Abstract
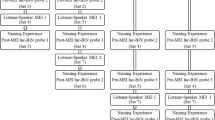
We tested the effect of multiple exemplar instruction on the transfer of stimulus function for unfamiliar pictures across listener responses (i.e., matching and pointing) and speaker responses (i.e., pure tacts and impure tacts). Three preschool students, who were 3- and 4-year-old males and did not have the listener to speaker component of the naming repertoire, participated in the experiment. The dependent variable was numbers of correct responses to probe trials of both untaught listener responses (“point to__”) and speaker responses (tact and impure tacts) following mastery of matching responses for two sets of five unfamiliar pictures (Set 1 and Set 3). After each participant mastered matching (e.g., “match Labrador”) for Set 1 pictures they were probed on the three untaught responses to Set 1 words. That is, they were asked to point to Labrador, tact the picture of Labrador, and respond to the picture of a Labrador and the question “What is this?” Next, the participants were taught mastery of all four types of responses using MEI for a second set of five pictures (Set 2) and probed again on the 3 untaught Set 1 responses. Finally, matching responses were taught to mastery for a novel set of pictures (Set 3) and then probed on the three untaught responses. The results showed that untaught speaker responses emerged at 60% to 85% for two participants, and 40%- 70% for one participant. We discuss the role of instructional history in the development of the listener to speaker component of naming.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahadorian, AJ. (2000). The effect of the learn unit on student’s performance in two university courses. Unpublished Ph.D. dissertation, Columbia University.
Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., & Cullinan, V (2001). Relational frame theory and Skinner’s Verbal behavior. The Behavior Analyst, 23, 69–84.
Becker, W. (1992). Direct instruction: A twenty-year review. In R. West & L. Hamerlynck, Design for educational excellence: The legacy ofB. F. Skinner (pp. 71–112). Longmont, CO: Sopris West.
Catania, A. C. (1998). Learning (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Donley, C. R., & Greer, R. D. (1993). Setting events controlling social verbal exchanges between students with developmental delays. Journal of Behavioral Education, 3 (4), 387–401.
Emurian, H. H., Hu, X., Wang, J., & Durham, D. (2000). Learning JAVA: A programmed instruction approach using applets. Computers in Human Behavior, 16, 395–422
Fields, L., Reeve, K. F., Mateneja, P., Varelas, A., Belanich, J., Fitzer, A., & Shannon, K. (2003). The formation of a generalized categorization repertoire: Effects of training with multiple domains, samples, and comparisons. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 78, 291–313
Greer, R. D. (2003). Designing teaching strategies: An applied behavior analysis systems approach. New York: Academic Press.
Greer, R. D., Chavez-Brown, M, Nirgudkar, A., Steffi, L., & Rivera-Valdes, (July 2003). The effects of a procedure to teach fluent listener responses to students with autism and changes in the numbers of learn units students required to meet instructional objectives. Paper presented at the First Congress of the European Association for Behavior Analysis, Parma, Italy.
Greer, R. D., & Keohane, D. (2004). The evolution of verbal behavior. Manuscript submitted for publication.
Greer, R. D., Keohane, D. D., & Healey, O. (2002). Quality and applied behavior analysis. The Behavior Analyst Today, 3 (1), 2002.
Greer, R. D. & McCorkle, N. (2003). CABAS® international curriculum and inventory of repertoires from preschool through kinder garten. Yonkers, NY: CABAS® and the Fred S. Keller School.
Greer, R. D., & McDonough, S. (1999). Is the learn-unit the fundamental measure of pedagogy? The Behavior Analyst, 20, 5–16.
Greer, R. D., Nirgudkar, A., & Park, H. (2003b). The effect of multiple exemplar instruction on the transformation of mand and tact functions. Paper Presented at the International Conference of the Association for Behavior Analysis, San Francisco, CA.
Greer, R. D., Yaun L., & Gautreaux, G (2005). Novel Dictation and Intraverbal Responses as a Function of a Multiple Exemplar Instructional History. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 21, 99–116.
Hayes, S. C, Gifford, E. V, Wilson, K. G, Barnes-Holmes, D., & Healy, O. (2001). Derived relational responding as learned behavior. In S. C. Hayes, D. Barnes-Holmes, & B. Roche (Eds.), Relationalframe theory: A post-Skinnerian account of human language and cognition (pp. 21–49). New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum.
Home, P. J., & Lowe, C. F. (1996). On the origins of naming and other symbolic behavior. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 65, 185–241.
Horner, R. D., & Baer, D. M. (1978). Multiple-probe technique: Avariation on the multiple baseline. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 11, 189–196.
Lodhi, S. & Greer, R.D. (1989). The speaker as listener. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 51, 353–360.
Lowe, C. F., Home, P. J., Harris, D. S., & Rändle, V. R. L. (2002). Naming and categorization in young children: Vocal tact training. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 78, 527–549.
Nuzzolo-Gomez, R. & Greer, R. D. (2004). Emergence of Untaught Mands or Tacts with Novel Adjective-Object Pairs as a Function of Instructional History. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 24, 30–47
Pinker, S. (1999). Words and rules. New York: Perennial.
Skinner, B. F. (1989). The behavior of the listener. In S. C. Hayes (Ed.), Rule-governed behavior: Cognition, contingencies and instructional control (85–96). New York: Plenum.
Skinner, B.F. (1957,1992). Verbal behavior. Acton, MA: Copley Publishing Group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
We thank the staff, students, and families of The Fred S. Keller School for their participation and continued support.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greer, R.D., Stolfi, L., Chavez-Brown, M. et al. The Emergence of the Listener to Speaker Component of Naming in Children as a Function of Multiple Exemplar Instruction. Analysis Verbal Behav 21, 123–134 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03393014
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03393014