Background
Hypoxia is the most important stimulus for the up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), one of the key cytokines for angiogenesis. We have investigated the possible relationship between tumor hypoxia and systemic levels of VEGF.
Patients and Methods: 56 patients with head and neck cancers underwent measurement of tumor volume (pretreatment CT scans), tumor oxygenation (pO2 histography) and serum levels of VEGF. The hemoglobin level ranged from 9.1 to 16 g/dl. The absolute amount of hypoxic tumor (hypoxic tumor volume) was determined as the product of the absolute tumor volume and the relative frequency of hypoxic (< 5 mm Hg) measurements in the pO2 histography.
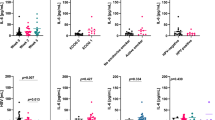
Results: The serum VEGF levels in the 56 head and neck cancer patietns ranged from 102 to 1699 pg/ml (median 405 pg/ml, mean 527 ± 396 pg/ml). Elevated serum-VEGF levels (> 700 pg/ml) were found in 14/56 patients (25%). Serum-levels of VEGF were significantly and independently correlated with hypoxic tumor volume (R2 = 0,63, p < 0.001), but also with total tumor volume, hemoglobin levels, platelet counts and tumor hypoxia. There was no correlation with T and N category, histological grading, and age.
Conclusions: The strong and independent impact of the hypoxic tumor volume on systemic VEGF levels suggests that the absolute amount of hypoxia within a tumor represents the most important stimulus for up-regulation of angiogenesis. Anemia acts as a co-factor via worsening of tumor tissue oxygenation.
Hintergrund
Hypoxie ist ein starker Stimulus für die Hochregulierung angiogenetischer Zytokine, vor allem des Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF). Wir haben bei Kopf-Hals-Tumoren einen möglichen Zusammenhang zwischen intratumoraler Hypoxie und systemischen Spiegeln von VEGF untersucht.
Patienten und Methodik: Bei 56 Patienten mit Kopf-Hals-Tumoren erfolgten gleichzeitige Messungen von Tumorvolumen (anhand des prätherapeutischen CT), Tumorhypoxie (mittels pO2-Histographie) und Serumkonzentration von VEGF. Das hypoxische Tumorvolumen wurde aus dem Produkt von Gesamttumorvolumen und relativem Anteil hypoxischer Messwerte (pO2-Werte < 5 mm Hg) berechnet. Die Hämoglobinkonzentration betrug 9,1–16 g/dl.
Ergebnisse: Die Serumkonzentrationen von VEGF lagen im Bereich zwischen 102 und 1699 pg/ml (Median 405 pg/ml, Mittelwert 527 ± 396 pg/ml). Erhöhte Serum-VEGF-Spiegel (> 700 pg/ml) fanden sich bei 14/56 Patienten (25%). Die Serumkonzentrationen von VEGF korrelierten signifikant mit dem hypoxischen Tumorvolumen (R2 = 0,63, p < 0,001), aber auch mit Gesamttumorvolumen, Hämoglobinkonzentration und Thrombozytenwerten. Es bestand kein Zusammenhang mit T- und N-Kategorie, histologischem Grading und Alter.
Schlussfolgerungen: Das absolute Ausmaß von intratumoraler Hypoxie spielt für die Hochregulierung der Angiogenese nach diesen Daten die entscheidende Rolle. Die Befund stützen die Hypothese, dass das Mikromilieu im Tumor einen unabhängigen prognostischen Faktor und damit auch ein mögliches Ziel für therapeutische Interventionen darstellt. Eine Anämie scheint über die Verstärkung der Tumorhypoxie als Kofaktor zu wirken.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: March 3, 2001; accepted: June 13, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunst, J., Stadler, P., Becker, A. et al. Tumor Hypoxia and Systemic Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in Head and Neck Cancers. Strahlenther Onkol 177, 469–473 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00002428
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00002428