Abstract
Purpose
To assess the relationship between glycaemic control and quality of life (QoL) among a sample of Malaysians with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
This study is a cross-sectional hospital-based study involving 256 patients from three major ethnic groups in Malaysia. Data about QoL were collected with the 18-item Audit of Diabetes Dependent QoL questionnaire. Other data about putative predictors of QoL including personal characteristics and disease-related factors were also collected. Hierarchical multiple linear regression was used to determine factors associated with QoL and to control for confounding variables.
Results
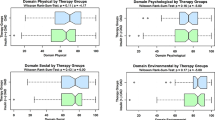
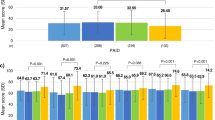
The mean age of participants was 56.79 years. Participants were mostly women, employed and married and had attained secondary education. More than a third of the patients had a disease duration of more than 10 years, and about two-thirds had HbA1c ≥ 6.5 %. Those with desired glycaemic control had poorer QoL than those with less than desired glycaemic control moderated by the use of insulin. Hierarchical multiple linear regression showed that desired glycaemic control (HbA1c), diabetes worry, use of insulin, more than 10 years’ duration of diabetes, neuropathy and retinopathy were associated with poor QoL, whereas being satisfied with waiting time for consultation was associated with better QoL.
Conclusions
The results of this study show that diabetes was associated with negative impact on quality of life. The use of insulin to achieve desired glycaemic control was particularly associated with negative impact on QoL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pandey, A., Tripathi, P., Pandey, R., Srivatava, R., & Goswami, S. (2011). Alternative therapies useful in the management of diabetes: A systematic review. Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences, 3(4), 504.
Population Distribution and Basic Demographic Characteristics 2010 (2011). Putra Jaya: Department of Statistics Malaysia.
Letchuman, G., Wan Nazaimoon, W., Wan Mohamad, W., Chandran, L., Tee, G., Jamaiyah, H., et al. (2010). Prevalence of diabetes in the Malaysian national health morbidity survey III 2006. Medical Journal of Malaysia, 65(3), 173–179.
Rampal, S., Rampal, L., Rahmat, R., Zain, A. M., Yap, Y. G., Mohamed, M., et al. (2010). Variation in the prevalence, awareness, and control of diabetes in a multiethnic population: A nationwide population study in Malaysia. Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health, 22(2), 194–202.
Causes of death in Malaysia 2008. Department of Statistics Malaysia. http://www.statistics.gov.my. Accessed 20 October 2011.
Faudzi, A. Y., Nasir, A., Gurpreet, K., Vos, T., Chalapati, V. P., & Stephen, B. (2004). Malaysia burden of disease and injury study. Kuala Lumpur: Institute for Public Health, Ministry of Health.
Abougalambou, S. S. I., & Abougalambou, A. S. (2013). A study evaluating prevalence of hypertension and risk factors affecting on blood pressure control among type 2 diabetes patients attending teaching hospital in Malaysia. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 7(2), 83–86.
Institute for Public Health. (2011). National Health and Morbidity Survey 2011 (NHMS 2011). Vol. 1: Methodology and general findings.
Lau, C., Qureshi, A., & Scott, S. (2004). Association between glycaemic control and quality of life in diabetes mellitus. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine, 50(3), 189–194.
Weinberger, M., Kirkman, M. S., Samsa, G. P., Cowper, P. A., Shortliffe, E. A., Simel, D. L., et al. (1994). The relationship between glycemic control and health-related quality of life in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Medical Care, 32(12), 1173–1181.
Shiu, A. T. Y., Thompson, D. R., & Wong, R. Y. M. (2008). Quality of life and its predictors among Hong Kong Chinese patients with diabetes. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 17(5a), 125–132.
Brown, G. C., Brown, M. M., Sharma, S., Brown, H., Gozum, M., & Denton, P. (2000). Quality of life associated with diabetes mellitus in an adult population. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications, 14(1), 18–24. doi:10.1016/S1056-8727(00)00061-1.
Bradley, C., Todd, C., Gorton, T., Symonds, E., Martin, A., & Plowright, R. (1999). The development of an individualized questionnaire measure of perceived impact of diabetes on quality of life: The ADDQoL. Quality of Life Research, 8(1), 79–91.
Costa, F. A., Guerreiro, J. P., & Duggan, C. (2006). An audit of diabetes dependent quality of life (ADDQoL) for Portugal: Exploring validity and reliability. Pharmacy Practice, 4(3), 123–128.
Soon, S. S., Goh, S. Y., Bee, Y. M., Poon, J. L., Li, S. C., Thumboo, J., et al. (2010). Audit of diabetes-dependent quality of life (ADDQoL) [Chinese version for Singapore] questionnaire. Applied Health Economics and Health Policy, 8(4), 239–249.
Klein, R., & Klein, B. E. (1998). Relation of glycemic control to diabetic complications and health outcomes. Diabetes Care, 21(Supplement 3), C39–C43.
Huang, E. S., Brown, S. E. S., Ewigman, B. G., Foley, E. C., & Meltzer, D. O. (2007). Patient perceptions of quality of life with diabetes-related complications and treatments. Diabetes Care, 30(10), 2478–2483.
Kamarul, Imran, M., Ismail, A., Naing, L., & Wan Mohamad, W. (2010). Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with poor glycaemic control have lower quality of life scores as measured by the Short Form-36. Singapore Medical Journal, 51(2), 157–162.
Akinci, F., Yildirim, A., Gözü, H., Sargın, H., Orbay, E., & Sargın, M. (2008). Assessment of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of patients with type 2 diabetes in Turkey. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 79(1), 117–123.
Fischer, J. S., McLaughlin, T., Loza, L., Beauchamp, R., Schwartz, S., & Kipnes, M. (2004). The impact of insulin glargine on clinical and humanistic outcomes in patients uncontrolled on other insulin and oral agents: An office-based naturalistic study. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 20(11), 1703–1710.
Houlden, R., Ross, S., Harris, S., Yale, J.-F., Sauriol, L., & Gerstein, H. C. (2007). Treatment satisfaction and quality of life using an early insulinization strategy with insulin glargine compared to an adjusted oral therapy in the management of Type 2 diabetes: The Canadian INSIGHT Study. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 78(2), 254–258.
Elbagir, M. N., Etayeb, N. O., Eltom, M. A., Mahadi, E. O., Wikblad, K., & Berne, C. (1999). Health-related quality of life in insulin-treated diabetic patients in the Sudan. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 46(1), 65–73.
Pibernik-Okanovic, M., Szabo, S., & Melko, Z. (1998). Quality of life following a change in therapy for diabetes mellitus. Pharmacoeconomics, 14(2), 201–207.
Menard, J., Payette, H., Dubuc, N., Baillargeon, J., Maheux, P., & Ardilouze, J. (2007). Quality of life in type 2 diabetes patients under intensive multitherapy. Diabetes and Metabolism, 33(1), 54–60.
DCCTR Group. (1996). Influence of intensive diabetes treatment on quality-of-life outcomes in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes Care, 19(3), 195–203.
De Grauw, W., Van de Lisdonk, E., Van Gerwen, W., Van den Hoogen, H., & Van Weel, C. (2001). Insulin therapy in poorly controlled type 2 diabetic patients: Does it affect quality of life? The British Journal of General Practice, 51(468), 527–532.
Pitale, S., Kernan-Schroeder, D., Emanuele, N., Sawin, C., Sacks, J., & Abraira, C. (2005). Health-related quality of life in the VA Feasibility Study on glycemic control and complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications, 19(4), 207–211.
Mafauzy, M., Hussein, Z., & Chan, S. (2011). The status of diabetes control in Malaysia: Results of DiabCare 2008. Medical Journal of Malaysia, 66(3), 175–181.
Cheah, W. L., Lee, P. Y., Lim, P. Y., AA, F. N., Luk, K. J., & Nur Irwana, A. T. (2012). Perception of quality of life among people with diabetes. Malaysian Family Physician, 7(2 & 3), 21–30.
Mazlina, M., Shamsul, A., & Jeffery, F. (2011). Health-related quality of life in patients with diabetic foot problems in Malaysia. Medical Journal of Malaysia, 66(3), 234–238.
Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. (2009). http://www.moh.gov.my. Accessed February 2010.
Sokal, R. R., & Rohlf, F. J. (1995). Biometry: The principals and practice of statistics in biological research. New York: WH Freeman.
Ashwell, S. G., Bradley, C., Stephens, J. W., Witthaus, E., & Home, P. D. (2008). Treatment satisfaction and quality of life with insulin glargine plus insulin lispro compared with NPH insulin plus unmodified human insulin in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 31(6), 1112–1117.
Holmanová, E., & Žiaková, K. (2009). Audit diabetes-dependent quality of life questionnaire: Usefulness in diabetes self-management education in the Slovak population. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 18(9), 1276–1286.
Wee, H.-L., Tan, C.-E., Goh, S.-Y., & Li, S.-C. (2006). Usefulness of the Audit of Diabetes-Dependent Quality-of-Life (ADDQoL) questionnaire in patients with diabetes in a multi-ethnic Asian country. Pharmacoeconomics, 24(7), 673–682.
Kamarul Imran, M., Ismail, A., Naing, L., & Wan Mohamad, W. (2004). Sf-36 and the Malay translated audit of dependent diabetes quality of life (ADDQOL) performances among type 2 diabetes patients. Community Health, 10(S), 55–58.
Wallace, T. M., & Matthews, D. R. (2000). Poor glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: A conspiracy of disease, suboptimal therapy and attitude. QJM, 93(6), 369–374. doi:10.1093/qjmed/93.6.369.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. (1999). Quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients is affected by complications but not by intensive policies to improve blood glucose or blood pressure control (UKPDS 37). Diabetes Care, 22(7), 1125–1136.
Goddijn, P., Bilo, H., Feskens, E., Groenier, K., Van der Zee, K., & De Jong, B. M. (1999). Longitudinal study on glycaemic control and quality of life in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus referred for intensified control. Diabetic Medicine, 16(1), 23–30.
Rubin, R. R., & Peyrot, M. (1999). Quality of life and diabetes. Diabetes/Metabolism Reviews, 15, 205–218.
Redekop, W. K., Koopmanschap, M. A., Stolk, R. P., Rutten, G. E. H. M., Wolffenbuttel, B. H. R., & Niessen, L. W. (2002). Health-related quality of life and treatment satisfaction in dutch patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 25(3), 458–463. doi:10.2337/diacare.25.3.458.
Wexler, D., Grant, R., Wittenberg, E., Bosch, J., Cagliero, E., Delahanty, L., et al. (2006). Correlates of health-related quality of life in type 2 diabetes. Diabtologia, 49(7), 1489–1497.
Rhee, M. K., Slocum, W., Ziemer, D. C., Culler, S. D., Cook, C. B., El-Kebbi, I. M., et al. (2005). Patient adherence improves glycemic control. The Diabetes Educator, 31(2), 240–250.
Gazmararian, J. A., Ziemer, D. C., & Barnes, C. (2009). Perception of barriers to self-care management among diabetic patients. The Diabetes Educator, 35(5), 778–788.
Lane, J. D., McCaskill, C. C., Williams, P. G., Parekh, P. I., Feinglos, M. N., & Surwit, R. S. (2000). Personality correlates of glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 23(9), 1321–1325.
Braun, A., Sämann, A., Kubiak, T., Zieschang, T., Kloos, C., Müller, U. A., et al. (2008). Effects of metabolic control, patient education and initiation of insulin therapy on the quality of life of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Patient Education and Counseling, 73(1), 50–59.
Undén, A. L., Elofsson, S., Andréasson, A., Hillered, E., Eriksson, I., & Brismar, K. (2008). Gender differences in self-rated health, quality of life, quality of care, and metabolic control in patients with diabetes. Gender Medicine, 5(2), 162–180.
Varghese, R. T., Salini, R., Abraham, P., Reeshma, K., & Vijayakumar, K. (2007). Determinants of the quality of life among diabetic subjects in Kerala, India. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews, 1(3), 173–179.
Adriaanse, M. C., Dekker, J. M., Spijkerman, A. M., Twisk, J. W., Nijpels, G., van der Ploeg, H. M., et al. (2005). Diabetes-related symptoms and negative mood in participants of a targeted population-screening program for type 2 diabetes: The hoorn screening study. Quality of Life Research, 14(6), 1501–1509.
Cryer, P. E. (2008). The barrier of hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes, 57(12), 3169–3176.
Lundkvist, J., Berne, C., Bolinder, B., & Jönsson, L. (2005). The economic and quality of life impact of hypoglycemia. The European Journal of Health Economics, 6(3), 197–202.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2013). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. London: Routledge.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to extend their thanks to Professor Dr. Clare Bradley from Royal Holloway, University of London for granting us permission to use the ADDQoL-18 via her spin-out company, Health Psychology Research Ltd www.healthpsychologyresearch.com. The authors wish to thank all participants who responded to the questionnaire. The authors wish to express gratitude to the Research Management Institute of the Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM) for providing a research Grants (600-RMI/ST/DANA 5/3/Dst (82/2011) that enables researcher to accomplish this humble work as a part of PhD project at UiTM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daher, A.M., AlMashoor, S.A.H. & Winn, T. Glycaemic control and quality of life among ethnically diverse Malaysian diabetic patients. Qual Life Res 24, 951–958 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-014-0830-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-014-0830-5