Abstract.
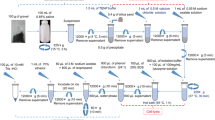
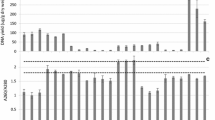
To optimize the cell lysis step for DNA extraction from activated sludge samples, two floc dispersion methods (sonication versus stirring with a cation exchange resin), and three cell lysis treatments (lysozyme + SDS, sonication in a water bath, and thermal shock) were tested. For dispersion, stirring with cation exchange resin was more efficient than sonication. The cell lysis procedures were applied in two sequences, and DNA was quantified after each cell lysis treatment. Lysozyme + SDS was the most effective step in the cell lysis procedures. The cell lysis treatment sequences giving the highest DNA yields were not the same for all the sludges. The differences in sludge microbial compositions and floc structures required specifically adapted cell lysis protocols. The proposed protocols were highly efficient for DNA extraction, yielding about 50 mg DNA g−1 volatile suspended solids, and allowed PCR amplification of 16S rDNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 September 1998 / Accepted: 13 February 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bourrain, M., Achouak, W., Urbain, V. et al. DNA Extraction from Activated Sludges. Curr Microbiol 38, 315–319 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006809
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006809