Abstract.
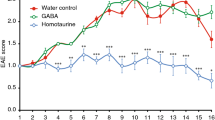
Copolymer 1 (Cop-1) is a synthetic amino acid copolymer effective in suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE). The suppressive effect of Cop-1 in EAE is a general phenomenon and is not restricted to a particular species, disease type or encephalitogen used for EAE induction. In phase III clinical trials Cop-1 was found to slow progression of disability and reduce the relapse rate in exacerbating-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS). In vivo and in vitro studies suggest that the mechanism for Cop-1 activity in EAE and MS involves the binding of Cop-1 to major histocompatibility complex class II molecules as an initial step. This binding results both in competition with myelin antigens for T-cell activation and in induction of specific suppressor cells of the Th2 type. As an antigen-specific intervention, Cop-1 has the advantage of reduced probability of long-term damage to the immune system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 11 October 1996; accepted 20 October 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teitelbaum, D., Arnon, R. & Sela, M. Copolymer 1: from basic research to clinical application. CMLS, Cell. mol. life sci. 53, 24–28 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000576
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000576