Abstract
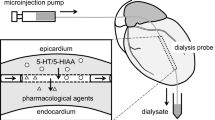
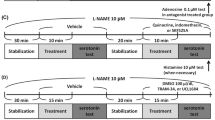
The aim of the present study was to further characterise the noradrenaline and 5hydroxytryptamine [5HT] transporters in rat lungs by examining the efflux of noradrenaline and 5HT, respectively. Lungs from rats were isolated and perfused via the pulmonary artery. After loading the tissue with 3H5HT or 3Hnoradrenaline the efflux of the relevant amine from the lungs was examined for 1525min. The rate constant for efflux of 3H5HT increased by 81% when Na+ ions were removed from the perfusion solution; increased gradually when a selective 5HT transporter inhibitor, 200nM citalopram, was added to the perfusion solution for the final 6min of efflux; and increased markedly and rapidly when substrates of the 5HT transporter, tryptamine (18μM) and 7methyltryptamine (12μM), were added for the final 6min of efflux. These effects of the substrates were abolished by 1μM citalopram, but were not significantly affected by 1μM desipramine, a selective uptake1 inhibitor. On the other hand, the previously described substrateinduced increase in the rate of efflux of noradrenaline was significantly reduced by desipramine but was unaffected by citalopram. The results show that efflux of 5HT is mediated only by the 5HT transporter, with no significant contribution of uptake1, and efflux of noradrenaline from rat lungs is mediated only by uptake1 and not by the 5HT transporter. The effects of dopamine on the efflux of noradrenaline over a concentration range of 100-600nM were investigated and the results showed that 50% of the maximal increase in the rate of efflux occurred at a concentration of 275nM. This value did not differ from the Km for uptake of dopamine. This result implies that the only factor affecting the substrate-induced increase in noradrenaline efflux is the affinity of the substrate for uptake1. The efflux of noradrenaline was also examined in the absence and presence of two concentrations of desipramine (0.35and 1.5μM). Analysis of these results showed that uptake1 contributed approximately 81% and diffusion 19% to the total efflux of noradrenaline and that 90% of the total noradrenaline efflux was subject to reuptake by uptake1 into the pulmonary endothelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 January 1997 / Accepted: 26 March 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
James, K., Bryan-Lluka, L. Efflux studies allow further characterisation of the noradrenaline and 5hydroxytryptamine transporters in rat lungs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 356, 126–133 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005019
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005019
- Key words Noradrenaline
- 5Hydroxytryptamine
- Efflux
- Uptake1
- 5Hydroxytryptamine transporter
- Pulmonary endothelial cells
- Abbreviations BSA bovine serum albumin
- COMT catechol-O-methyltransferase
- DOPEG 3’
- 4’dihydroxyphenylglycol
- EC50concentration of substrate required to induce a half maximal increase in efflux of amine
- FRL fractional rate of loss of amine
- 5HT 5hydroxytryptamine
- Km Michaelis or half-saturation constant for uptake
- kout rate constant for efflux of amine
- kuptake rate constant for uptake of amine
- MAO monoamine oxidase
- U0521 3’
- 4’dihydroxy2methylpropiophenone
- Vmaxmaximal initial rate of uptake