Abstract
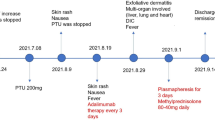
An association of granulocytopenia, eosinophilia, skin reaction and hepatitis during propylthiouracil (PTU) therapy for thyrotoxicosis in a 47 year old black female is reported. Clinical and biochemical abnormalities disappeared soon after discontinuation of PTU. That the drug was directly responsible for the observed complications is suggested by the clinical course and by in vitro lymphocyte transformation studies. The latter revealed sensitization to PTU during the acute phase of the disease, which was greatly reduced 5 weeks after discontinuation of the drug and was completely absent after 5 months. 1 Supported in part by U.S. Public Service Grants AM 15070 and RR 55.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrhein J.A., Kenny F.M., Ross D. Granulocytopenia, lupus-like syndrome, and other complications of propylthiouracil therapy. J. Pediatr. 76: 54, 1970.
Colwell A.R. Jr., Sando D.E., Lang S.J. Propylthiouracil-induced agranulocytosis, toxic hepatitis, and death: Report of a case. J.A.M.A. 148: 639, 1952.
Juliar B., Harris T.L. Fatal agranulocytosis occurring during propylthiouracil therapy: Report of a case. J.A.M.A. 139: 646, 1979.
Beebe R.I., Propp S., McClintock J.C., Versaei A. Fatal agranulocytosis during treatment of toxic goiter with propylthiouracil. Ann. Intern. Med. 34: 1035, 1951.
Livingston H., Livingston S.F. Agranulocytosis and hepatocellular jaundice: Toxic manifestations following PTU therapy. J.A.M.A. 135: 422, 1947.
Walzer R.A., Einbinder J. Immunoleukopenia as an aspect of hypersensitivity to propylthiouracil. J.A.M.A. 184: 743, 1963.
Mihas A.A., Holley P., Koff R.S., Hirschowitz B.I. Fulminant hepatitis and lymphocyte sensitization due to propylthiouracil. Gastroenterol. 70: 770, 1976.
Weiss M., Hassin D., Bank H. Propylthiouracil-induced hepatic damage. Arch. Intern. Med. 140: 1184, 1980.
Fedotin M.S., Lefer L.G. Liver disease caused by propylthiouracil. Arch. Intern. Med. 135: 319, 1975.
Parker L.N. Hepatitis and propylthiouracil. Arch. Intern. Med. 82: 228, 1975.
Eisen J.J. Fulminant hepatitis during treatment with propylthiouracil. N. Engl. J. Med. 249: 814, 1953.
Ishisuki Y. Two case of liver disease caused by thyroid antagonist. Clin. Endocrinol. (Tokio) 22: 1083, 1974.
Griswold W.R., Mendoza S.A., Johnston W., Nichols L.S. Vasculitis associated with propylthiouracil: Evidence for immune complex pathogenesis and response to therapy. Western J. Med. 128: 543, 1978.
Best M.M., Duncan C.H. A lupus-like syndrome following PTU administration. J. Kentucky Med. Ass. 62: 47, 1964.
Librik L., Sussman L., Bejar R., Clayton G.W. Thyrotoxicosis and collagen-like disease in three sisters of American Indian extraction. J. Pediatr. 76: 64, 1970.
Hung W., August G.P. A “collagen-like” syndrome associated with antithyroid therapy. J. Pediatr. 8: 852, 1973.
Williams R.H., Bakke J.L The thyroid. In: Williams R.H. (Ed.), Textbook of endocrinology, W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, 1962, vol. 3, p. 178.
Martelo O.J., Katims R.B., Yunis A.A. Bone marrow aplasia following propylthiouracil therapy: Report of a case with complete recovery. Arch. Intern. Med. 120: 587, 1967.
Sammon T.J., Peden V.H., Witzleben C., King J.P. Disseminated intravascular coagulation complicating PTU therapy. Clin. Pediatr. 10: 739, 1971.
Movitt E., Gerstl B., Davis A. Needle biopsy to thyrotoxicosis. Arch. Intern. Med. 91: 729, 1953.
Mathews K.P., Pan P.M., Well J.H. Experience with lymphocyte transformation tests in evaluating allergy to aminosalicyclic acid, isoniazid and streptomycin. Int. Arch. Allergy. Appl. Immunol. 42: 653, 1972.
Sarkani I. Lymphocyte transformation in drug hypersensitivity. Lancet 1: 743, 1967.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by U.S. Public Service Grants AM 15070 and RR 55.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pacini, F., Sridama, V. & Refetoff, S. Multiple complications of propylthiouracil treatment: granulocytopenia, eosinophilia, skin reaction and hepatitis with lymphocyte sensitization. J Endocrinol Invest 5, 403–407 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350541
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350541