Abstract
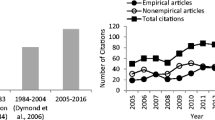
The present paper comments on and extends the citation analysis of verbal operant publications based on Skinner’s Verbal Behavior (1957) by Dymond, O’Hora, Whelan, and O’Donovan (2006). Variations in population parameters were evaluated for only those studies that Dymond et al. categorized as empirical. Preliminary results indicate that the majority of empirical research in the area of verbal behavior has been conducted with the younger developmentally disabled population and has focused on verbal operants from the introductory chapters of Skinner’s book. It is clear that Verbal Behavior has influenced empirical research over the past 50 years. We believe, however, that there are many underdeveloped research areas originating from Verbal Behavior that have not yet been addressed. Suggestions for extended areas of research are provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert, C. L., & Kaiser, A. P. (1992). Training parents as milieu teachers. Journal of Early Intervention, 16, 31–52.
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., text rev.). Washington, DC: Author.
Arntzen, E., & Almas, I. K. (2002). Effects of mand-tact versus tact-only training on the acquisition of tacts. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 35, 419–422.
Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., & Cullinan, V. (2000). Relational frame theory and Skinner’s Verbal Behavior: A possible synthesis. The Behavior Analyst, 23, 69–84.
Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., Roche, B., & Smeets, P. M. (2001). Exemplar training and a derived transformation of function in accordance with symmetry. The Psychological Record, 51, 287–308.
Bourret, J., Vollmer, T. R., & Rapp, J. T. (2004). Evaluation of a vocal mand assessment and vocal mand training procedures. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 37, 129–144.
Bowman, L. G., Fisher, W. W., Thompson, R. H., & Piazza, C. C. (1997). On the relation of mands and the function of destructive behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 30, 251–265.
Braam, S. J., & Sundberg, M. L. (1991). The effects of specific versus nonspecific re-inforcement on verbal behavior. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 9, 19–28.
Brown, K. A., Wacker, D. P., Derby, K. M., Peck, S. M., Richman, D. M., Sasso, G. M., et al. (2000). Evaluating the effects of functional communication training in the presence and absence of establishing operations. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 33, 53–71.
Brown-Gorton, R., & Wolery, M. (1998). Teaching mothers to imitate their handicapped children: Effects on maternal mands. The Journal of Special Education, 22, 97–107.
Calculator, S. N. (2002). Use of enhanced natural gestures to foster interaction between children with Angelman syndrome and their parents. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 11, 340–355.
Carr, J. E., & Stewart, K. K. (2005). Citation performance of behaviorally oriented journals. The Behavior Analyst Today, 6, 83–87.
Carroll, R. J., & Hesse, B. E. (1987). The effects of alternating mand and tact training on the acquisition of tacts. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 5, 55–65.
Chambers, M., & Rehfeldt, R. A. (2003). Assessing the acquisition and generalization of two mand forms with adults with severe developmental disabilities. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 24, 265–280.
Charlop, M. H., Schreibman, L., & Thibodeau, M. G. (1985). Increasing spontaneous verbal responding in autistic children using a time delay procedure. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 18, 155–166.
Charlop, M. H., & Trasowech, J. E. (1991). Increasing autistic children’s daily spontaneous speech. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 24, 747–761.
Charlop-Christy, M. H., Carpenter, M., LeBlanc, L. A., & Kellet, K. (2002). Using the picture exchange communication system (PECS) with children with autism: Assessment of PECS acquisition, speech, social-communicative behavior, and problem behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 35, 213–231.
Chase, P. N., Johnson, K. R., & Sulzer-Azaroff, B. (1985). Verbal relations within instruction: Are there subclasses of the intraverbal? Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 43, 301–313.
Daly, P. M. (1987). A description of the verbal behavior of students during two reading instruction methods. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 5, 67–76.
DeLeon, I. G., Fisher, W. W., Herman, K. M., & Crosland, K. C. (2000). Assessment of a response bias for aggression over functionally equivalent appropriate behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 33, 73–77.
Derby, K. M., Fisher, W. W., Piazza, C. C., Wilke, A. E., & Johnson, W. (1998). The effects of noncontingent and contingent attention for self-injury, manding, and collateral responses. Behavior Modification, 22, 474–484.
Derby, K. M., Wacker, D. P., Berg, W., DeRaad, A., Ulrich, S., Asmus, J., et al. (1997). The long-term effects of functional communication training in home settings. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 30, 507–531.
Didden, R., Korzilius, H., Duker, P., & Curfs, L. M. G. (2004). Communicative functioning in individuals with Angelman syndrome: A comparative study. Disability & Rehabilitation, 26, 1263–1267.
Drasgow, E., Halle, J. W., & Ostrosky, M. M. (1998). Effects of differential reinforcement on the generalization of a replacement mand in three children with severe language delays. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 31, 357–374.
Drasgow, E., Halle, J. W., & Phillips, B. (2001). Effects of different social partners on the discriminated requesting of a young child with autism and severe language delays. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 22, 125–139.
Drash, P. W., High, J. W., & Tudor, R. M. (1999). Using mand training to establish an echoic repertoire in young children with autism. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 16, 29–44.
Duker, P. C., Dortmans, A., & Lodder, E. (1993). Establishing the manding function of communicative gestures with individuals with severe/profound mental retardation. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 14, 39–49.
Duker, P. C., Kraaykamp, M., & Visser, E. (1994). A stimulus control procedure to increase requesting with individuals who are severely/profoundly intellectually disabled. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 38, 177–186.
Duker, P. C., van Driel, S., & Bercken, J. (2002). Communication profiles of individuals with Down’s syndrome, Angelman syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 46, 35–40.
Dymond, S., O’Hora, D., Whelan, R., & O’Donovan, A. (2006). Citation analysis of Skinner’s Verbal Behavior: 1984–2004. The Behavior Analyst, 29, 75–88.
Eikeseth, S., & Nesset, R. (2003). Behavioral treatment of children with phonological disorder: The efficacy of vocal imitation and sufficient-response-exemplar training. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 36, 325–337.
Ericsson, K. A., & Simon, H. A. (1993). Protocol analysis: Verbal reports as data. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Ewing, C. B., Magee, S. K., & Ellis, J. (2001). The functional analysis of problematic verbal behavior. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 18, 51–60.
Farmer, J. A., Gast, D. L., Wolery, M., & Winterling, V. (1991). Small group instruction for students with severe handicaps: A study of observational learning. Education and Training in Mental Retardation, 26, 190–201.
Finkel, A. S., Weber, K. P., & Derby, K. M. (2004). Use of a Braille exchange communication system to improve articulation and acquire mands with a legally blind and developmentally disabled female. Journal of Developmental & Physical Disabilities, 16, 321–336.
Finkel, A. S., & Williams, R. L. (2001). A comparison of textual and echoic prompts on the acquisition of intraverbal behavior in a six-year-old boy with autism. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 18, 61–70.
Gobbi, L., Cipani, E., Hudson, C., & Lapenta-Neudeck, R. (1986). Developing spontaneous requesting among children with severe mental retardation. Mental Retardation, 24, 357–363.
Goh, H. L., Iwata, B. A., & DeLeon, I. G. (2000). Competition between noncontingent and contingent reinforcement schedules during response acquisition. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 33, 195–205.
Hall, G., & Sundberg, M. L. (1987). Teaching mands by manipulating conditioned establishing operations. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 5, 41–53.
Hancock, T. B., & Kaiser, A. P. (1996). Siblings’ use of milieu teaching at home. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 16, 168–190.
Henry, L. M., & Horne, P. J. (2000). Partial remediation of speaker and listener behaviors in people with severe dementia. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 33, 631–634.
Hersh, S. B. (1990). A description of teacher-student verbal interactions in a resource room versus regular classroom. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 8, 101–112.
Horne, P. J., Lowe, C. F., & Randle, V. R. L. (2004). Naming and categorization in young children: II. Listener behavior training. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 81, 267–288.
Howard, J. S., & Rice, D. E. (1988). Establishing a generalized autoclitic repertoire in preschool children. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 6, 45–59.
Johnson, L., McComas, J., Thompson, A., & Symons, F. J. (2004). Obtained versus programmed reinforcement: Practical considerations in the treatment of escape reinforced aggression. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 37, 239–242.
Kaiser, A. P., & Hester, P. P. (1994). Generalized effects of enhanced milieu teaching. Journal of Speech & Hearing Research, 37, 1320–1340.
Kern, L., Carberry, N., & Haidara, C. (1997). Analysis and intervention with two topographies of challenging behavior exhibited by a young woman with autism. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 18, 275–287.
Khang, S., Hendrickson, D. J., & Vu, C. P. (2000). Comparison of single and multiple functional communication training responses for the treatment of problem behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 33, 321–324.
Kritch, K. M., & Bostow, D. E. (1993). Verbal response to past events: Intraverbal relations, or tacts to private events? The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 11, 1–7.
Lalli, J. S., & Browder, D. M. (1993). Comparison of sight word training procedures with validation of the most practical procedure in teaching reading for daily living. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 14, 107–127.
Lalli, J. S., Mauro, B. C., & Mace, F. C. (2000). Preference for unreliable reinforcement in children with mental retardation: The role of conditioned reinforcement. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 33, 533–544.
Lamarre, J., & Holland, J. G. (1985). The functional independence of mands and tacts. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 43, 5–19.
Leigland, S. (1996). An experimental analysis of ongoing behavior, reinforcement, verbal operants and superstitious behavior. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 20, 3–10.
Lerman, D. C., Iwata, B. A., Smith, R. G., & Vollmer, T. R. (1994). Restraint fading and the development of alternative behavior in the treatment of self-restraint and self-injury. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 38, 135–148.
Leung, J. P., & Wu, K. I. (1997). Teaching receptive naming of Chinese characters to children with autism by incorporating echolalia. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 30, 59–68.
Lodhi, S., & Greer, R. D. (1989). The speaker as listener. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 51, 353–359.
Lowe, C. F., Horne, P. J., Harris, F. D. A., & Randle, V. R. L. (2002). Naming and categorization in young children vocal tact training. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 78, 527–549.
Lowenkron, B., & Colvin, V. (1992). Joint control and generalized nonidentity matching: Saying when something is not. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 10, 1–10.
Luciano, M. C. (1986). Acquisition, maintenance, and generalization of productive intraverbal behavior through transfer of stimulus control procedures. Applied Research in Mental Retardation, 7, 1–20.
Luciano, M. C., Gomez Becerra, I., & Rodriguez Valverde, M. (2007). The role of multiple-exemplar training and naming in establishing derived equivalence in an infant. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 87, 349–365.
MacGreene, D., & Hafer Bry, B. (1991). A descriptive analysis of family discussions about everyday problems and decisions. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 9, 29–39.
Marcus, B. A., & Vollmer, T. R. (1996). Combining noncontingent reinforcement and differential reinforcement schedules as treatment for aberrant behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 29, 43–51.
Marion, C., Vause, P., Harapiak, S., Martin, G. L., Yu, D. C. T., Sakko, G., et al. (2003). The hierarchical relationship between several visual and auditory discriminations and three verbal operants among individuals with developmental disabilities. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 19, 91–105.
McPherson, A., Bonem, M., Green, G., & Osborne, J. G. (1984). A citation analysis of the influence on research of Skinner’s Verbal Behavior. The Behavior Analyst, 7, 157–167.
Miguel, C. F., Carr, J. E., & Michael, J. (2002). The effects of a stimulus-stimulus pairing procedure on the vocal behavior of children diagnosed with autism. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 18, 3–13.
Murphy, C., Barnes-Holmes, D., & BarnesHolmes, Y. (2005). Derived manding in children with autism: Synthesizing Skinner’s Verbal Behavior with relational frame theory. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 38, 445–462.
Northup, J., Vollmer, T. R., & Serrett, K. (1993). Publication trends in 25 years of the Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 26, 527–537.
Nuzzolo-Gomez, R., & Greer, R. D. (2004). Emergence of untaught mands or tacts of novel adjective-object pairs as a function of instructional history. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 20, 63–76.
O’Conner, J. T., Sorensen-Burnworth, R. J., Rush, K. S., & Eidman, S. L. (2003). A mand analysis and levels of treatment in an outpatient clinic. Behavioral Interventions, 18, 139–150.
O’Neill, R. E., Faulkner, C., & Horner, R. H. (2000). The effects of general case training of manding responses on children with severe disabilities. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 12, 43–60.
Partington, J. W., & Bailey, J. S. (1993). Teaching intraverbal behavior to preschool children. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 11, 9–18.
Partington, J. W., Sundberg, M. L., Newhouse, L., & Spengler, S. M. (1994). Overcoming an autistic child’s failure to acquire a tact repertoire. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 27, 733–734.
Peck, S. M., Wacker, D. P., Berg, W. K., Cooper, L. J., Brown, K. A., Richman, D., et al. (1996). Choice-making treatment of young children’s severe behavior problems. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 29, 263–290.
Polson, D. A. D., Grabavac, D. M., & Parsons, J. A. (1997). Intraverbal stimulus-response reversibility: Fluency, familiarity effects, and implications for stimulus equivalence. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 14, 19–40.
Potter, B., Huber, S., & Michael, J. (1997). The role of mediating verbal behavior in selection-based responding. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 38, 101–105.
Ribeiro, A. D. (1998). Correspondence in children’s self-report: Tacting and manding aspects. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 51, 361–367.
Richman, D. M., Wacker, D. P., & Winborn, L. (2001). Response efficiency during functional communication training: Effects of effort on response allocation. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 34, 73–76.
Robbins, J. K., Layng, T. V. J., & Karp, H. J. (1995). Ambiguity and the abstract tact: A signal detection analysis. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 12, 1–11.
Romer, L. T., Cullian, T., & Schoenberg, B. (1994). General-case training of requesting: A demonstration and analysis. Education and Training in Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities, 29, 57–68.
Ross, D. E., & Greer, R. D. (2003). Generalized imitation and the mand: Inducing first instances of speech in young children with autism. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 24, 58–74.
Sautter, R. A., & LeBlanc, L. A. (2006). The empirical applications of Skinner’s analysis of verbal behavior with humans. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 22, 35–48.
Schussler, N. G., & Spradlin, J. E. (1991). Assessment of stimuli controlling the requests of students with severe mental retardation during a snack routine. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 24, 791–797.
Sigafoos, J. (1998). Assessing conditional use of graphic mode requesting in a young boy with autism. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 10, 133–151.
Sigafoos, J., & Couzens, D. (1995). Teaching functional use of an eye gaze communication board to a child with multiple disabilities. British Journal of Developmental Disabilities, 41, 114–125.
Sigafoos, J., Doss, S., & Reichle, J. (1989). Developing mand and tact repertoires in persons with severe developmental disabilities using graphic symbols. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 10, 183–200.
Sigafoos, J., Reichle, J., Doss, S., Hall, K., & Pettitt, L. (1990). Spontaneous transfer of stimulus control from tact to mand contingencies. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 11, 165–176.
Sigafoos, J., Roberts, D., Kerr, M., Couzens, D., & Baglioni, A. J. (1994). Opportunities for communication in classrooms serving children with development disabilities. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24, 259–279.
Sigafoos, J., Woodyatt, G., Tucker, M., Toberts-Pennell, D., & Pittendreigh, N. (2000). Assessment of potential communicative acts in three individuals with Rett syndrome. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 12, 203–216.
Skinner, B. F. (1957). Verbal behavior New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Smith, R., Michael, J., & Sundberg, M. L. (1996). Automatic reinforcement and automatic punishment in infant vocal behavior. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 13, 39–48.
Sprague, J. R., & Horner, R. H. (1992). Covariation within functional-response classes: Implications for treatment of severe problem behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 25, 735–745.
Stafford, M. W., Sundberg, M. L., & Braam, S. J. (1988). A preliminary investigation of the consequences that define the mand and the tact. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 6, 61–71.
Sundberg, C. T., & Sundberg, M. L. (1990). Comparing topography-based verbal behavior with stimulus selection-based verbal behavior. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 8, 31–34.
Sundberg, M. L. (1985). Teaching verbal behavior to pigeons. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 3, 11–18.
Sundberg, M. L., Endicott, K., & Eigenheer, P. (2000). Using intraverbal prompts to establish tacts for children with autism. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 18, 15–29.
Sundberg, M. L., Michael, J., Partington, J. W., & Sundberg, C. A. (1996). The role of automatic reinforcement in early language acquisition. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 13, 21–37.
Tenenbaum, H. A., & Wolking, W. D. (1989). Effects of oral reading rate and inflection on intraverbal responding. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 7, 83–89.
Tiger, J. H., & Hanley, G. P. (2004). Developing stimulus control of preschooler mands: An analysis of schedule-correlated and contingency-specifying stimuli. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 37, 517–521.
Tincani, M. J., Castrogiovanni, A., & Axelrod, S. A. (1999). Comparison of the effectiveness of brief versus traditional functional analyses. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 20, 327–338.
Twyman, J. S. (1996). The functional independence of impure mands and tacts of abstract stimulus properties. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 13, 1–19.
Vollmer, T. R., Borrero, J. C., Lalli, J. S., & Daniel, D. (1999). Evaluating self-control and impulsivity in children with severe behavior disorders. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 32, 451–466.
Warren, S. F., McQuarter, R. J., & Rogers-Warren, A. K. (1984). The effects of mands and models on the speech of unresponsive language-delayed preschool children. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 49, 43–52.
Watkins, C. L., Pack-Teixeira, L., & Howard, J. (1989). Teaching intraverbal behavior to severely retarded children. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 7, 69–81.
Woods, T. S. (1984). Generality in the verbal tacting of autistic children as a function of naturalness in antecedent control. Journal of Behavior Therapy & Experimental Psychiatry, 15, 27–32.
Yamamoto, J., & Mochizuki, A. (1988). Acquisition and functional analysis of manding with autistic students. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 21, 57–64.
Yoon, Y. S., & Bennett, G. M. (2000). Effects of a stimulus-stimulus pairing procedure on conditioning vocal sounds as reinforcers. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 17, 75–88.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dixon, M.R., Small, S.L. & Rosales, R. Extended analysis of empirical citations with Skinner’s Verbal Behavior: 1984–2004. BEHAV ANALYST 30, 197–209 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03392155
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03392155