Abstract
Background
Most knee surgeons have believed during TKA neutral mechanical alignment should be restored. A number of patients may exist, however, for whom neutral mechanical alignment is abnormal. Patients with so-called “constitutional varus” knees have had varus alignment since they reached skeletal maturity. Restoring neutral alignment in these cases may in fact be abnormal and undesirable and would likely require some degree of medial soft tissue release to achieve neutral alignment.
Questions/purposes
We investigated what percentage of the normal population has constitutional varus knees and what are the contributing factors.
Subjects and Methods
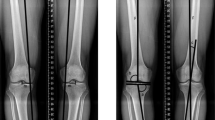
We recruited a cohort of 250 asymptomatic adult volunteers between 20 and 27 years old for this cross-sectional study. All volunteers had full-leg standing digital radiographs on which 19 alignment parameters were analyzed. The incidence of constitutional varus alignment was determined and contributing factors were analyzed using multivariate prediction models.
Results
Thirty-two percent of men and 17% of women had constitutional varus knees with a natural mechanical alignment of 3° varus or more. Constitutional varus was associated with increased sports activity during growth, increased femoral varus bowing, an increased varus femoral neck-shaft angle, and an increased femoral anatomic mechanical angle.
Conclusions
An important fraction of the normal population has a natural alignment at the end of growth of 3° varus or more. This might be a consequence of Hueter-Volkmann’s law. Restoration of mechanical alignment to neutral in these cases may not be desirable and would be unnatural for them.
Level of Evidence
Level I, diagnostic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Buzzi R. Posteriorly stabilized total-condylar knee replacement: three to eight years’ follow-up of 85 knees. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988:70;211–216.
Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MA. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty: correlated biomechanical and clinical observations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;173:178–183.
Bellemans J, Carpentier K, Vandenneucker H, Vanlauwe J, Victor J. The John Insall Award. Both morphotype and gender influence the shape of the knee in patients undergoing TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;468:29–36.
Benjamin J. Component alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2006;55:405–412.
Berend ME, Ritter MA, Meding JB, Faris PM, Keating EM, Redelman R, Faris GW, Davis KE. Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;428:26–34.
Cates HE, Ritter MA, Keating EM, Faris PM. Intramedullary versus extramedullary femoral alignment systems in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;286:32–39.
Chao EY, Neluheni EV, Hsu RW, Paley D. Biomechanics of malalignment. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994;25:379–386.
Colebatch AN, Hart DJ, Zhai G, Williams FM, Spector TD, Arden NK. Effective measurement of knee alignment using AP knee radiographs. Knee. 2009;16:42–45.
Cook SD, Lavernia CJ, Burke SW, Skinner HB, Haddad RJ. A biomechanical analysis of the etiology of tibia vara. J Pediatric Orthop. 1983;3:449–454.
Cooke D, Scudamore A, Li J, Wyss U, Bryant, Costigan P. Axial lower-limb alignment: comparison of knee geometry in normal volunteers and osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997;5:39–47.
Cooke TD, Li J, Scudamore RA. Radiographic assessment of bony contributions to knee deformity. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994;25:387–393.
Cooke TD, Sled EA. Optimizing limb position for measuring knee anatomical axis alignment from standing knee radiographs. J Rheumatol. 2009;36:472–477.
Cooke TD, Sled EA, Scudamore RA. Frontal plane knee alignment: a call for standardized measurement. J Rheumatol. 2007;34:1796–1801.
Eastwood DM, Sanghrajka AP. Guided growth: recent advances in a deep-rooted concept. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93:12–18.
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(6 Suppl):39–42.
Howell SM, Howell SJ, Hull ML. Assessment of the radii of the medial and lateral femoral condyles in varus and valgus knees with osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:98–104.
Howell SM, Kuznik K, Hull ML, Siston RA. Results of an initial experience with custom-fit positioning total knee arthroplasty in a series of 48 patients. Orthopedics. 2008;31:857–863.
Hsu RW, Himeno S, Coventry MB, Chao EY. Normal axial alignment of the lower extremity and load-bearing distribution at the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;255:215–227.
Hueter C. Anatomische Studien an den Extremitatengelenken Neugeborener und Erwachsener. Virchow Arch Pathol Anat. 1862;26:484–519.
Hungerford DS, Hungerford MW. Alignment of the human knee: relationship to total knee replacement. In: Bellemans J, Ries M, Victor J, eds. Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Guide to Better Performance. 1st ed. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 2005:25–32.
Hunt MA, Birmingham TB, Jenkyn TR, Giffin JR, Jones IC. Measures of frontal plane lower limb alignment obtained from static radiographs and dynamic gait analysis. Gait Posture. 2008;27:635–640.
Jenny JY, Boeri C, Ballonzoli L. Coronal alignment of the lower limb. Acta Orthop. 2005;76:403–407.
Krackow KA, Bayers-Thering M, Phillips MJ, Bayers-Thering M, Mihalko WM. A new technique for determining proper mechanical axis alignment during total knee arthroplasty: progress toward computer-assisted TKA. Orthopedics. 1999;22:698–702.
Lotke PA, Ecker ML. Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:77–79.
Mihalko WM, Krackow KA. Differences between extramedullary, intramedullary, and computer-aided surgery tibial alignment techniques for total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2006;19:33–36.
Moreland JR, Basset LW, Hanke GJ. Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69:745–749.
Nguyen AD, Shultz SJ. Sex differences in clinical measures of lower extremity alignment. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2007;37:389–398.
Paley D. Principles of Deformity Correction. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 2003:1–60.
Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ. Effect of mechanical axis alignment on fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:2143–2149.
Rauth MA, Mihalko WM, Krackow KA. Optimizing alignment. In: Bellemans J, Ries M, Victor J, eds. Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Guide to Better Performance. 1st ed. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 2005:165–169.
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB. Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement: its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;299:153–156.
Sabharwal S, Zhao C, Edgar M. Lower limb alignment in children: reference values based on a full-length standing radiograph. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28:740–746.
Saran N, Rathjen KE. Guided growth for the correction of pediatric lower limb angular deformity. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18:528–536.
Sikorski JM. Alignment in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90:1121–1127.
Stokes IA. Mechanical effects on skeletal growth. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2002;2:277–280.
Tang WM, Zhu YH, Chiu KY. Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:1603–1608.
Tew M, Waugh W. Tibiofemoral alignment and the results of knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985;67:551–556.
Vanwanseele B, Parker D, Coolican M. Frontal knee alignment: three-dimensional marker positions and clinical assessment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:504–509.
Victor J, Urlus M, Bellemans J, Fabry G. Femoral intramedullary instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty: the role of pre-operative X-ray analysis. Knee. 1994;1:123–125.
Volkmann R. Chirurgische Erfahrungen uber Knochenverbiegung und Knochenwachtsum. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat. 1862;24:512–540.
Willy C, Schneider P, Engelhardt M, Hargens AR, Mubarak SJ. Richard Von Volkmann: surgeon and Renaissance man. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:500–506.
Witvrouw E, Danneels L, Thijs Y, Cambier D, Bellemans J. Does soccer participation lead to genu varum? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17:422–427.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Myrthe Boymans for her illustrations included in this manuscript. The statistical analysis was performed by the Biostatistical Centre of the School of Public Health of the Catholic University Leuven.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The institution of the authors has received research funding from Smith and Nephew, Inc (Memphis, TN), Sanofi-Aventis (Bridgewater, NJ), DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc (Warsaw, IN), Biomet, Inc (Warsaw, IN), Technische Orthopedie Belgium (Wetteren, Belgium), Synthes, Inc (West Chester, PA), and Pfizer, Inc (Princeton, NJ). Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
About this article
Cite this article
Bellemans, J., Colyn, W., Vandenneucker, H. et al. The Chitranjan Ranawat Award: Is Neutral Mechanical Alignment Normal for All Patients?: The Concept of Constitutional Varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470, 45–53 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1936-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1936-5