Abstract
Background
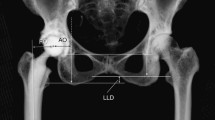
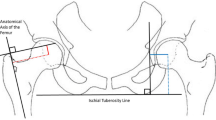
Offset in THA correlates to abductor muscle function, wear, and impingement. Femoral offset after THA is not independent of the cup center of rotation (COR) so hip offset, a combination of femoral offset and change in hip COR, becomes the important measurement.
Questions/purposes
We therefore asked whether hip offset in arthritic hips would correlate with cup COR; whether offset could always be balanced within 6 mm of contralateral normal hips; and whether hip length could also be kept within 6 mm.
Methods
We compared hip offset of arthritic and contralateral normal hips on radiographs in 82 patients (82 hips) who had THA. We used computer navigation in all patients with the aim of reconstructing the hip offset and to compare hip offset change to the quantitative change of the hip COR.
Results
The preoperative radiographic change to equalize the offset ranged from −12 to +21 mm (mean, 1.5); postoperatively the change was 1.4 ± 6.4 mm and was within ± 6 mm in 78 of 82 hips. As COR displaced superiorly from 3 to 6+ mm the offset had to be substantially increased. Only with COR 0–3 mm superior and 0–5 mm medial was offset always within 5 mm.
Conclusions
Hip offset reconstruction was directly related to the position of the hip COR, and navigation allowed quantitative control of offset and hip length.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asayama I, Chamnongkich S, Simpson KJ, Kinsey TL, Mahoney OM. Reconstructed hip joint position and abductor muscle strength after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:414–420.
Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH. Soft tissue balancing: The hip. J Arthroplasty. 2002; 17(Suppl 1):17–22.
Charles MN, Bourne RB, Davey JR, Greenwald AS, Morrey BF, Rorabeck CH. Soft-tissue balancing of the hip: the role of femoral offset restoration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:1078–1088.
Dolhain P, Tsigaras H, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Mac Donald S, Mc Calden R. The effectiveness of dual offset stems in restoring offset during total hip replacement. Acta Orthop Belg, 2002;68:490–499.
Dorr LD. Hip Arthroplasty: Minimally Invasive Techniques and Computer Navigation. 1st ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; 2005.
Flecher X, Parratte S, Brassart N, Aubaniac JM, Argenson JN. Evaluation of the hip center in total hip arthroplasty for old development dysplasia. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23:1189–1196.
Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51:737–755.
Heaton K, Dorr LD. Surgical release of iliopsoas tendon for groin pain after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:779–781.
Johnston RC, Brand RA, Crownenshield RD. Reconstruction of the hip. A mathematical approach to determine optimum geometric relationships. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61:639–652.
Karachalios T, Hartofilakidis G, Zacharakis N, Tsekoura M. A 12- to 18-year radiographic follow-up study of Charnley low-friction arthroplasty. The role of the center of rotation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;296:140–147.
Krishnan SP, Carrington RW, Mohiyaddin S, Garlick N. Common misconceptions of normal hip joint relations on pelvic radiographs. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21:409–412.
Kurtz WB, Ecker TM, Reichmann WM, Murphy SB. Factors affecting bony impingement in hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25:624–634.
Little NJ, Busch CA, Gallagher JA, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB. Acetabular polyethylene wear and acetabular inclination and femoral offset. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:2895–2900.
Long WT, Dastane M, Harris MJ, Wan Z, Dorr LD. Failure of the Durom Metasul acetabular component. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:400–405.
Loughead JM, Chesney D, Holland JP, McCaskie AW. Comparison of offset in Birmingham hip resurfacing and hybrid total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:163–166.
Malik A, Maheshwari A, Dorr LD. Impingement with total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:1832–1842.
McGrory BJ, Morrey BJ, Cahalan TD, An KN, Cabanela ME. Effect of femoral offset on range of motion and abductor muscle strength after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77:865–869.
Pagnano MW, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG, Shaughnessy WJ. Effect of superior placement of the acetabular component on the rate of loosening after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78:1004–1014.
Ranawat CS, Dorr LD, Inglis AE. Total hip arthroplasty in protusio acetabuli of rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62:1059–1065.
Ranawat CS, Rao RR, Rodriguez JA, Bhende HS. Correction of limb-length inequality during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16:715–720.
Ranawat CS, Rodriguez JA. Functional leg-length inequality following total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12:359–364.
Renkawitz T, Schuster T, Herold T, Goessmann H, Sendtner E, Grifka J, Kalteis T. Measuring leg length and offset with an imageless navigation system during total hip arthroplasty: is it really accurate? Int J Med Robot. 2009;5:192–197.
Resnick D. Bone and Joint Imaging. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2005.
Sakalkale DP, Sharkey PF, Eng K, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH. Effect of femoral component offset on polyethylene wear in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;388:125–134.
Silva, M, Lee KH, Heisel C, Dela Rosa MS, Schmalzried TP. The biomechanical results of total hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A:40–60.
Stans AA, Pagnano MW, Shaughnessy WJ, Hanssen AD. Results of total hip arthroplasty for Crowe type III developmental hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;348:149–157.
Sugano N, Noble PC, Kamaric E. Predicting the position of the femoral head center. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14:102–107.
Yoder SA, Brand RA, Pedersen DR, O’Gorman TW. Total hip acetabular component position affects component loosening rates. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;228:79–87.
Acknowledgments
We thank Patricia J. Paul for preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (LDD) received royalties from Zimmer, Inc.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
About this article
Cite this article
Dastane, M., Dorr, L.D., Tarwala, R. et al. Hip Offset in Total Hip Arthroplasty: Quantitative Measurement with Navigation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469, 429–436 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1554-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1554-7