Abstract
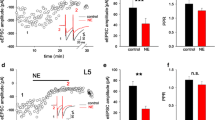
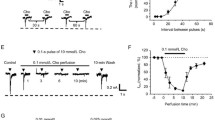
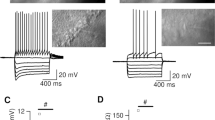
The present study examines the ability of muscarinic receptor activation to modulate glutamatergic responses in the in vitro rat auditory cortex. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were obtained from layer II-III pyramidal neurons and responses elicited by either stimulation of deep gray matter or iontophoretic application of glutamate receptor agonists. Iontophoresis of the muscarinic agonist acetyl-β-methylcholine (MCh) produced an atropine-sensitive reduction in the amplitude of glutamate-induced membrane depolarizations that was followed by a long-lasting (at least 20 min) response enhancement. Glutamate depolarizations were enhanced by MCh when elicited in the presence of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA)/ kainate receptor antagonists 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) or 2,3-diyhdroxy-6-nitro-7-sulfamoyl, benzo(F)quinoxaline (NBQX) but not the NMDA antagonists d-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (APV) or MK-801 hydrogen maleate. The magnitude of enhancement was voltage-dependent with the percentage increase greater at more depolarized membrane potentials. An involvement of NMDA receptors in these MCh-mediated effects was tested by using AMPA/kainate receptor antagonists to isolate the NMDA-mediated slow excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) from other synaptic potentials. The slow EPSP and iontophoretic responses to NMDA were similarly modified by MCh, i.e., both being reduced during and enhanced (15–55 min) following MCh application. Cholinergic modulation of NMDA responses involves the engagement of G proteins, as enhancement was prevented by intracellular infusion with the nonhydrolyzable GDP analog guanosine-5′-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) trilithium salt (GDPβS). GDPβS was without effect on the early MCh-induced response suppression. Our results suggest that acetylcholine, acting at muscarinic receptors, produces a long-lasting enhancement of NMDA-mediated neurotansmisson in auditory cortex, and that this modulatory effect is dependent upon a G protein-mediated event.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 March 1996 / Accepted: 14 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aramakis, V., Bandrowski, A. & Ashe, J. Activation of muscarinic receptors modulates NMDA receptor-mediated responses in auditory cortex. Exp Brain Res 113, 484–496 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005601
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005601