Abstract.
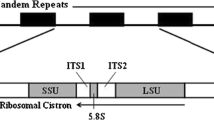
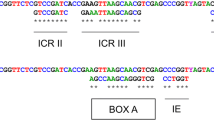
We have determined the full sequence of the ribosomal DNA intergenic spacer (IGS) of the swimming crab, Charybdis japonica, by long PCR for the first time in crustacean decapods. The IGS is 5376 bp long and contains two nonrepetitive regions separated by one long repetitive region, which is composed mainly of four subrepeats (subrepeats I, II, III, and IV). Subrepeat I contains nine copies of a 60-bp repeat unit, in which two similar repeat types (60 bp-a and 60 bp-b) occur alternatively. Subrepeat II consists of nine successive repeat units with a consensus sequence length of 142 bp. Subrepeat III consists of seven copies of another 60-bp repeat unit (60 bp-c) whose sequence is complementary to that of subrepeat I. Immediately downstream of subrepeat III is subrepeat IV, consisting of three copies of a 391-bp repeat unit. Based on comparative analysis among the subrepeats and repeat units, a possible evolutionary process responsible for the formation of the repetitive region is inferred, which involves the duplication of a 60-bp subrepeat unit (60 bp-c) as a prototype.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 April 1999 / Accepted: 2 August 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho Ryu, S., Kyung Do, Y., Wook Hwang, U. et al. Ribosomal DNA Intergenic Spacer of the Swimming Crab, Charybdis japonica . J Mol Evol 49, 806–809 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006603
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006603