Abstract.
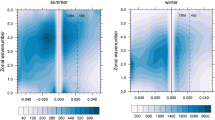
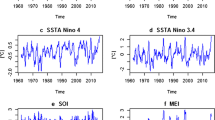
Using the ΔT (integrated variation of the Earth's rotation measured in terestrial time) series (1891.5–1955.5) derived from lunar occultation observations and the UT1–UTC (universal time–coordinated universal time) series (1955.5–1997.5) of the Bureau International de L'Heure/International Earth Rotation Service, a new ΔLOD (variation of the length of day) series in monthly intervals from 1892.0 to 1997.0 is calculated. Using digital filtering, the interannual and decadal components of the ΔLOD series are separated and then compared with those inferred from other geophysical quantities. It is shown that, on the interannual time scale, atmospheric processes can play an important role in exciting astronomical ΔLOD. However, the main oscillation with a mean period of about 5.8 years and peak-to-peak amplitude of about 0.3 ms in the residuals of ΔLOD(Astr) −ΔLOD(Wind) for 1968.0–1997.0 suggests that about half of the amplitude in astronomical ΔLOD must be excited by other geophysical processes, while on the decadal time scale the atmospheric excitation is too small. Geomagnetic core–mantle coupling may be a plausible source of the excitation of ΔLOD on the decadal time scale, but the geomagnetic data are still insufficient and an improved model of core–mantle coupling is required.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 April 1998 / Accepted: 31 May 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, D., Greiner-Mai, H. A new ΔLOD series in monthly intervals (1892.0–1997.0) and its comparison with other geophysical results. Journal of Geodesy 73, 466–477 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00004002
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00004002