Abstract.
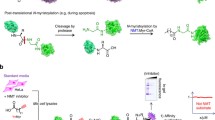
Protein farnesylation, catalyzed by protein farnesyltransferase, plays important roles in the membrane association and protein-protein interaction of a number of eukaryotic proteins. Recent development of farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs) has led to further insight into the biological significance of farnesylation in cancer cells. A number of reports point to the dramatic effects FTIs exert on cancer cells. In addition to inhibiting anchorage-independent growth, FTIs cause changes in the cell cycle either at the G1/S or at the G2/M phase. Furthermore, induction of apoptosis by FTIs has been reported. FTIs also affects the actin cytoskeleton and cell morphology. This review summarizes these reports and discusses implications for farnesylated proteins responsible for these FTI effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 17 April 2001; received after revision 28 May 2001; accepted 28 May 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamanoi, F., Gau, CL., Jiang, C. et al. Protein farnesylation in mammalian cells: effects of farnesyltransferase inhibitors on cancer cells. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58, 1636–1649 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000802
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000802