Abstract.
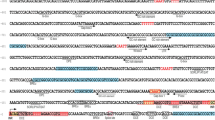
Sponges (Porifera) are the phylogenetically oldest metazoan organisms. From one member of the siliceous sponges, Geodia cydonium, the cDNA encoding a putative SOS protein, the AidB-like protein of the Ada system from bacteria, was isolated and characterized. The cDNA, GCaidB, comprises an open reading frame of 446 amino acid (aa) residues encoding a polypeptide with a calculated M r of 49,335. This molecule shows high similarity to the bacterial AidB proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Escherichia coli and somewhat lower similarities to acyl-CoA dehydrogenases (ADHs) and acyl-CoA oxidases (AOXs). Northern blot analysis confirmed the presence of the complete transcript. The deduced sponge aa sequence, GC_aidB, possesses the two characteristic acyl-CoA dehydrogenase signatures 1 and 2. Incubation of the sponge with N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine causes a strong increase in the 2.1-kb large transcript of GCaidB; maximal expression is seen after 24 h of incubation with this DNA methylating agent. ADHs and AOXs can be grouped, depending on the position of the catalytically important Glu residue, into the Glu–Gly (Glu adjacent to Gly) class and the Glu–Arg (Glu adjacent to Arg) class. The phylogenetically oldest metazoan AidB-like molecule, GC_aidB of G. cydonium, belongs to the Glu–Gly class of ADHs. Phylogenetic analyses of the Glu–Gly class enzymes, with the described AidB-like protein from G. cydonium and the bacterial AidB polypeptides, together with metazoan ADHs and AOXs, revealed that the AidB(-like) proteins diverged first from a common ancestor, while the eukaryotic AOX and ADA polypeptides as well as the GHDs appeared later. According to the analyses, the very long-chain ADHs are older than the medium-chain, short-chain, and branched-chain ADHs. Inclusion of the phylogenetical oldest member of the Glu–Arg class of enzymes, the bacterial ADH–CaiA sequence in these analyses, revealed that this class of enzymes appeared later in evolution and arose from the Glu–Gly class perhaps after gene duplication.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 January 1998 / Accepted: 20 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krasko, A., Schröder, H., Hassanein, H. et al. Identification and Expression of the SOS Response, aidB-Like, Gene in the Marine Sponge Geodia cydonium: Implication for the Phylogenetic Relationships of Metazoan Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenases and Acyl-CoA Oxidases. J Mol Evol 47, 343–352 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006392
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006392