Abstract.
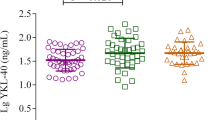
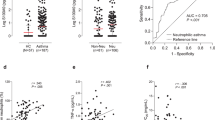
Clara cell 10-kDa protein (CC10), the predominant product from nonciliated cells in the epithelial lining of bronchioles (Clara cells), has been shown to have immunomodulatory and antiinflammatory activity and may play a role in controlling airway inflammation. This study was designed to measure serum CC10 concentrations in healthy and asthmatic nonsmokers. Serum CC10 concentrations in asthmatic nonsmokers were significantly lower than in healthy nonsmokers. Asthmatic patients with a long duration of the disease (≥10 years) had significantly lower serum CC10 levels than those with a short duration of the disease (<10 years). There was no significant difference in serum CC10 levels in asthmatic patients between the time of the asthmatic attack and the stable condition. Serum CC10 levels may reflect decreased production of CC10 caused by remodeling of the small airways in asthma.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted for publication: 30 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shijubo, N., Itoh, Y., Yamaguchi, T. et al. Serum Levels of Clara Cell 10-kDa Protein Are Decreased in Patients with Asthma. Lung 177, 45–52 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00007626
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00007626