Abstract
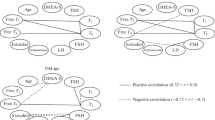
The circadian variation in the levels of Cortisol (C), pregnenolone (Δ5P), 17-hydroxypregnenolone (17-HO-Δ5P), dehydroepiandrosterone (DHA), 20 α-dihydroprogesterone (20-HO-P), 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-HO-P), androstenedione (A), testosterone (T), 5 α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) as well as of the sulphurylated forms of pregnenolone (Δ5P-S), 17-hydroxypregnenolone (17-HO-Δ5P-S), dehydroepiandrosterone (DHA-S), testosterone (T-S) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT-S) was assessed, or re-assessed together with the levels of FSH and LH in peripheral blood samples collected from 12 healthy men at 3-hour intervals during 24 hours. The plasma levels of all unconjugated steroids and of Δ5P-S exhibited a significant circadian rhythm. No circadian variation was found in the levels of the other sulphurylated steroids or of FSH and LH. The relative amplitudes of the variation were: 17-HO-Δ5P: 310%, C: 290%, DHA: 210%, A: 170%, 17-HO-P: 110%, DHT: 73%, T: 65%, Δ5P-S: 59%, and 20-HO-P: 21%. The individual peak values of 17-HO-P, 20-HO-P, T and DHT were more scattered than those of C and A, or of the Δ5-steroids. A significant correlation was found between the levels of C, on the one hand, and those of Δ5P, 17-HO-Δ5P and DHA, on the other hand, and also between the levels of A and those of 17-HO-Δ5P and DHA. Furthermore, the levels of T were significantly correlated to those of 17-HO-P; however, no correlation was found between the levels of these two steroids and those of any other hormonal parameter studied. The insertion of a short catheter at 18.00 h resulted in an extra peak in C levels in 5 subjects. This was associated with a simultaneous peak in Δ5P, 17-HO-Δ5P, DHA and A levels, but not in those of 17-HO-P, T and DHT. It is concluded that in men the circadian rhythm of the major gonadal steroids is independent of the rhythm of adrenal steroids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pincus G. A diurnal rhythm in the urinary excretion of ketosteroidsby young men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 3: 195, 1943.
Bliss E.L, Sandberg A.A., Nelson D.H., EikNes K. The normal levels of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids in the peripheral blood of man. J. Clin. Invest. 32: 818, 1953.
Dray F., Reinberg A., Sebaoun J. Rythme biologique de la testosterone libre du plasma chez I’Homme adulte sain: existence d’une variation circadienne. C.R. Acad. Sc. Paris 261: 573, 1965.
Southren A.L, Tochimoto S., Carmody N.C., Isurugi K. Plasma production rates of testosterone in normal adult men and women and in patients with the syndrome of feminizing testes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 25: 1441, 1965.
de La Torre B., Noren S., Hedman M., Diczfalusy E. Studies on the relationship between sperm count and steroid levels in the spermatic and cubital veins of patients with varicocele. International Journal of Andrology 1: 297, 1978.
Brenner P.F., Guerrero R., Cekan Z., Diczfalusy E. Radioimmunoassay method for six steroids in human plasma. Steroids 22: 775, 1973.
Aedo A.-R., Landgren B.-M., Cekan Z., Diczfalusy E. Studies on the pattern of circulating steroids in the normal menstrual cycle. 2. Levels of 20cr-dihydroprogesterone, 17-hydroxypregnenolone and 17-hydroxyprogesterone and the assessment of their values for ovulation prediction. Acta Endocrinol. (Kbh.) 82: 600, 1976.
Purvis K., Brenner P.F., Landgren B.-M., Cekan Z., Diczfalusy E. Indices of gonadal function in the human male. I. Plasma levels of unconjugated steroids and gonadrotrophins under normal and pathological conditions. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 4: 237, 1975.
Cekan Z. Reliability of steroid radioimmunoassays. Acta Univ. Upsal. 14: 1, 1976.
Burstein S., Lieberman S. Hydrolysis of ketosteroid hydrogen sulfates by solvolysis procedures. J. Biol. Chem. 233: 331, 1958.
Jbnsson G., Olsson A.M., Luttrop W., Cekan Z., Purvis K., Diczfalusy E. Treatment of prostatic carcinoma with various types of estrogen derivatives. Vitamins and Hormones 33: 351, 1975.
Kirschner M.A., Lipsett M.B., Collins D.R. Plasmaketosteroids and testosterone in man: A study of the pituitary-testicular axis. J. Clin. Invest. 44: 657, 1965.
Kobayashi T., Lobotsky J., Lloyd C.W. Plasma testosterone and urinary 17-ketosteroids in Japanese and Occidentals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 26: 610, 1966.
Boon D.A., Keenan R.E., Slaunwhite W.R., Jr. Plasma testosterone in men: Variation, but not circadian rhythm. Steroids 20: 269, 1972.
Alford P., Baker H.W.G., Patel Y.C., Rennie C., Youatt G., Burger H.G., Hudson B. Temporal patterns of circulating hormones as assessed by continuous blood sampling. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 36: 108, 1973.
Saxena B.B., Leyendecker G., Chen W., Gandy H.M., Peterson R.E. Radioimmunoassay of follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing (LH) hormones by chromatoelectrophoresis. Acta Endocrinol. (Kbh.) Suppl. 142: 185, 1969.
de Lacerda L., Kowarski A., Johanson A.J., Athanasiou R., Migeon C.J. Integrated concentration and circadian variation of plasma testosterone in normal men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 37: 366, 1973.
Faiman C., Winter J.S.D. Diurnal cycles in plasma FSH, testosterone and Cortisol in men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 33: 186, 1971.
Leymarie P., Roger M., Castanier M., Scholler R. Circadian variations in plasma testosterone and estrogens in normal men. A study by frequent sampling. J. Steroid Biochem. 5: 167, 1974.
Rowe P.H., Lincoln G.A., Racey P.A., Lehane J., Stephenson M.J., Shenton J.C., Glover T.D. Temporal variations of testosterone levels in the peripheral blood plasma of men. J. Endocrinol. 61: 63, 1974.
Baker H.W.G., Santen R.J., Burger H.G., de Kretser D.M., Hudson B., Pepperell R.J., Bardin C.W. Rhythms in the secretion of gonadotropins and gonadal steroids. J. Steroid Biochem. 6: 793, 1975
Southren A.L., Gordon G.G. Rhythms and testosterone metabolism. J. Steroid Biochem. 6: 809, 1975.
McKenna T.J., Brown R.D. Pregnenolone in man: Plasma levels in states of normal and abnormal steroidogenesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 38: 480, 1974.
Pirke K.M., Doerr P. Plasma dihydrotestosterone in normal adult males and its relation to testosterone. Acta Endocrinol. (Kbh) 79: 357, 1975.
Laatikainen T., Vihko R. Diurnal variation in the concentrations of solvolyzable steroids in human plasma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 28: 1356, 1968.
Aedo A.R., Nunez M., Landgren B.-M., Cekan S.Z., Diczfalusy E. Studies on the pattern of circulating steroids in the normal menstrual cycle. 3. Circadian variation in the periovulatory period. Acta Endocrinol. (Kbh.) 84: 320, 1977.
McKenna T.J., DiPietro D.L., Brown R.D., Strott C.A., Liddle G.W. Plasma 17-HO-pregnenolone in normal subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 39: 833, 1974.
Rosenfeld R.S., Hellman L., Roffwarg H., Weitzman E.D., Fukushima D.K., Gallagher T.F. Dehydroisoandrosterone is secreted episodically and synchronously with Cortisol by normal man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 33: 87, 1971.
Judd H.L., Parker D.C., Rakoff J.S., Hopper B.R., Yen S.S.C. Elucidation of mechanism(s) of the nocturnal rise of testosterone in men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 38: 134, 1973.
Rosenfeld R.S., Rosenberg B.J., Fukushima D.K., Hellman L. 24-Hour secretory pattern of dehydroisoandrosterone and dehydroisoandrosterone sulfate. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 40: 850, 1975.
de Jong F.H., van der Molen H.J. Determination of dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate in human plasma using electron capture detection on 4-androstene-3,6, 17-trione after gas-liquid chromatography. J. Endocrinol. 53: 461, 1972.
Nieschlag E., Loriaux D.L., Ruder H.J., Zucker I.R., Kirschner M.A., Lipsett M.B. The secretion of dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate in man. J. Endocrinol. 57: 123, 1973.
Horth C.E., Craig A.C., Shelton J.R., Palmer R.F., Tidd M.J. Circadian blood follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, thyroxine Cortisol and aldosterone levels measured simultaneously in men. J. Endocrinol. 64: 56P, 1975.
Nillius S.J., Wide L. Effects of estrogen on serum levels of LH and FSH. Acta Endocrinol. (Kbh.) 65: 583, 1970.
Krieger D.T., Ossowski R., Fogel M., Allen W. Lack of circadian periodicity of human serum FSH and LH levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 35: 619, 1972.
Boyar R., Perlow M., Hellman L., Kapen S., Weitzman E. Twenty-four hour pattern of luteinizing hormone secretion in normal men with sleep stage recording. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 35: 73, 1972.
Bodenheimer S., Winter J.S.D., Faiman C. Diurnal rhythms of serum gonadotropins, testosterone, estradiol and Cortisol in blind men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 37: 472, 1973.
Rowe P.H., Racey P.A., Lincoln G.A., Ellwood M., Lehane J., Shenton J.C. The temporal relationship between the secretion of luteinizing hormone and testosterone in man. J. Endocrinol. 64: 17, 1975.
Michael R.P., Setchell K.D.R., Plant T.M. Diurnal changes in plasma testosterone and studies on plasma corticosteroids in non-anaesthetized male rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). J. Endocrinol. 63: 325, 1974.
Goodman R.L., Hotchkiss J., Karsch F.J., Knobil E. Diurnal variations in serum testosterone concentrations in the adult male rhesus monkey. Biol. Reprod. 11: 624, 1974.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Holder of a World Health Organization Research Training Grant. Present address: Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sjöberg, B., de la Torre, B., Hedman, M. et al. Circadian variation in systemic hormone levels in healthy men. J Endocrinol Invest 2, 131–137 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03349304
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03349304