Abstract
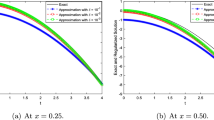
The method of solving the two-dimensional nonlinear inverse heat conduction problems is presented. The time- and space temperature distribution inside a solid and heat transfer coefficient distribution on the boundary of the solid is determined based on the temperature histories measured in several selected inside locations. The problem is overdetermined because the number of measuring points is higher than the number of calculated parameters (components of heat transfer coefficient).
Zusammenfassung
In der Arbeit wird eine Methode zur Lösung des nichtlinearen inversen Wärmeleitungsproblems dargestellt. Instationäre Temperaturverteilung und örtliche Änderungen des Wärmeübergangskoeffizienten an der Außenoberfläche des Körpers werden auf der Basis der in inneren Punkten gemessenen Temperaturen berechnet. Das Problem ist überbestimmt, weil die Anzahl der Meßstellen größer als die Anzahl der gesuchten Parameter ist. Thermophysikalische Stoffgrößen sind temperaturabhängig. Nach einer Diskretisierung der Verteilung des Wärmeübergangskoeffizienten wird zur Lösung des direkten Wärmeleitungsproblem das Finite Volumen Runge - Kutta Verfahren verwendet. Die Komponenten des Wärmeübergangskoeffizienten werden mit dem SOR -Verfahren bestimmt. Die Anwendung des entwickelten Verfahrens wird anhand von drei Beispielen illustriert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck JV, Blackwell B, Clair Ch R St (1985) Inverse heat conduction, Ill-posed Problems. Wiley-Interscience Publication, New York
Alifanov OM (1994) Inverse Heat Transfer Problems. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, New York
Osman AM, Beck JV (1990) Investigation of transient heat transfer coefficients in quenching experiments. Transactions of the ASME, Journal Heat Transfer, Vol.112, 843–848
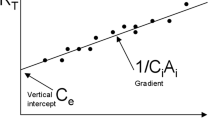
Taler J, Zima W (1999) Solution of inverse heat conduction problems using control volume approach. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 42, 1123–1140
Grądziel S (1997) Identification of the transient thermal state of thick-walled boiler components. Cracow University of Technology, Mechanics z.79, Kraków (in Polish)
Taler J, Węglowski B, Zima W, Grądziel S, Zborowski M (1999) Analysis of thermal stresses in a boiler drum during start-up, Transactions of the ASME, Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, Vol. 121, 84–93
Taler J (1992) Numerical solutions for general inverse heat conduction problem. Wärme — und Stoffübertragung 27 505–513
Richter F (1983) Physikalische Eigenschaften von Stählen und ihre Temperaturabhängingkeit. Polynome und graphische Darstellungen. Mitteilung aus dem Forschungsinstytut der Mannesmann AG. Stahleisen -Sonderberichte, H. 10, Verlag Stahleisen, Düsseldorf
Subroutine NORNG -Normal Random Number Generator. (1984) FORTRAN: Scientific Subroutine Library, IBM
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taler, J., Grądziel, S. An overdeterrnined two-dimensional transient inverse heat conduction problem. Forsch Ing-Wes 65, 98–106 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00010870
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00010870