R., & Vogel, D. (2013). Predicting user acceptance of collaborative technologies: An extension of the technology acceptance model for e-learning. Computers & Education, 63, 160–175.
Clarke, L., & Abbott, L. (2016). Young pupils’, their teacher’s and classroom assistants’ experiences of i P ads in a N orthern I reland school: “four and five years old, who would have thought they could do that?”. British Journal of Educational Technology, 47(6), 1051–1064.
Conner, M., & Armitage, C. J. (1998). Extending the theory of planned behavior: A review and avenues for further research. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 28(15), 1429–1464.
Cottrell, S. P. (2003). Influence of sociodemographics and environmental attitudes on general responsible environmental behavior among recreational boaters. Environment and Behavior, 35(3), 347–375.
Damalas, C. A., & Koutroubas, S. D. (2018). Farmers' behaviour in pesticide use: A key concept for improving environmental safety. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 4, 27–30.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. Management Information Systems Quarterly, 319–340.
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989). User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science, 35(8), 982–1003.
Dornhoff, M., Sothmann, J. N., Fiebelkorn, F., & Menzel, S. (2019). Nature relatedness and environmental concern of young people in Ecuador and Germany. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 453. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00453 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term¼Dornhoff%20M%5BAuthor%5D&cauthor¼true&cauthor_uid¼30899233.
Ducey, A. J., & Coovert, M. D. (2016). Predicting tablet computer use: An extended technology acceptance model for physicians. Health Policy and Technology, 5(3), 268–284.
Dündar, H., & Akçayır, M. (2014). Implementing tablet PCs in schools: Students’ attitudes and opinions. Computers in Human Behavior, 32, 40–46.
Eskandari-Damaneh, H., Noroozi, H., Ghoochani, O. M., Taheri-Reykandeh, E., & Cotton, M. (2020). Evaluating rural participation in wetland management: A contingent valuation analysis of the set-aside policy in Iran. Science of the Total Environment, 747, 141127.
FAO. (2018). Global consumption of agricultural fertilizer by nutrient from 2013 to 2018 (in million metric tons). In Food and agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Italy.
Farani, A. Y., Mohammadi, Y., & Ghahremani, F. (2019). Modeling farmers’ responsible environmental attitude and behaviour: A case from Iran. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(27), 28146–28161.
Ferguson, J. M. (2017). Middle school students’ reactions to a 1: 1 iPad initiative and a paperless curriculum. Education and Information Technologies, 22(3), 1149–1162.
Field, A. (2013). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics. Sage.
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975a). Belief, attitude, intention and behaviour. Addison-Wesley.
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975b). Belief, attitude, intention, and behavior: An introduction to theory and research. Philosophy and Rhetoric, 10(2), 1–8.
Flett, R., Alpass, F., Humphries, S., Massey, C., Morriss, S., & Long, N. (2004). The technology acceptance model and use of technology in New Zealand dairy farming. Agricultural Systems, 80(2), 199–211.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(3), 328–388.
Fransson, N., & Gärling, T. (1999). Environmental concern: Conceptual definitions, measurement methods, and research findings. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 19(4), 369–382.
Frittief. C. (2015). “Hidden bonds: Combining the biological and social spheres of life in sustainability”. Translation by Mohammad Hariri Akbar, Tehran, [In Persian].
Gangadharappa, H., Pramod, K., & Shiva, K. H. (2007). Gastric floating drug delivery systems: a review. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, 41(4), 295–305.
Gao, L., Wang, S., Li, J., & Li, H. (2017). Application of the extended theory of planned behavior to understand individual’s energy saving behavior in workplaces. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 127, 107–113.
Gautam, S., Schreinemachers, P., Uddin, M. N., & Srinivasan, R. (2017). Impact of training vegetable farmers in Bangladesh in integrated pest management (IPM). Crop Protection, 102, 161–169.
Gebrezgabher, S. A., Meuwissen, M. P., Kruseman, G., Lakner, D., & Lansink, A. G. O. (2015). Factors influencing adoption of manure separation technology in the Netherlands. Journal of Environmental Management, 150, 1–8.
Gefen, D. (2003). Assessing unidimensionality through LISREL: An explanation and an example. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 12(1), 2.
Ghorbani, M., Eskandari-Damaneh, H., Cotton, M., Ghoochani, O. M., & Borji, M. (2021). Harnessing indigenous knowledge for climate change-resilient water management–lessons from an ethnographic case study in Iran. Climate and Development, 1–14.
Ghorbannezhad, M., Choobchian, S., & Farhadian, H. (2019). Investigating factors affecting farmer’s intention of adopting renewable energy technology in Larestan County. Iranian Journal of Agricultural Economics and Development Research, 50(2), 347–365.
Gokcearslan, S. (2017). Perspectives of students on acceptance of tablets and self-directed learning with technology. Contemporary Educational Technology, 8(1), 40–55.
Greaves, M., Zibarras, L. D., & Stride, C. (2013). Using the theory of planned behavior to explore environmental behavioral intentions in the workplace. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 34, 109–120.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2017). A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) (2nd ed.).
Henseler, J., & Sarstedt, M. (2013). Goodness-of-fit indices for partial least squares path modeling. Computational Statistics, 28(2), 565–580.
Hirsh, J. B. (2014). Environmental sustainability and national personality. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 38, 233–240.
Hori, S., Kondo, K., Nogata, D., & Ben, H. (2013). The determinants of household energy-saving behavior: Survey and comparison in five major Asian cities. Energy Policy, 52, 354–362.
Hsu, C., & Lin, J. (2008). Acceptance of blog usage: The roles of technology acceptance, social influence and knowledge sharing motivation. Information & Management, 45, 65–74.
Huang, P. S., & Shih, L. H. (2009). Effective environmental management through environmental knowledge management‖. Environmental Science Technology (Environ Sci Technol), 6(1), 35–50.
Husk, B. R., Anderson, B. C., Whalen, J. K., & Sanchez, J. S. (2017). Reducing nitrogen contamination from agricultural subsurface drainage with denitrification bioreactors and controlled drainage. Biosystems Engineering, 153, 52–62.
Hynes, N., & Wilson, J. (2016). I do it, but don't tell anyone! Personal values, personal and social norms: Can social media play a role in changing pro-environmental behaviours? Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 111, 349–359.
Ifenthaler, D., & Schweinbenz, V. (2016). Students' acceptance of tablet PCs in the classroom. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 48(4), 306–321.
Janmaimool, P., & Denpaiboon, C. (2016). Evaluating determinants of rural Villagers’ engagement in conservation and waste management behaviors based on integrated conceptual framework of Pro-environmental behavior. Life Sciences, Society and Policy, 12(1), 12.
Jimenez, I. A. C., García, L. C. C., Violante, M. G., Marcolin, F., & Vezzetti, E. (2021). Commonly used external TAM variables in e-learning, agriculture and virtual reality applications. Future Internet, 13(1), 7.
Kabir, M. H., Rainis, R., & Azad, M. J. (2017). Are spatial factors important in the adoption of eco-friendly agricultural technologies? Evidence on integrated pest management (IPM). Journal of Geographic Information System, 9(2), 98–113.
Kalantari, K. (2003). Data processing and analysis in socio-economic research. Sharif.
Kamal, S. A., Shafiq, M., & Kakria, P. (2020). Investigating acceptance of telemedicine services through an extended technology acceptance model (TAM). Technology in Society, 60, 101212.
Kanter, D. R. (2018). Nitrogen pollution: A key building block for addressing climate change. Climatic Change, 147(1–2), 11–21.
Khanpae, M., Karami, E., Maleksaeidi, H., & Keshavarz, M. (2020). Farmers’ attitude towards using treated wastewater for irrigation: The question of sustainability. Journal of Cleaner Production, 243, 118541.
Khoshmaram, M., Shiri, N., Shinnar, R. S., & Savari, M. (2020). Environmental support and entrepreneurial behavior among Iranian farmers: The mediating roles of social and human capital. Journal of Small Business Management, 58(5), 1064–1088.
Kien, A. (2015). Factors influencing safety pesticide use behavior among farmers in Thingyan Province, Vietnam (doctoral dissertation, doctoral dissertation, MSc Thesis. Faculty of Nursing, Burapha University, Thailand).
Kim, H. J., & Jang, H. Y. (2015). Factors influencing students' beliefs about the future in the context of tablet-based interactive classrooms. Computers & Education, 89, 1–15.
Knowler, D., & Bradshaw, B. (2007). Farmers’ adoption of conservation agriculture: A review and synthesis of recent research. Food Policy, 32(1), 25–48.
Lai, H. J. (2018). Investigating older adults’ decisions to use mobile devices for learning, based on the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. Interactive Learning Environments, 28(7), 890–901.
Li, D., Zhaoc, L., Mab, S., Shaoe, S., & Zhang, L. (2019). What influences an individual’s pro-environmental behavior? A literature review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 146, 28e34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.024.
Liu, I. F., Chen, M. C., Sun, Y. S., Wible, D., & Kuo, C. H. (2010). Extending the TAM model to explore the factors that affect intention to use an online learning community. Computers & Education, 54(2), 600–610.
Macgregor, C. J., & Warren, C. R. (2006). Adopting sustainable farm management practices within a nitrate vulnerable zone in Scotland: The view from the farm. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 113(1–4), 108–119.
Mahdi, S. S., Hassan, G. I., Samoon, S. A., Rather, H. A., Dar, S. A., & Zehra, B. (2010). Bio-fertilizers in organic agriculture. Journal of Phytology, 2(10), 42–54.
Maleksaeidi, H., & Keshavarz, M. (2019). What influences farmers' intentions to conserve on-farm biodiversity? An application of the theory of planned behavior in Fars province, Iran. Global Ecology and Conservation, 20, e00698.
Mason, A. M., & Triplett, J. R. (2016). Controlling environmental crisis messages in uncontrollable media environments: The 2011 case of blue-green algae on grand Lake O ‘the Cherokees, OK. In Communicating Climate-Change and Natural Hazard Risk and Cultivating Resilience, 189–204.
Milfont, T. L., & Schultz, P. W. (2016). Culture and the natural environment. Current Opinion in Psychology, 8, 194–199.
Neo, S. M., Choong, W. W., & Ahamad, R. B. (2017). Differential environmental psychological factors in determining low carbon behaviour among urban and suburban residents through responsible environmental behaviour model. Sustainable Cities and Society, 31, 225–233.
Nikou, S. A., & Economides, A. A. (2018). Mobile-based micro-learning and assessment: Impact on learning performance and motivation of high school students. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 34(3), 269–278.
Raykov, T. (2001). Bias of coefficient afor fixed congeneric measures with correlated errors. Applied Psychological Measurement, 25(1), 69–76.
Rezaei, R., Mianaji, S., & Ganjloo, A. (2018). Factors affecting farmers’ intention to engage in on-farm food safety practices in Iran: Extending the theory of planned behavior. Journal of Rural Studies, 60, 152–166.
Rezaei, R., Safa, L., & Ganjkhanloo, M. M. (2020). Understanding farmers’ ecological conservation behavior regarding the use of integrated pest management-an application of the technology acceptance model. Global Ecology and Conservation, 22, e00941.
Rho, M. J., Young Choi, I., & Lee, J. (2014). Predictive factors of telemedicine service acceptance and behavioral intention of physicians. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 83(8), 559–571.
Rogers, E. M. (1995). Diffusion of innovations (4th Eds.) ACM, the Free Press (Sept. 2001). New York, pp. 15–23.
Savari, M., & Gharechaee, H. (2020). Application of the extended theory of planned behavior to predict Iranian farmers’ intention for safe use of chemical fertilizers. Journal of Cleaner Production, 263, 121512.
Savari, M., & Shokati Amghani, M. (2021). Factors influencing farmers’ adaptation strategies in confronting the drought in Iran. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23, 4949–4972.
Savari, M., & Zhoolideh, M. (2021). The role of climate change adaptation of small-scale farmers on households' food security in Iran. Development in Practice, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1080/09614524.2021.1911943.
Savari, M., Ebrahimi-Maymand, R., & Mohammadi-Kanigolzar, F. (2013). The Factors influencing the application of organic farming operations by farmers in Iran. Agris on-line Papers in Economics and Informatics, 5(665–2016-44970), 179–187.
Savari, M., Damaneh, H. E., & Damaneh, H. E. (2020a). Factors influencing local people’s participation in sustainable forest management. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13(13), 1–13.
Savari, M., Eskandari Damaneh, H., & Damaneh, H. E. (2020b). Factors influencing farmers’ management behaviors toward coping with drought: Evidence from Iran. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 1–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2020.1855128
Savari, M., Abdeshahi, A., Gharechaee, H., & Nasrollahian, O. (2021). Explaining farmers’ response to water crisis through theory of the norm activation model: Evidence from Iran. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 60, 102284.
Schenk, A., Hunziker, M., & Kienast, F. (2007). Factors influencing the acceptance of nature conservation measures A qualitative study in Switzerland. Journal of Environmental Management, 83(1), 66–79.
Schwartz, S. H. (1977). Normative influences on altruism. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 10(1), 221–279.
Shafiei, A., & Maleksaeidi, H. (2020). Pro-environmental behavior of university students: Application of protection motivation theory. Global Ecology and Conservation, 22, e00908.
Shamsi Paikiadeh, Z., & Shobairi, M. (2019). Investigation of socio-economic factors affecting women's environmental awareness. Journal of Women and Society, 10(2), 319 [In Persian].
Sharifzadeh, M. S., Damalas, C. A., Abdollahzadeh, G., & Ahmadi-Gorgi, H. (2017). Predicting adoption of biological control among Iranian rice farmers: An application of the extended technology acceptance model (TAM2). Crop Protection, 96, 88–96.
Shiri, N., Faghiri, M., Pirmoradi, A., & Agahi, H. (2014). Attitudes of agricultural extension workers towards organic farming in Iran. Journal of Organic Systems, 9(1), 5–15.
Silva, A., Canavari, M., & Sidali, K. L. (2017). A technology acceptance model of common bean growers’ intention to adopt integrated production in the Brazilian central region= Ein Technologie-Akzeptanzmodell zur Absicht von Bohnenproduzenten, integrate production in brasilianischen Zentralgebiet einzuführen. Bodenkultur-Wien and Munchen, 68(3), 131–143.
Simms, L. J. (2008). Classical and modern methods of psychological scale construction. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 2(1), 414–433.
Sopha, B. M., Christian, A. K., Bjørnstad, E., & Matthies, E. (2011). Literature research on energy behavior:Behavioral models. Determinants, Indicators, Barriers and Interventions. Report in the Enova project Indicators of determinants of household energy behaviours. Enova, Trondheim, Norway.
Steg, L., & De Groot, J. (2010). Explaining prosocial intentions: Testing causal relationships in the norm activation model. British Journal of Social Psychology, 49(4), 725–743.
Steg, L., & Vlek, C. (2009). Encouraging pro-environmental behaviour: An integrative review and research agenda. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 29(3), 309–317.
Steg, L., Bolderdijk, J. W., Keizer, K., & Perlaviciute, G. (2014). An integrated framework for encouraging pro-environmental behavior: The role of values, situational factors and goals. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 38, 104–115.
Stern, P. C., Dietz, T., Abel, T., Guagnano, G. A., & Kalof, L. (1999). A value-belief-norm theory of support for social movements: The case of environmentalism. Human Ecology Review, 81–97.
Sung, H. Y., Hwang, G. J., Chen, C. Y., & Liu, W. X. (2019). A contextual learning model for developing interactive e-books to improve students’ performances of learning the analects of Confucius. Interactive Learning Environments, 1–14.
Świtek, S., & Sawinska, Z. (2017). Farmer rationality and the adoption of greening practices in Poland. Scientia Agricola, 74(4), 275–284.
Tang, Y., Geng, L., Schultz, P. W., Zhou, K., & Xiang, P. (2017). The effects of mindful learning on pro-environmental behavior: A self-expansion perspective. Consciousness and Cognition, 51, 140–148.
Telles, T. S., Righetto, A. J., da Costa, G. V., Volsi, B., & de Oliveira, J. F. (2019). Conservation agriculture practices adopted in southern Brazil. International Journal of Agricultural Sustainability, 17(5), 338–346.
Thondhlana, G., & Hlatshwayo, T. N. (2018). Pro-environmental behaviour in student residences at Rhodes University, South Africa. Sustainability, 10(8), 2746.
Veisi, H. (2012). Exploring the determinants of adoption behaviour of clean technologies in agriculture: A case of integrated pest management. Asian Journal of Technology Innovation, 20(1), 67–82.
Venkatesh, V. (2000). Determinants of perceived ease of use: Integrating control, intrinsic motivation, and emotion into the technology acceptance model. Information Systems Research, 11(4), 342–365.
Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Management Science, 46(2), 186–204.
Verma, P., & Sinha, N. (2018). Integrating perceived economic wellbeing to technology acceptance model: The case of mobile based agricultural extension service. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 126, 207–216.
Vicente-Molina, M., Fernández-Sáinz, A., Izagirre-Olaizola, A., & J. (2013). Environmental knowledge and other variables affecting pro-environmental behaviour: Comparison of university students from emerging and advanced countries‖. Journal of Cleaner Production, 61, 130–138.
Wang, S., Fan, J., Zhao, D., Yang, S., & Fu, Y. (2016). Predicting consumers’ intention to adopt hybrid electric vehicles: Using an extended version of the theory of planned behavior model. Transportation, 43(1), 123–143.
Webb, D., Soutar, G. N., Mazzarol, T., & Saldaris, P. (2013). Self-determination theory and consumer behavioral change: Evidence from a household energy-saving behavior study. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 35, 59–66.
Yadav, R., & Pathak, G. S. (2016). Young consumers’ intention towards buying green products in a developing nation: Extending the theory of planned behavior. Journal of Cleaner Production, 135, 732–739.
Yuan, F., Tang, K., & Shi, Q. (2021). Does internet use reduce chemical fertilizer use? Evidence from rural households in China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(5), 6005–6017.
Zarafshani, K., Solaymani, A., D’Itri, M., Helms, M. M., & Sanjabi, S. (2020). Evaluating technology acceptance in agricultural education in Iran: A study of vocational agriculture teachers. Social Sciences & Humanities Open, 2(1), 100041.
Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., & Zhou, G. (2014). Determinants of employee electricity saving: The role of social benefits, personal benefits and organizational electricity saving climate. Journal of Cleaner Production, 66, 280–287.
Zheng, J., & Li, S. (2020). What drives students’ intention to use tablet computers: An extended technology acceptance model. International Journal of Educational Research, 102, 101612.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the support provided by Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources University of Khuzestan, Iran.
Funding
The authors are grateful for the support provided by Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources University of Khuzestan, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest with respect to their authorship or the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savari, M., Zhoolideh, M. & Khosravipour, B. Explaining pro-environmental behavior of farmers: A case of rural Iran. Curr Psychol 42, 7752–7770 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02093-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02093-9