Abstract
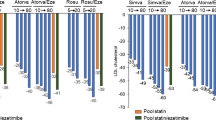
Several pieces of evidence support a role of inflammatory processes in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis; it is also known that endothelial dysfunction is the initial lesion of the atherosclerotic process. Among other markers of endothelial dysfunction, some adhesion molecules seem to play an interesting role. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of atorvastatin vs placebo on some indexes of leukocytes adhesion in a group of Type 2 diabetic patients. Twenty-five Type 2 diabetic patients free from microangiopathic complications and with LDL-cholesterol lower than 180 mg/dl were randomized to receive either atorvastatin (T2DA) or placebo (T2DP) for twelve months. BMI, fasting plasma glucose, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), albumin excretion rate (AER), lipid profile, and serum concentrations of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM1), E-selectin and cadherin-5 were measured at baseline and at the end of the follow-up. At T0 E-selectin was 16±6 ng/ml in T2DA and 17±13 in T2DP; VCAM1 was 413±112 ng/ml in T2DA and 411±112 in T2DP. At T12 VCAM1 and E-selectin did not vary in T2DP, while a significant reduction was observed in T2DA (VCAM1 275±104 ng/ml and E-selectin 8±3 ng/ml; p<0.001 and p<0.01, respectively). T2DA also showed a reduction of total and LDL cholesterol and an improved glycemic control respect to T2DP. Hypolipidemic therapy was the strongest independent predictor of the cytokines variations along the time. These results confirm the role of statins in modulating endothelial function also in Type 2 diabetes, outlining a therapeutic role of these molecules probably independent from the hypolipidemic effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ross R. Atherosclerosis: an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340: 115–126.
Frenette P.S., Wagner D.D. Insight into selectin function knock-out mice. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 78: 60–64.
Springer T.A. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration — the multistep paradigm. Cell 1994, 76: 301–314.
Hwang S.J., Ballantyne C.M., Sharrett A.R. et al. Circulating adhesion molecules VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin in carotid atherosclerosis and incident coronary heart disease cases: the Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation 1997, 96: 4219–4225.
Ridker P.M., Hennekens C.H., Roitman-Johnson B., Stampfer M.J., Allen J. Plasma concentration of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and risks of future myocardial infarction in apparently healthy men. Lancet 1998, 351: 88–92.
Steiner M., Reinhardt K.M., Kramer B., Ernst B., Blann A.D. Increased levels of soluble adhesion molecules in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus are independent of glycaemic control. Thromb. Haemost. 1994, 72: 979–984.
Ceriello A., Faletti E., Bortolotti N. et al. Increased circulating ICAM-1 levels in type 2 diabetic patients: the possible role of metabolic control and oxidative stress. Metabolism 1996, 45: 498–501.
Kado S., Wakatsuki T., Yamamoto M., Nagata N. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 induced by high glucose concentrations in human aortic endothelial cells. Life Sci. 2001, 68: 727–737.
Schmidt A.M., Yan S.D., Wautier J.L., Stern D. Activation of receptor for advanced glycation end products. A mechanism for chronic vascular dysfunction in diabetic vasculopathy and atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 1999, 84: 489–497.
Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study Group. Randomized trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 participants with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study. Lancet 1994, 344: 1383–1389.
The Long Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischemic Heart Disease (Lipid) Study Groups. Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary artery disease and broad range of initial cholesterol levels N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339: 1349–1357.
Kwang K.K. Effects of statins on vascular wall: vasomotor function, inflammation, and plaque stability. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 47: 648–657.
Williams K.V., Erbey J.R., Becker D., Arslanian S., Orchard T.J. Can clinical factors estimate insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes? Diabetes 2000, 49: 626–632.
Gearing A.J.H., Newman W. Circulating adhesion molecules in disease. Immunol. Today 1993, 14: 506–512.
Cominacini L., Fratta P.A., Garbin U. et al. E-selectin plasma concentration is influenced by glycaemic control in NIDDM patients: possibile role of oxidative stress. Diabetologia 1997, 40: 584–589.
Otzuki M., Hashimoto K., Morimoto Y., Kishimoto T., Kasayama S. Circulating vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in atherosclerotic NIDDM patients. Diabetes 1997, 46: 2096–2101.
Sardo M.A., Castaldo M., Cinquegrani M. et al. Effects of simvastatin treatment on sICAM-1 and sE-selectin levels in hypercholesterolemic subjects Atherosclerosis 2001, 155: 143–147.
Ryssy L., Yki-Järvinen H. Improvement of glycemic control by 1 year of insulin therapy leads to a sustained decrease in sE-selectin concentrations in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001, 24: 549–554.
Carmeliet P., Collen D. Molecular basis of angiogenesis. Role of VEGF and VE-cadherin. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 902: 249–264.
Targher G., Bonadonna R.C., Alberiche M., Zenere M.B., Muggeo M., Bonora E. Relation between soluble adhesion molecules and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic individuals. Diabetes Care 2001, 24: 1961–1966.
Rosenson R.S., Tangney C.C., Casey L.C. Inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine production by pravastatin. Lancet 1999, 353: 983–984.
Hardardottir I., Grünfeld C., Feingold K.R. Effects of endotoxins and cytokines on lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1994, 5: 207–215.
Stuhlmeier K.M., Tarn C., Sizmadia V., Bach F.H. Selective suppression of endothelial cells activation by arachidonic acid. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26: 1417–1423.
Sernè E.H., Stehouwer C.D.A., ter Maaten J.C. et al. Microvascular function relates to insulin sensitivity and blood pressure in normal subjects. Circulation 1999, 99: 896–902.
Burnett J.R. Wilcox L.T., Telford D.E. et al. Inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase by atorvastatin decreases both VLDL and LDL apolipoprotein B production in miniature pigs. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997, 11: 2589–2600.
Ferri C., Bellini C., Desideri G. et al. Clustering of endothelial markers of vascular damage in human salt-sensitive hypertension: influence of dietary sodium load and depletion. Hypertension 1998, 32: 862–868.
De Caterina R., Ghiadoni L., Taddei S. et al. Soluble Eselectin in essential hypertension: a correlate of vascular structural changes. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14: 259–266.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalla Nora, E., Passaro, A., Zamboni, P.F. et al. Atorvastatin improves metabolic control and endothelial function in Type 2 diabetic patients: A placebo-controlled study. J Endocrinol Invest 26, 73–78 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345126
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345126