Abstract.
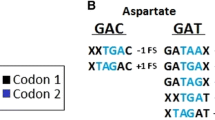
The synonymous divergence between Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium is explained in a model where there is a large variation between mutation rates at different nucleotide sites in the genome. The model is based on the experimental observation that spontaneous mutation rates can vary over several orders of magnitude at different sites in a gene. Such site-specific variation must be taken into account when studying synonymous divergence and will result in an apparent saturation below the level expected from an assumption of uniform rates. Recently, it has been suggested that codon preference in enterobacteria has a very large site-specific variation and that the synonymous divergence between different species, e.g., E. coli and Salmonella, is saturated. In the present communication it is shown that when site-specific variation in mutation rates is introduced, there is no need to invoke assumptions of saturation and a large variability in codon preference. The same rate variation will also bring average mutation rates as estimated from synonymous sequence divergence into numerical agreement with experimental values.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 July 1998 / Accepted: 20 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berg, O. Synonymous Nucleotide Divergence and Saturation: Effects of Site-Specific Variations in Codon Bias and Mutation Rates. J Mol Evol 48, 398–407 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006484
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006484