Abstract
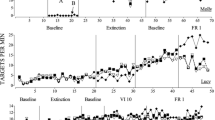
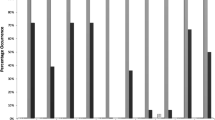
The frequency and intensity of hitting an automated Bobo doll were continuously recorded for 8 female and 8 male nursery school children receiving pennies for bar pressing on a continuous reinforcement-extinction schedule. Hitting was distributed throughout extinction and baseline periods but did not occur during continuous reinforcement. No sex differences were found. The results parrallel data obtained from infrahuman organisms and suggest that schedule-elicited aggression in humans may be viewed as an adjunctive behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AZRIN, N. H., HUTCHINSON, R. R., & HAKE, D. F. 1966. Extinction-induced aggression. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 9, 191–204.
CHEREK, D. R., & HEISTAJD, G. T. 1971. Fixed-interval-induced aggression. Psychonomic Science, 25, 7–8.
DAVIS, H., & DONENFELD, I. 1967. Extinction induced social interaction in rats. Psychonomic Science, 7, 85–86.
DEUR, J. L., & PARKE, R. D. 1970. Effects of inconsistent punishment on aggression in children. Developmental Psychology, 2, 403–411.
FREDERIKSEN, L., & PETERSON, G. 1973. Aggression during various fixed-ratio schedules of reinforcement. Proceedings of the 81st Annual Convention of the American Psychological Association, (in press.)
GENTRY, W. D. 1970. Effect of time-out from positive reinforcement on aggressive behavior in young children. Psychological Reports, 26, 283–288.
HUTCHINSON, R. R., AZRIN, N. H., & HUNT, G. M. 1968. Attack produced by intermittent reinforcement of a concurrent operant response. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 11, 489–495.
KELLY, J. F., & HAKE, D. F. 1970. An extinction-induced increase in an aggressive response with humans. Journal of Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 14, 153–164.
KNUTSON, J. F. 1970. Aggression during the fixed-ratio and extinction components of a multiple schedule of reinforcement. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 13, 221–231.
KNUTSON, J. F., & KLEINKNECHT, R. A. 1970. Attack during differential reinforcement of a low rate of responding. Psychonomic Science, 19, 289–290.
PETERSON, G. L. 1971. The relationship between fixed ratio schedules of reinforcement and aggression in children. Paper presented at the Southeastern Psychological Association, Miami, April.
RILLING, M., & CAPLAN, H. J., 1973; Extinction-induced aggression during errorless discrimination learning. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 20, 85–92.
STAUB, E., & CONN, L. K. 1970. Aggression. In C. G. Costello (Ed.), Symptoms of Psychopathology: A handbook. New York: Wiley.
THOMPSON, T., & BLOOM, W. 1966. Aggressive behavior and extinction-induced response rate increase. Psychonomic Science, 5, 335–336.
ULRICH, R. E., & AZRIN, N. H. 1962. Reflexive fighting in response to aversive stimulation. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 5, 511–520.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
These data are based on a thesis submitted by the first author to the Department of Psychology, Ohio University, in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the M.S. degree. The authors wish to thank Ms. Frederiksen and Drs. H. Kotses and P. Lewis for their assistance in the preparation and completion of this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frederiksen, L.W., Peterson, G.L. Schedule-Induced Aggression in Nursery School Children. Psychol Rec 24, 343–351 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394252
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394252