Abstract
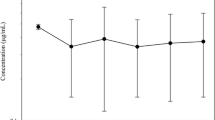
The plasma levels and milk excretion of eprinomectin were determined in goats following topical application at doses of 0.5 mg kg−1 and 1.0 mg kg−1. The area under the concentration–time curve (AUC) was 2 times lower for 0.5 mg kg−1 (8.24 ± 3.50 ng day−1 ml−1) than for 1.0 mg kg−1 (15.68 ± 8.84 ng day−1 ml−1), suggesting that the pharmacokinetics of eprinomectin in goats is dose independent. The bioavailability of eprinomectin in lactating compared with non-lactating goats is low. This is probably due to the physiological status of dairy animals, which present a marked decrease in body fat. Comparison of the eprinomectin concentrations in the milk and plasma demonstrated a parallel disposition of the drug with a milk-to-plasma ratio of 0.10–0.25. The amount of drug recovered in the milk was 0.3–0.5% of the total administered dose. In all cases, the maximum level of residue in milk remained below the maximum acceptable level of 30 ng ml−1 permitted in lactating cattle.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 April 2000 / Accepted: 6 September 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dupuy, J., Chartier, C., Sutra, J. et al. Eprinomectin in dairy goats: dose influence on plasma levels and excretion in milk. Parasitol Res 87, 294–298 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008581
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008581