Abstract
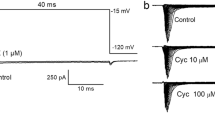
Using the whole-cell configuration of the patch clamp technique, calcium-activated potassium currents (IK,Ca) were investigated in ramified murine brain macrophages. In order to induce IK,Ca the intracellular concentration of nominal free Ca2+ was adjusted to 1μM. The Ca2+-activated K+ current of brain macrophages did not show any voltage dependence at test potentials between –120 and +30mV. A tenfold change in extracellular K+ concentration shifted the reversal potential of IK,Ca by 51mV. The bee venom toxin apamin applied at concentrations of up to 1μM did not affect IK,Ca. Ca2+-activated K+ currents of ramified brain macrophages were highly sensitive to extracellularly applied charybdotoxin (CTX). The half-maximal effective concentration of CTX was calculated to be 4.3nM. In contrast to CTX, the scorpion toxin kaliotoxin did not inhibit IK,Ca at concentrations between 1 and 50nM. Tetraethylammonium (TEA) blocked 8.0% of IK,Ca at a concentration of 1mM, whereas 31.4% of current was blocked by 10mM TEA. Several inorganic polyvalent cations were tested at a concentration of 2mM for their ability to block IK,Ca. La3+ reduced IK,Ca by 72.8%, whereas Cd2+ decreased IK,Ca by 17.4%; in contrast, Ni2+ did not have any effect on IK,Ca. Ba2+ applied at a concentration of 1mM reduced IK,Ca voltage-dependently at hyperpolarizing potentials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 January / Accepted: 5 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eder, C., Klee, R. & Heinemann, U. Pharmacological properties of Ca2+-activated K+ currents of ramified murine brain macrophages. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 356, 233–239 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005046
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005046