Abstract
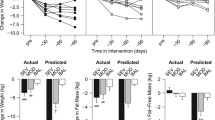
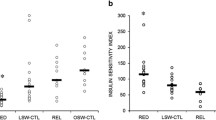
The effects of short-term (3 weeks) integrated body weight reduction (BWR) program (including energy-restricted diet, aerobic and strength exercise (5 days/week), nutritional education and psychological counseling) on plasma leptin levels and body composition were investigated in 54 morbidly obese patients (38 females/ 16 males; mean BMI±SE: 41.8±0.1 kg/m2, range 35–58 kg/m2; mean age: 29.8±1.0 yr, age range: 18–46 yr). The BWR program induced a significant (p<0.001) weight loss (BMI reduction: −4.8%) and a significant modification in body composition, consisting in a fat mass (FM) decrease (−7.0±0.4%, p<0.001) with a concomitant fat-free (FFM) mass increase (1.8±0.3%, p<0.001). On average, plasma leptin levels decreased significantly both in males (from 19.4±2.6 ng/ml to 11.6±1.3 ng/ml, p<0.001) and in females (from 41.1±3.6 ng/ml to 29.9±3.0 ng/ml, p<0.001). Both before and after weight loss, leptin levels were positively correlated (p<0.001) with BMI and percent fat mass (FM) values. Weight changes after the BWR program were negatively correlated with baseline leptin concentrations both in absolute terms and expressed per unit FM. In conclusion, a short-term diet plus aerobic/strength training effectively induces body composition changes and reduces plasma leptin levels. Body FM reduction appears to be not the unique determinant of leptin levels regulation and the degree of leptin over-expression may negatively affect weight loss in morbidly obese patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Considine R.V., Sinha M.K., Heiman M.L., et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334: 292–295.
Rissanen P., Makimattila S., Vehmas T., Taavitsainen M., Rissanen A. Effect of weight loss and regional fat distribution on plasma leptin concentration in obese women. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1999, 23: 645–649.
Wing R.R., Sinha M.K., Considine R.V., Lang W., Caro J.F. Relationship between weight loss manteinance and changes in serum leptin levels. Horm. Metab. Res. 1996, 28: 698–703.
Wadden T.A., Considine R.V., Foster G.D., Anderson D.A., Sarwer D.B., Caro J.S. Short- and long-term changes in serum leptin in dieting obese women: effects of caloric restriction and weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83: 214–218.
Minocci A, Savia G, Lucantoni R, et al. Leptin plasma concentrations are dependent on body fat distribution in obese patients. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24: 1139–1144.
Misra A., Arora N., Mondal S, et al. Relation between plasma leptin and anthropometric and metabolic covariates in lean and obese diabetic and hyperlipidaemic Asian Northern Indian subjects. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. 2001, 14: 18–26.
Duduc G.R., Phinney S.D., Stern J.S., Havel P.J. Changes of serum leptin and endocrine and metabolic parameters after 7 days of energy restriction in men and women. Metabolism 1998, 47: 429–434.
Wisse B.E., Campfield L.A., Marliss E.B., Morais J.A., Tenenbaum R., Gougeon R. Effect of prolonged moderate and severe energy restriction and refeeding on plasma leptin concentration in obese women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70: 321–330.
Mavri A., Stegnar M., Sabovic M. Do baseline serum leptin levels predict weight regain after dieting in obese women? Diabetes Obes Metab 2001, 3: 293–296.
Di Pietro L. Physical activity in the prevention of obesity: current evidence and research issues. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31: S542–S546.
Wing R.R. Physical activity in the treatment of adulthood overweight and obesity: current evidence and research issues. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31: S547–S552.
Ross R., Rissanen J., Pedwell H., Clifford J., Shragge P. Influence of diet and exercise on skeletal muscle and adipose tissue in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81: 2445–2455.
Skender M.L., Goodrick G.K., Del Junco D.J., et al. Comparison of 2-year weight loss trends in behavioral treatment of obesity: diet, exercise, and combinated interventions. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1996, 96: 342–346.
Kraemer W.J., Volek J.S., Clark K.L., et al. Influence of exercise training on physiological and performance changes with weight loss in men. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31: 1320–1329.
Sartorio A., Lafortuna C.L., Silvestri G., Narici M.V. Effects of short-term, integrated body mass reduction program on maximal oxygen consumption and anaerobic alactic performance in obese subjects. Diab. Nutr. Metab. 2003, in press.
Sartorio A., Lafortuna C.L., Conte G., Faglia G., Narici M.V. Changes in motor control and performance after a short term body mass reduction program in obese subjects. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2001, 24: 393–398.
Pérusse L., Collier G., Gagnon J., et al. Acute and chronic effects of exercise on leptin levels in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 83: 5–10.
Pasman W.J., Westerterp-Plantenga M.S., Saris W.H. The effect of exercise training on leptin levels in obese males. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274: E280–E286.
ACSM’s resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. 6th edition, Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 2000.
Lohmann T.G., Roche A.F., Martorell R. Anthropometric standardization reference manual. Human Campaign, IL, Human Kinetics Books, 1988.
Deurenberg P. International consensus conference on impedance in body composition. Age Nutr. 1994, 5: 142–145.
Lonnqvist F., Wennlund A., Arner P. Relationship between circulating leptin and peripheral fat distribution in obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1997, 21: 255–260.
Montague C.T., Prins J.B., Sanders L., Digby J.E., O’Rahilly S. Depot and sex-specific differences in human leptin mRNA expression: implications for the control of regional fat distribution. Diabetes 1997, 46: 342–347.
Ishii T., Yamakita T., Yamagami K., et al. Effect of exercise training on serum leptin levels in type 2 diabetic patients. Metabolism 2001, 50: 1136–1140.
Thong F.S.L., Hudson R., Ross R., Janssen I., Graham T.E. Plasma leptin in moderately obese men: independent effects of weight loss and aerobic exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 279: E307–E313.
Essig D.A., Alderson N.L., Ferguson M.A., Bartoli W.P., Durstine J.L. Delayed effects of exercise on plasma leptin concentration. Metabolism 2000, 49: 395–399.
Di Stefano G., Bini V., Papi F., et al. Leptin serum concentrations predict the responsiveness of obese children and adolescents to weight excess reduction program. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24: 1586–1591.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
partially supported by Progetti di Ricerca Corrente, Italian Institute for Auxology, Milan, Italy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sartorio, A., Agosti, F., Resnik, M. et al. Effects of a 3-week integrated body weight reduction program on leptin levels and body composition in severe obese subjects. J Endocrinol Invest 26, 250–256 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345165
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345165