Abstract
Background
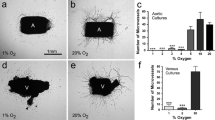
New vessel growth is often associated with ischemia, and hypoxic tissue has been identified as a potential source of angiogenic factors. In particular, ischemia is associated with the development of neovascularization in a number of ocular pathologies. For this reason, we have studied the induction of endothelial cell mitogens by hypoxia in retinal cells.
Materials and Methods
Human retinal pigment epithelium (hRPE) were grown under normoxic and hypoxic conditions and examined for the production of endothelial mitogens. Northern analysis, biosynthetic labeling and immunoprecipitation, and ELISA were used to assess the levels of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor (VEGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), two endothelial cell mitogens and potent angiogenic factors. Soluble receptors for VEGF were employed as competitive inhibitors to determine the contribution of the growth factor to the hypoxia-stimulated mitogen production.
Results
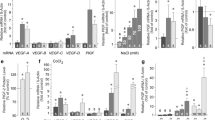
Following 6–24 hr of hypoxia, confluent and growing cultures of hRPE increase their levels of VEGF mRNA and protein synthesis. Biosynthetic labeling studies and RT-PCR analysis indicate that the cells secrete VEGF121 and VEGF165, the soluble forms of the angiogenic factor. In contrast, hRPE cultured under hypoxic conditions show reduced steady-state levels of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) mRNA and decreased bFGF protein synthesis. Unlike VEGF, bFGF is not found in conditioned media of hRPE following 24 hr of hypoxia. Using a soluble high-affinity VEGF receptor as a competitive inhibitor of VEGF, we demonstrate that a VEGF-like activity is the sole hypoxia-inducible endothelial mitogen produced by cultured hRPE.
Conclusions
From this comparison we conclude that hRPE do not respond to hypoxia with a general, nonspecific increase in the overall levels of growth factors, as is seen during cell wounding responses or serum stimulation. The physiological relevance of data from this in vitro model are affirmed by separate studies in an animal model of retinal ischemia-induced ocular neovascularization (1) in which retina-derived VEGF levels have been shown to correlate spatio-temporally with the onset of angiogenesis. Taken together, these data support the hypothesis that the induction of VEGF by hypoxia mediates the rapid, initial angiogenic response to retinal ischemia.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller JW, Adamis AP, Shima DT, D’Amore PA, Moulton RS, O’Reilly MS, et al. (1994) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial cell growth factor is temporally and spatially correlated with ocular angiogenesis in a primate model. Am. J. Pathol. 145: 574–584.
Adair TH, Gay WJ, Montani JP. (1990) Growth regulation of vascular system: evidence for a metabolic hypothesis. Am. J. Physiol. 259: R1–R12.
Heacock CS, Sutherland RM. (1990) Enhanced synthesis of stress proteins by hypoxia and relation to altered cell growth and metabolism. Br. J. Cancer 62: 217–225.
Kourembanas S, Marsden PA, McQuillan LP, Faller, DV. (1991) Hypoxia induced endothelin gene expression and secretion in cultured human endothelium. J. Clin. Invest. 88: 1054–1057.
Kourembanas S, Hannan RL, Faller, DV. (1990) Oxygen tension regulates the expression of platelet-derived growth factor-B chain in human endothelial cells. J. Clin. Invest. 86: 670–764.
Goldberg MA, Dunning SP, Bunn HF. (1988) Regulation of the erythropoietin gene: Evidence that the oxygen sensor is a heme protein. Science 242: 1412–1414.
Knighton DR, Hunt TK, Scheuenstahl H, Halliday BJ, Werb Z, Banda MJ. (1983) Oxygen tension regulates the expression of angiogenesis factor by macrophages. Science 221: 1283–1285.
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E. (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature 359: 843–845.
Shreeniwas R, Ogawa S, Cozzolino F, Torcia G, Braunstein N, Butura C, et al. (1991) Macrovascular and microvascular endothelium during long-term hypoxia: Alterations in cell growth, monolayer permeability, and cell surface coagulant properties. J. Cell. Phys. 146: 8–17.
Michaelson IC. (1948) The mode of development of the vascular system of the retina with some observations on its significance for certain retinal diseases. Trans. Ophthalmol. Soc. U.K. 68: 137–180.
Ashton N, Ward B, Serpell G. (1954) Effect of oxygen on developing retinal vessels with particular reference to the problem of retrolental fibroplasia. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 38: 397–432.
McAvoy JW, Chamberlain CG. (1990) Growth factors in the eye. Prog. Growth Factor Res. 2: 29–43.
Sarks SH. (1980) Drusen and their relationship to senile macular degeneration. Aust. J. Ophthalmol. 8: 117–130.
Seaton AD, Turner JE. (1992) RPE transplants stabilize retinal vasculature and prevent neovascularization in the RCS rat. Invest. Ophthal. Vis. Sci. 33: 83–91.
Sternfeld MD, Robertson JE, Shipley GD, Tsai J, Rosenbaum JT. (1989) Cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells express basic fibroblast growth factor and its receptor. Curr. Eye Res. 8: 1029–1037.
Einer VM, Strieter RM, Einer SG, Baggioline M, Lindley I, Kunkel SL. (1990) Neutrophil chemotactic factor (IL-8) gene expression by cytokine-treated retinal pigment epithelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 136: 745–750.
Kitaoka T, Bost LM, Ishigooka H, Aotaki-Keen AE, Hjemeland L. (1993) Increasing cell density down-regulates the expression of aFGF by human RPE cells in vitro. Curr. Eye Res. 12: 993–999.
Adamis AP, Shima DT, Yeo K-T, Yeo T-K, Brown LF, Berse B, et al. (1993) Synthesis and secretion of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor by human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 193: 631–638.
Ferrara N, Houck KA, Jakeman LB, Winer J, Leung, DW. (1991) The vascular endothelial growth factor family of polypeptides. J. Cell. Biochem. 47: 211–218.
Clauss M, Gerlach M, Gerlach H, Brett J, Want F, Familletti PC, et al. (1990) Vascular permeability factor: A tumor-derived polypeptide that induces endothelial cell and monocyte procoagulant activity, and promotes monocyte migration. J. Exp. Med. 172: 1535–1545.
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Peruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF. (1983) Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science 219: 983–985.
Keck PJ, Hauser SD, Krivi G, Sanzo K, Warren T, Feder J, et al. (1989) Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science 246: 1309–1312.
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara, N. (1989) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 246: 1306–1309.
Yeo T-K, Senger DR, Dvorak HF, Freter L, Yeo, K-T. (1991) Glycosylation is essential for efficient secretion but not for permeability-enhabcing activity of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 179: 1568–1575.
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Risau, W. (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature 359: 845–848.
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett N, Phillips HS, et al. (1993) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis supprresses tumor growth in vivo. Nature 362: 841–844.
Klagsbrun M, Soker, S. (1994) VEGF/VPF: The angiogenesis factor found? Curr. Biol. 3: 699–702.
McGookin ED, Stopa EG, Kuo-LeBlanc V, Baird A, Gonzales A-M, Hanneken A, et al. (1992) Vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) has a different distribution than basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in the adult human retina. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 15: 821a.
Shing Y, Folkman J, Sullivan R, Butterfield C, Murray J, Klagsbrun, M. (1984) Heparin affinity: Purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science 223: 1296–1298.
Ferrara N, Leung DW, Cachanes G, Winer J, Henzel, WJ. (1991) Purification and cloning of vacular endothelial growth factor secreted by pituitary folliculostellate cells. Meth. Enzymol. 198: 391–405.
Park JE, Chen HH, Winer J, Houck KA, Ferrara N. (1994) Placenta growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 2564–2565.
Yeo K-T, Sioussat TM, Faix JD, Senger DR, Yeo, T-K. (1992) Development of time-resolved immunofluorometric assay of vascular permeability factor. Clin. Chem. 38: 71–75.
Watanabe H, Hori A, Seno M, Kozai Y, Igarishi K, Ichimori Y, et al. (1991) A sensitive enzyme immunoassay for human basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 175: 229–235.
Yeo KT, Wang HH, Nagy JA, Sioussat TM, Ledbetter SR, Hoogewerf AJ, et al. (1993) Vascular permeability factor (Vascular endothelial growth factor) in guinea pig and human tumor and inflammatory effusions. Cancer Res. 53: 2912–2918.
Kandel J Bossy-Wetzel, E Radvany, F Klagsbrun, M Folkman, J Hanahan, D. (1991) Neovascularization is associated with a switch to the export of bFGF in the multistep development of fibrosarcoma. Cell 66: 1095–1104.
Ferrara N, Houck K, Jakeman L, Leung DW. (1992) Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins. Endocrine Rev. 13: 18–32.
Houck KA, Ferrara N, Winer J, Cachiane G. (1991) The vascular endothelial growth factor family: Identification of a 4th molecular species and characterization of alternative splicing of RNA. Mol. Endocrinol. 5: 1806–1814.
Kendall RL, Thomas KA. (1993) Inhibition of vascular endothelial cell growth factor activity by an endogenously encoded soluble receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90: 10705–10709.
Dvorak HF, Sioussat TM, Brown LF, Berse B, Nagy JA, Sotrel A, et al. (1991) Distribution of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) in tumors: Concentration in tumor blood vessels. J. Exp. Med. 174: 1275–1278.
Korte GE, Repucci V, Henkind P. (1984) RPE destruction causes choriocapillary atrophy. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 25: 1135–1145.
Li L, Turner JE. (1988) Inherited retinal dystrophy in the RCS rat: Prevention of photoreceptor degeneration by pigment epithelium cell transplantation. Exp. Eye Res. 47: 911–917.
Padua RR, Kardami E. (1993) Increased basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) accumulation and distinct patterns of localization in isoproterenol-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Growth Factors 8: 291–306.
Finklestein SP, Apostolides PJ, Caday CG, Prosser J, Philips MF, Klagsbrun M. (1988) Increased basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) immunoreactivity at the site of focal brain wounds. Brain Res. 460: 253–259.
Kostyk SK, D’Amore PA, Herman IM, Wagner JA. (1994) Optic nerve injury alters basic fibroblast growth factor localization in the retina and optic tract. J. Neurosci. 14: 1441–1449.
Pertovaara L, Kaipainen A, Mustonen T, Orpana A, Ferrara N, Saksela O, et al. (1994) Vascular endothelial growth factor is induced in response to transforming growth factor-beta in fibroblastic and epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 6271–6274.
Bost LM, Aotaki-Keen AE, Hjelmeland, LM. (1992) Coexpression of FGF-5 and bFGF by the retinal pigment epithelium in vitro. Exp. Eye Res. 55: 727–734.
Campochiaro P. (1993) Cytokine production by retinal pigment epithelial cells (review). Int. Rev. Cyt. 146: 75–82.
McNeil PL. (1993) Cellular and molecular adaptations to injurious mechanical stress. Trends Cell Biol. 3: 302–307.
D’Amore PA. (1990) Modes of FGF release in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Met. Rev. 9: 227–238.
Adamis AP, Miller JW, Bernai M-T, D’Amico DJ, Folkman J, Yeo T-K, et al. (1994) Elevated vascular permeability factor/Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the vitreous of eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 118: 445–450.
Brown LF, Berse B, Jackman RW, Tognazzi K, Manseau EJ, Senger DR, et al. (1993) Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in adenocarcinomas of the gastrointestinal tract. Cancer Res. 53: 4727–4735.
Brown LF, Berse B, Jackman RW, Tognazzi K, Manseau EJ, Dvorak HF, et al. (1993) Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in kidney and bladder carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 143: 1255–1262.
Sivalingam A, Kenney J, Brown GC, Benson WE, Donoso, L. (1990) Basic fibroblast growth factor levels in the vitreous of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 108: 869–872.
Nguyen M, Watanabe H, Budson A, Richie J, Folkman J. (1993) Elevated levels of an angiogenic peptide, basic fibroblast growth factor, in urine of bladder cancer patients. J. Natl. Canc. Instit. 85: 241–242.
Pepper MS, Ferrara N, Orci L, Montesano R. (1992) Potent synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in the induction of angiogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 189: 824–831.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from EY05985 (PAD), CA45548 (PAD), EY00325 (APA), and Beth Israel Hospital Pathology Foundation, Inc. (KTY, TKY).
We thank Donald Senger for the anti-VEGF antisera used in the immunoassay, Ying Zhou for the excellent technical assistance, Dr. Harold Dvorak for his helpful comments, Dr. Stella Kourembanas for generously sharing her insights regarding hypoxic regulation of bFGF gene expression, and Sandra R. Smith for her assistance in performing the proliferation assays.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shima, D.T., Adamis, A.P., Ferrara, N. et al. Hypoxic Induction of Endothelial Cell Growth Factors in Retinal Cells: Identification and Characterization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) as the Mitogen. Mol Med 1, 182–193 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03401566
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03401566