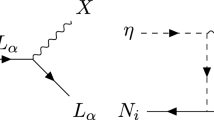Abstract
Within a supersymmetric (SUSY) type-I seesaw framework with SO(10)-inspired mass relations and flavor-blind universal boundary conditions, we study the consequences of requiring that the observed baryon asymmetry of the Universe be explained by either thermal or non-thermal leptogenesis. In the former case, we find that the parameter space is very constrained. In the bulk and stop-coannihilation regions of mSUGRA parameter space (that are consistent with the measured dark matter abundance), lepton flavor-violating (LFV) processes are accessible at MEG and future experiments. However, the very high reheat temperature of the Universe needed after inflation (of about 1012 GeV) leads to a severe gravitino problem, which disfavors either thermal leptogenesis or neutralino dark matter. Non-thermal leptogenesis in the preheating phase from SUSY flat directions relaxes the gravitino problem by lowering the required reheat temperature. The baryon asymmetry can then be explained while preserving neutralino dark matter, and for the bulk or stop-coannihilation regions LFV processes should be observed in current or future experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WMAP collaboration, E. Komatsu et al., Five-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Cosmological interpretation, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 180 (2009) 330 [arXiv:0803.0547] [SPIRES].
V. Barger, D. Marfatia and K. Whisnant, Progress in the physics of massive neutrinos, Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 12 (2003) 569 [hep-ph/0308123] [SPIRES].
H. Fritzsch and P. Minkowski, Vector-like weak currents, massive neutrinos and neutrino beam oscillations, Phys. Lett. B 62 (1976) 72 [SPIRES].
P. Minkowski, μ→eγ at a rate of one out of 1-billion muon decays?, Phys. Lett. B 67 (1977) 421 [SPIRES].
M. Gell-Mann, P. Ramond and R. Slansky, Color embeddings, charge assignments, and proton stability in unified gauge theories, in proceedings of the workshop Supergravity, Stony Brook, NY, U.S.A., North-Holland, Amsterdam (1979).
T. Yanagida, Horizontal gauge symmetry and masses of neutrinos, KEK Report No. 79-18 (1979).
S. Glashow, The future of elementary particle physics, in Quarks and leptons, Cargese, France, Plenum, New York, U.S.A. (1980).
R.N. Mohapatra and G. Senjanović, Neutrino mass and spontaneous parity nonconservation, Phys. Rev. Lett. 44 (1980) 912 [SPIRES].
V. Barger, D. Marfatia and A. Mustafayev, Neutrino sector impacts SUSY dark matter, Phys. Lett. B 665 (2008) 242 [arXiv:0804.3601][SPIRES].
V. Barger, D. Marfatia, A. Mustafayev and A. Soleimani, SUSY dark matter and lepton flavor violation, Phys. Rev. D 80 (2009) 076004 [arXiv:0908.0941] [SPIRES].
M. Fukugita and T. Yanagida, Baryogenesis without grand unification, Phys. Lett. B 174 (1986) 45 [SPIRES].
E.K. Akhmedov, M. Frigerio and A.Y. Smirnov, Probing the seesaw mechanism with neutrino data and leptogenesis, JHEP 09 (2003) 021 [hep-ph/0305322] [SPIRES].
R. Barbieri, P. Creminelli, A. Strumia and N. Tetradis, Baryogenesis through leptogenesis, Nucl. Phys. B 575 (2000) 61 [hep-ph/9911315] [SPIRES].
A. Abada, S. Davidson, F.-X. Josse-Michaux, M. Losada and A. Riotto, Flavour issues in leptogenesis, JCAP 04 (2006) 004 [hep-ph/0601083] [SPIRES].
E. Nardi, Y. Nir, E. Roulet and J. Racker, The importance of flavor in leptogenesis, JHEP 01 (2006) 164 [hep-ph/0601084] [SPIRES].
P. Di Bari, Seesaw geometry and leptogenesis, Nucl. Phys. B 727 (2005) 318 [hep-ph/0502082] [SPIRES].
O. Vives, Flavor dependence of CP asymmetries and thermal leptogenesis with strong right-handed neutrino mass hierarchy, Phys. Rev. D 73 (2006) 073006 [hep-ph/ 0512160] [SPIRES].
A. Abada, P. Hosteins, F.-X. Josse-Michaux and S. Lavignac, Successful leptogenesis in SO(10) unification with a left-right symmetric seesaw mechanism, Nucl. Phys. B 809 (2009) 183 [arXiv:0808.2058] [SPIRES].
P. Di Bari and A. Riotto, Successful type-I leptogenesis with SO(10)-inspired mass relations, Phys. Lett. B 671 (2009) 462 [arXiv:0809.2285] [SPIRES].
S. Davidson and A. Ibarra, A lower bound on the right-handed neutrino mass from leptogenesis, Phys. Lett. B 535 (2002) 25 [hep-ph/0202239] [SPIRES].
G.F. Giudice, A. Notari, M. Raidal, A. Riotto and A. Strumia, Towards a complete theory of thermal leptogenesis in the SM and MSSM, Nucl. Phys. B 685 (2004) 89 [hep-ph/0310123] [SPIRES].
W. Buchmüller, P. Di Bari and M. Plümacher, Leptogenesis for pedestrians, Ann. Phys. 315 (2005) 305 [hep-ph/0401240] [SPIRES].
S. Blanchet and P. Di Bari, Flavor effects on leptogenesis predictions, JCAP 03 (2007) 018 [hep-ph/0607330] [SPIRES].
M.Y. Khlopov and A.D. Linde, Is it easy to save the gravitino?, Phys. Lett. B 138 (1984) 265 [SPIRES].
J.R. Ellis, D.V. Nanopoulos, K.A. Olive and S.-J. Rey, On the thermal regeneration rate for light gravitinos in the early universe, A stropart. Phys. 4 (1996) 371 [hep-ph/9505438] [SPIRES].
T. Moroi, H. Murayama and M. Yamaguchi, Cosmological constraints on the light stable gravitino, Phys. Lett. B 303 (1993) 289 [SPIRES].
M. Kawasaki, K. Kohri and T. Moroi, Big-bang nucleosynthesis and hadronic decay of long-lived massive particles, Phys. Rev. D 71 (2005) 083502 [astro-ph/0408426] [SPIRES].
J. Pradler and F.D. Steffen, Constraints on the reheating temperature in gravitino dark matter scenarios, Phys. Lett. B 648 (2007) 224 [hep-ph/0612291] [SPIRES].
M. Kawasaki, K. Kohri, T. Moroi and A. Yotsuyanagi, Big-Bang nucleosynthesis and gravitino, Phys. Rev. D 78 (2008) 065011 [arXiv:0804.3745] [SPIRES].
T. Asaka, K. Hamaguchi, M. Kawasaki and T. Yanagida, Leptogenesis in inflationary universe, Phys. Rev. D 61 (2000) 083512 [hep-ph/9907559] [SPIRES].
T. Asaka, K. Hamaguchi, M. Kawasaki and T. Yanagida, Leptogenesis in inflaton decay, Phys. Lett. B 464 (1999) 12 [hep-ph/9906366] [SPIRES].
F. Hahn-Woernle and M. Plümacher, Effects of reheating on leptogenesis, Nucl. Phys. B 806 (2009) 68 [arXiv:0801.3972] [SPIRES].
G.F. Giudice, M. Peloso, A. Riotto and I. Tkachev, Production of massive fermions at preheating and leptogenesis, JHEP 08 (1999) 014 [hep-ph/9905242] [SPIRES].
G.N. Felder, L. Kofman and A.D. Linde, Instant preheating, Phys. Rev. D 59 (1999) 123523 [hep-ph/9812289] [SPIRES].
G.F. Giudice, L. Mether, A. Riotto and F. Riva, Supersymmetric leptogenesis and the gravitino bound, Phys. Lett. B 664 (2008) 21 [arXiv:0804.0166] [SPIRES].
W. Konetschny and W. Kummer, Nonconservation of total lepton umber with scalar bosons, Phys. Lett. B 70 (1977) 433 [SPIRES].
T.P. Cheng and L.-F. Li, Neutrino masses, mixings and oscillations in SU(2) × Υ(1) models of electroweak interactions, Phys. Rev. D 22 (1980) 2860 [SPIRES].
M. Magg and C. Wetterich, Neutrino mass problem and gauge hierarchy, Phys. Lett. B 94 (1980) 61 [SPIRES].
G. Lazarides, Q. Shafi and C. Wetterich, Proton lifetime and fermion masses in an SO(10) model, Nucl. Phys. B 181 (1981) 287 [SPIRES].
J. Schechter and J.W.F. Valle, Neutrino masses in SU(2) × Υ(1) theories, Phys. Rev. D 22 (1980) 2227 [SPIRES].
R.N. Mohapatra and G. Senjanović, Neutrino masses and mixings in gauge models with spontaneous parity violation, Phys. Rev. D 23 (1981) 165 [SPIRES].
P. Hosteins, S. Lavignac and C.A. Savoy, Quark-lepton unification and eight-fold ambiguity in the left-right symmetric seesaw mechanism, Nucl. Phys. B 755 (2006) 137 [hep-ph/0606078] [SPIRES].
C.H. Albright, Normal vs. inverted hierarchy in type-I seesaw models, Phys. Lett. B 599 (2004) 285 [hep-ph/0407155] [SPIRES].
L. Covi, E. Roulet and F. Vissani, CP violating decays in leptogenesis scenarios, Phys. Lett. B 384 (1996) 169 [hep-ph/9605319] [SPIRES].
A. Abada et al., Flavour matters in leptogenesis, JHEP 09 (2006) 010 [hep-ph/0605281] [SPIRES].
M. Flanz, E.A. Paschos, U. Sarkar and J. Weiss, Baryogenesis through mixing of heavy Majorana neutrinos, Phys. Lett. B 389 (1996) 693 [hep-ph/9607310] [SPIRES].
L. Covi and E. Roulet, Baryogenesis from mixed particle decays, Phys. Lett. B 399 (1997) 113 [hep-ph/9611425] [SPIRES].
A. Pilaftsis, CP violation and baryogenesis due to heavy Majorana neutrinos, Phys. Rev. D 56 (1997) 5431 [hep-ph/9707235] [SPIRES].
S. Blanchet and P. Di Bari, New aspects of leptogenesis bounds, Nucl. Phys. B 807 (2009) 155 [arXiv:0807.0743 ][SPIRES].
J. Racker and E. Roulet, Leptogenesis, Z’ bosons and the reheating temperature of the universe, JHEP 03 (2009) 065 [arXiv:0812.4285] [SPIRES].
H. Baer, C. Balázs, J.K. Mizukoshi and X. Tata, Can precision measurements of slepton masses probe righthanded neutrinos?, Phys. Rev. D 63 (2001) 055011 [hep-ph/0010068] [SPIRES].
K. Kadota and K.A. Olive, Heavy right-handed neutrinos and dark matter in the νCMSSM, Phys. Rev. D 80 (2009) 095015 [arXiv:0909.3075] [SPIRES].
Daya-Bay collaboration, X. Guo et al., A precision measurement of the neutrino mixing angle θ(13) using reactor antineutrinos at Daya Bay, hep-ex/0701029 [SPIRES].
Double CHOOZ collaboration, F. Ardellier et al., Double CHOOZ: A search for the neutrino mixing angle θ(13), hep-ex/0606025 [SPIRES].
W. Buchmüller and M. Plümacher, Spectator processes and baryogenesis, Phys. Lett. B 511 (2001) 74 [hep-ph/0104189] [SPIRES].
E. Nardi, Y. Nir, J. Racker and E. Roulet, On Higgs and sphaleron effects during the leptogenesis era, JHEP 01 (2006) 068 [hep-ph/0512052] [SPIRES].
A. Basboll and S. Hannestad, Decay of heavy Majorana neutrinos using the full Boltzmann equation including its implications for leptogenesis, JCA P 01 (2007) 003 [hep-ph/0609025] [SPIRES].
F. Hahn-Woernle, M. Plümacher and Y.Y.Y. Wong, Full Boltzmann equations for leptogenesis including scattering, JCA P 08 (2009) 028 [arXiv:0907.0205] [SPIRES].
M. Garny, A. Hohenegger, A. Kartavtsev and M. Lindner, Systematic approach to leptogenesis in nonequilibrium QFT: self-energy contribution to the CP-violating parameter, Phys. Rev. D 81 (2010) 085027 [arXiv:0911.4122] [SPIRES].
M. Garny, A. Hohenegger, A. Kartavtsev and M. Lindner, Systematic approach to leptogenesis in nonequilibrium QFT: vertex contribution to the CP-violating parameter, Phys. Rev. D 80 (2009) 125027 [arXiv:0909.1559] [SPIRES].
A. Anisimov, W. Buchmüller, M. Drewes and S. Mendizabal, Leptogenesis from quantum interference in a thermal bath, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 (2010) 121102 [arXiv:1001.3856] [SPIRES].
M. Beneke, B. Garbrecht, M. Herranen and P. Schwaller, Finite number density corrections to leptogenesis, Nucl. Phys. B 838 (2010) 1 [arXiv:1002.1326] [SPIRES].
M. Garny, A. Hohenegger and A. Kartavtsev, Medium corrections to the CP-violating parameter in leptogenesis, Phys. Rev. D 81 (2010) 085028 [arXiv:1002.0331] [SPIRES].
F. Borzumati and A. Masiero, Large muon and electron number violations in supergravity theories, Phys. Rev. Lett. 57 (1986) 961 [SPIRES].
MEGA collaboration, M.L. Brooks et al., New limit for the family-number non-conserving decay μ + → e +γ , Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 (1999) 1521 [hep-ex/9905013] [SPIRES].
Belle collaboration, K. Hayasaka et al., New search for τ → μγ and τ → eγ decays at Belle, Phys. Lett. B 666 (2008) 16 [arXiv:0705.0650] [SPIRES].
BABAR collaboration, B. Aubert et al., Searches for lepton flavor violation in the decays τ → eγ and τ → μγ, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 (2010) 021802 [arXiv:0908.2381] [SPIRES].
SINDRUM collaboration, U. Bellgardt et al., Search for the decay μ + → e + e + e −, Nucl. Phys. B 299 (1988) 1 [SPIRES].
Belle collaboration, Y. Miyazaki et al., Search for lepton flavor violating τ decays into three leptons, Phys. Lett. B 660 (2008) 154 [arXiv:0711.2189] [SPIRES].
SINDRUM II. collaboration, C. Dohmen et al., Test of lepton flavor conservation in μ → e conversion on titanium, Phys. Lett. B 317 (1993) 631 [SPIRES].
MEG collaboration, S. Ritt, Status of the MEG expriment μ → eγ, Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 162 (2006) 279 [SPIRES].
T. Mori, MEG: The experiment to search for μ → eγ, Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 169 (2007) 166 [SPIRES].
M. Bona et al., SuperB: A high-luminosity asymmetric e + e − super flavor factory. Conceptual design report, arXiv:0709.0451 [SPIRES].
SuperKEKB Physics Working Group collaboration, A. G. Akeroydetal., Physics at super B factory, hep-ex/0406071 [SPIRES].
W.J. Marciano, T. Mori and J.M. Roney, Charged lepton flavor violation experiments, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 58 (2008) 315 [SPIRES].
The PRIME Working Group, Y. Mori et al., An experimental search for the μ − − e − conversion process at an ultimate sensitivity of the order of 10−18 with PRISM, http://www-ps.kek.jp/jhf-np/LOIlist/LOIlist.html.
Mu2e collaboration, E.C. Dukes et al., Proposal to search for μ − N → e − N with a single event sensitivity below 10−16, http://mu2e.fnal.gov/public/hep/index.shtml.
A. De Simone, M. Garny, A. Ibarra and C. Weniger, Supersymmetric leptogenesis with a light hidden sector, JCAP 07 (2010) 017 [arXiv:1004.4890] [SPIRES].
A. Boyarsky, J. Lesgourgues, O. Ruchayskiy and M. Viel, Lyman-alpha constraints on warm and on warm-plus-cold dark matter models, JCAP 05 (2009) 012 [arXiv:0812.0010] [SPIRES].
K. Enqvist and A. Mazumdar, Cosmological consequences of MSSM flat directions, Phys. Rept. 380 (2003) 99 [hep-ph/0209244] [SPIRES].
M. Dine, L. Randall and S.D. Thomas, Supersymmetry breaking in the early universe, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 (1995) 398 [hep-ph/9503303] [SPIRES].
W. Buchmüller, L. Covi, K. Hamaguchi, A. Ibarra and T. Yanagida, Gravitino dark matter in R -parity breaking vacua, JHEP 03 (2007) 037 [hep-ph/0702184] [SPIRES].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ArXiv ePrint: 1006.2857
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanchet, S., Marfatia, D. & Mustafayev, A. Examining leptogenesis with lepton flavor violation and the dark matter abundance. J. High Energ. Phys. 2010, 38 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP11(2010)038
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP11(2010)038