Abstract
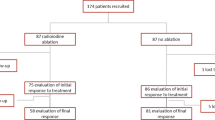
Background: Retinoic acid (RA) treatment has been used for redifferentiation of metastatic thyroid neoplasia that have lost radioiodine (131I) uptake with heterogeneous results. Aim: Retrospective analysis of the recovery rate of 1311 uptake after RA treatment in patients from 11 Spanish hospitals. Methods: Twenty-seven patients (14 men, 13 women) with papillary [21], follicular [4], and oncocytic [2] thyroid cancer initially treated with total thyroidectomy plus 131I, and with 131I negative metastatic disease, were given 13-cis RA (0.66–1.5 mg/kg for 5–12 weeks) followed by a therapeutic 131I dose (3700–7400 MBq); 3 months later thyroglobulin levels and computed tomography imaging were performed. Results: In 9 out 27 cases (33%) (8 papillary, 1 follicular) optimal positive 131I scan was observed after RA treatment; in the remaining 18, 10 had a suboptimal uptake (7 papillary, 2 follicular, 1 oncocytic) and in the rest there was no 131I uptake recovery (6 papillary, 1 follicular, 1 oncocytic). In 17 positive responses to RA (either optimal or suboptimal) in which image follow-up was available, decrease or stabilization of metastatic growth was observed in 7, while tumor mass increased at short term in the remaining 10. No major side effects were detected. Conclusion: Quite a high rate of 131I uptake recovery after RA treatment may be obtained in advanced differentiated thyroid cancer, but the potential modification of the natural course of the disease is uncertain. A better biological characterization of these tumors allowing the identification of potential responders to RA may improve the outcome of RA coadjuvant therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mazzaferri EL. Long-term outcome of patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma: effect of therapy. Endocr Pract 2000, 6: 469–76.
Mazzaferri EL and Kloos RT. Clinical review 128: Current approaches to primary therapy for papillary and follicular thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001, 86: 1447–63.
Gérard AC, Daumerie C, Mestdagh C, et al. Correlation between the loss of thyroglobulin iodination and the expression of thyroidspecific proteins involved in iodine metabolism in thyroid carcinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 4977–83.
Arturi F, Russo D, Schlumberger M, et al. Iodide symporter gene expression in human thyroid tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998, 83: 2493–6.
Schlumberger M, Challeton C, De Vathaire F, et al. Radioactive iodine treatment and external radiotherapy for lung and bone metastases from thyroid carcinoma. J Nucl Med 1996, 37: 598–605.
Brown SK, Shalita A. Acne vulgaris. Lancet 1998, 351: 1871–6.
Tallman MS. Therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia: all-trans retinoic acid and beyond. Leukemia 1998, 12: S37–40.
Altucci L, Leibowitz MD, Ogilvie KM, de Lera AR, Gronemeyer H. RAR and RXR modulation in cancer and metabolic. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007, 6: 793–810.
Schmutzler C, Brtko J, Winzer R, et al. Functional retinoid and thyroid hormone receptors in human thyroid-carcinoma cell lines and tissues. Int J Cancer 1998, 76: 368–76.
Schmutzler C, Winzer R, Meissner-Weigl J, Köhrle J. Retinoic acid increases sodium/iodide symporter mRNA levels in human thyroid cancer cell lines and suppresses expression of functional symporter in nontransformed FRTL-5 rat thyroid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997, 240: 832–8.
Schmutzler C, Kohrle J. Retinoic acid redifferentiation therapy for thyroid cancer. Thyroid 2000, 10: 393–406.
Grünwald F, Menzel C, Bender H, et al. Redifferentiation therapyinduced radioidine uptake in thyroid cancer. J Nucl Med 1998, 39: 1903–6.
Simon D, Koehrle J, Reiners C, et al. Redifferentiation therapy with retinoids: Therapeutic option for advanced follicular and papillary thyroid carcinoma. World J Surg 1998, 22: 569–74.
Simon D, Körber C, Krausch M, et al. Clinical impacts of retinoids in redifferentiation therapy of advanced thyroid cancer: final results of a pilot study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002, 29: 775–82.
Grüning T, Tiepolt C, Zöphel K, Bredow J, Kropp J, Franke WG. Retinoic acid for redifferentiation of thyroid cancer: does it holds its promise? Eur J Endocrinol 2003, 148: 395–402.
Coelho SM, Corbo R, Buescu A, Carvalho DP, Vaisman M. Retinoic acid in patients with radioiodine non-responsive thyroid cancer. J Endocrinol Invest 2004, 27: 334–9.
Short SC, Suovuori A, Cook G, Vivian G, Harmer C. A phase II study using retinoids as redifferentiation agents to increase iodine uptake in metastatic thyroid cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2004, 16: 569–74.
Liu YY, Stokkel MP, Pereira AM, et al. Bexarotene increases uptake of radioiodide in metastases of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Endocrinol 2006, 154: 525–31.
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000, 92: 205–16.
Huang Y, de la Chapelle A, Pellegata NS. Hypermethylation, but not LOH, is associated with the low expression of MT1G and CRABP1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2003, 104: 735–44.
Courbon F, Zerdoud S, Bastie D, et al. Defective efficacy of retinoic Acid treatment in patients with metastatic thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 2006, 16: 1025–31.
Shattuck T, Westra W, Ladenson P, Arnold A. Independent clonal origins of distinct tumor foci in multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2005, 352: 2406–12.
Park SY, Park YJ, Lee YJ, et al. Analysis of differential BRAF (V600E) mutational status in multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma: evidence of independent clonal origin in distinct tumor foci. Cancer 2006, 107: 1831–8.
Riesco-Eizaguirre G, Gutiérrez-Martínez P, García-Cabezas MA, Nistal M, Santisteban P. The oncogene BRAF V600E is associated with a high risk of recurrence and less differentiated papillary thyroid carcinoma due to the impairment of Na+/I-targeting to the membrane. Endocr Relat Cancer 2006, 13: 257–69.
Schmutzler C, Brtko J, Bienert K, Köhrle J. Effects of retinoids and role of retinoic acid receptors in human thyroid carcinomas and cell lines derived therefrom. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 1996, 104 (Suppl 4): 16–9.
Haugen BR, Larson LL, Pugazhenthi U, et al. Retinoic acid and retinoid X receptors are differentially expressed in thyroid cancer and thyroid carcinoma cell lines and predict response to treatment with retinoids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89: 272–80.
Vini L, Harmer C. Management of thyroid cancer. Lancet Oncol 2002, 3: 407–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, C.A., Puig-Domingo, M., Lomeña, F. et al. Effectiveness of retinoic acid treatment for redifferentiation of thyroid cancer in relation to recovery of radioiodine uptake. J Endocrinol Invest 32, 228–233 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346457
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346457