Abstract
Background
The aim of the study was to describe the surgical outcomes of a retrospective series of consecutive patients treated with laparoscopic and robotic approach for adrenal masses in two tertiary referral centers.
Methods
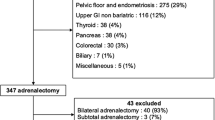
We retrospectively gathered data of 477 patients submitted to adrenalectomy performed at two Institutions from March 2008 to February 2018 by six highly experienced surgeons. We excluded from the analysis 43 patients that had an open approach for tumors or for anesthetic contraindications to minimally invasive surgery (MIS). Patients were selected for surgery after a radiologic and an endocrinology work up. Preoperative, perioperative and postoperative data were recorded.
Results
Overall, 477 patients were included in the study. The robotic and the laparoscopic group included 110 and 367 patients, respectively. The preoperative characteristics were similar in both groups except for ASA score with a median (IQR) of 3 and 2 in the robotic and in the laparoscopic group, respectively (p = 0.03). Tumor size of adrenal tumors treated robotically (4, IQR 2.6–6 cm) was significantly larger than those treated laparoscopically (3, IQR 2.3–4.1 cm) (p = 0.01). The intraoperative complication rates were similar between robotic and laparoscopic groups (6.3% and 6%, respectively). The postoperative complication rate was 5.4% for robotic group and similarly 3.5% for laparoscopic adrenalectomy strategy. We analyzed the tumor ≥ 6 cm, with 29 patients in the robotic group and 43 in the laparoscopic one, with an overall complication rate of 19.5%. At multivariable analyses tumor size (OR 1.287; CI 1.128–1.468; p < 0.001) was the only independent predictor of overall complication.
Conclusion
Adrenal tumors can be safely treated either by robotic or laparoscopic strategy. MIS seems to be feasible also in larger adrenal masses (≥ 6 cm). Tumor size represents the only predictive factors for overall complication.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Lairmore TC, Folek J, Govednik CM, Snyder SK (2016) Improving minimally invasive adrenalectomy: selection of optimal approach and comparison of outcomes. World J Surg 40(7):1625–1631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-016-3471-8
Alemanno G, Bergamini C, Prosperi P, Valeri A (2017) Adrenalectomy: indications and options for treatment. Updates Surg 69:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-017-0441-0
Samreen S, Fluck M, Hunsinger M, Wild J, Shabahang M, Blansfield JA (2019) Laparoscopic versus robotic adrenalectomy: a review of the national inpatient sample. J Robot Surg 13:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-018-0808-3
Gagner M, Lacroix A, Bolte E (1992) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy in Cushing’s syndrome and pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med 327:1033
Smith CD, Weber CJ, Amerson JR (1999) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy: new gold standard. World J Surg 23:389–396
Ball MW, Hemal AK, Allaf ME (2017) International Consultation on Urological Diseases and European Association of Urology International Consultation on Minimally Invasive Surgery in Urology: laparoscopic and robotic adrenalectomy. BJU Int 119:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13592
Piazza L, Caragliano P, Scardilli M, Sgroi AV, Marino G, Giannone G (1999) Laparoscopic robot-assisted right adrenalectomy and left ovariectomy (case reports). Chir Ital 51:465–466
Pineda-Solis K, Medina-Franco H, Heslin MJ (2013) Robotic versus laparoscopic adrenalectomy: a comparative study in a high-volume center. Surg Endosc 27:599–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2496-9
Mishra K, Maurice MJ, Bukavina L, Abouassaly R (2019) Comparative efficacy of laparoscopic versus robotic adrenalectomy for adrenal malignancy. Urology 123:146–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2018.08.037
Stefanidis D, Goldfarb M, Kercher KW, Hope WW, Richardson W, Fanelli RD (2013) SAGES guidelines for minimally invasive treatment of adrenal pathology. Surg Endosc 27:3960–3980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3169-z
Schwaibold H, Wiesend F, Bach C (2018) The age of robotic surgery—is laparoscopy dead? Arab J Urol 16:262–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aju.2018.07.003
Agcaoglu O, Aliyev S, Karabulut K, Mitchell J, Siperstein A, Berber E (2012) Robotic versus laparoscopic resection of large adrenal tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 19:2288–2294. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2296-4
de Groot V, Beckerman H, Lankhorst GJ, Bouter LM (2003) How to measure comorbidity. A critical review of available methods. J Clin Epidemiol 56:221–229
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P-A (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240:205–213
Gagner M, Lacroix A, Bolte E, Pomp A (1994) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy. The importance of a flank approach in the lateral decubitus position. Surg Endosc 8:135–138
Brandao LF, Autorino R, Zargar H, Krishnan J, Laydner H, Akca O, Mir MC, Samarasekera D, Stein R, Kaouk J (2014) Surgery in motion robot-assisted laparoscopic adrenalectomy: step-by-step technique and comparative outcomes. Eur Urol 66:898–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.04.003
Greilsamer T, Nomine-Criqui C, Thy M, Ullmann T, Zarnegar R, Bresler L, Brunaud L (2019) Robotic-assisted unilateral adrenalectomy: risk factors for perioperative complications in 303 consecutive patients. Surg Endosc 33:802–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6346-2
Pavan N, Autorino R, Lee H, Porpiglia F, Sun Y, Greco F, Chueh SJ, Hyun D (2016) Impact of novel techniques on minimally invasive adrenal surgery: trends and outcomes from a contemporary international large series in urology. World J Urol 34(10):1473–1479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-016-1791-9
Wu JC-H, Wu H-S, Lin M-S, Chou D-A, Huang M-H (2008) Comparison of robot-assisted laparoscopic adrenalectomy with traditional laparoscopic adrenalectomy—1 year follow-up. Surg Endosc 22:463–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9488-1
Economopoulos KP, Mylonas KS, Stamou AA, Theocharidis V, Sergentanis TN, Psaltopoulou T, Richards ML (2017) Laparoscopic versus robotic adrenalectomy: a comprehensive meta- analysis. Int J Surg 38:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.12.118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Simone Sforza, Andrea Minervini, Riccardo Tellini, Changwei Ji, Carlo Bergamini, Alessio Giordano, Qun Lu, Wei Chen, Feifei Zhang, Hao Ji, Fabrizio Di Maida, Paolo Prosperi, Lorenzo Masieri, Marco Carini, Andrea Valeri and Hongqian Guo have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sforza, S., Minervini, A., Tellini, R. et al. Perioperative outcomes of robotic and laparoscopic adrenalectomy: a large international multicenter experience. Surg Endosc 35, 1801–1807 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07578-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07578-5