Abstract
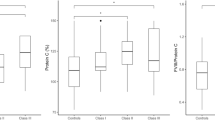
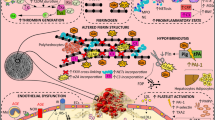
Abnormalities in coagulation and haemostasis represent a well-known link between obesity and thrombosis (both arterial and venous). Several studies have shown that obese patients have higher plasma concentrations of all pro-thrombotic factors (fibrinogen, vonWillebrand factor (vWF), and factor VII), as compared to non-obese controls, with a positive association with central fat. Similarly, plasma concentrations of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) have been shown to be higher in obese patients as compared to non-obese controls and to be directly correlated with visceral fat. Furthermore, obesity is characterized by higher plasma concentrations of anti-thrombotic factors, such as tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) and protein C, as compared to non-obese controls, the increase in these factors being likely to represent a protective response partly counteracting the increase in pro-thrombotic factors. The issue of whether adipose tissue contributes directly to plasma PAI-1, its products stimulating other cells to produce PAI-1, or whether it primarily contributes indirectly has not yet been resolved. It has been proposed that the secretion of interleukin-6 (IL-6) by adipose tissue, combined with the actions of adipose tissue-expressed TNF-α in obesity, could underlie the association of insulin resistance with endothelial dysfunction, coagulopathy, and coronary heart disease. The role of leptin in impairing haemostasis and promoting thrombosis has been recently reported. Finally, some hormonal abnormalities (androgen, F, catecholamines) associated with the accumulation of body fat may contribute to the impairment of coagulative pathway in obesity. As to intervention strategies, dietary (i.e., low-fat high-fiber diet) and lifestyle (i.e., physical activity) measures have been demonstrated to be effective in improving the obesity-associated pro-thrombotic risk profile.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Despres J.P. Health consequences of visceral obesity. Ann. Med., 2001, 33: 534–541.
De Pergola G., De Mitrio V., Giorgino F. et al. Increase in both pro-thrombotic and anti-thrombotic factors in obese premenopausal women: relationship with body fat distribution. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1997, 21: 527–535.
De Pergola G., De Mitrio V., Sciaraffia M. et al. Lower androgenicity is associated with higher plasma levels of prothrombotic factors irrespective of age, obesity, body fat distribution, and related metabolic parameters in men. Metabolism 1997, 46: 1287–1293.
Cigolini M., Targher G., Bergamo Andreis I.A., Tonoli M., Agostino G., De Sandre G. Visceral fat accumulation and its relation to plasma hemostatic factors in healthy men. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1996, 16: 368–374.
Sakkinen P.A., Wahl P., Cushman M., Lewis M.R., Tracy R.P. Clustering of procoagulation, inflammation, and fibrinolysis variables with metabolic factors in insulin resistance syndrome. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152: 897–907.
Kario K., Matsuo T., Kobayashi H., Matsuo M., Sakata T., Miyata T. Activation of tissue factor-induced coagulation and endothelial cell dysfunction in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients with microalbuminuria. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15: 1114–1120.
Gallistl S., Sudi K.M., Borkenstein M., Weinhandl G., Zotter H., Muntean W. Correlation between cholesterol, soluble P-selectin, and D-dimer in obese children and adolescents. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2000, 11: 755–760.
Hong Y., Pedersen N.L., Egberg N., de Faire U. Moderate genetic influences on plasma levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and evidence of genetic and environmental influences shared by plasminogen activator inhibitor- 1, triglycerides, and body mass index. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997, 17: 2776–2782.
Sartori M.T., Vettor R., De Pergola G. et al. Role of the 4G/5G polymorphism of PaI-1 gene promoter on PaI-1 levels in obese patients: influence of fat distribution and insulin-resistance. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86: 1161–1169.
Vambergue A., Rugeri L., Gaveriaux V. et al. Factor VII, tissue factor pathway inhibitor, and monocyte tissue factor in diabetes mellitus: influence of type of diabetes, obesity index, and age. Thromb. Res. 2001, 101: 367–375.
Lowe GD, Rumley A, Woodward M, Reid E, Rumley J. Activated protein C resistance and the FV:R506Q mutation in a random population sample: associations with cardiovascular risk factors and coagulation variables. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 81: 918–924.
Pannacciulli N., De Mitrio V., Sciaraffia M., Giorgino R., De Pergola G. A family history of type 2 diabetes is associated with lower sensitivity to activated protein C in overweight and obese premenopausal women. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86: 1593–1594.
Mavri A., Alessi M.C., Bastelica D. et al. Subcutaneous abdominal, but not femoral fat expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) is related to plasma PAI-1 levels and insulin resistance and decreases after weight loss. Diabetologia 2001, 44: 2025–2031.
Alessi M.C., Morange P., Juhan-Vague I. Fat cell function and fibrinolysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2000, 32: 504–508.
Eriksson P., Van Harmelen V., Hoffstedt J. et al. Regional variation in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in adipose tissue from obese individuals. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83: 545–548.
Loskutoff D.J., Fujisawa K., Samad F. The fat mouse. A powerful genetic model to study hemostatic gene expression in obesity/NIDDM. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 902: 272–282.
Seki T., Miyasu T., Noguchi T. et al. Reciprocal regulation of tissue-type and urokinase-type plasminogen activators in the differentiation of murine preadipocyte line 3T3-L1 and the hormonal regulation of fibrinolytic factors in the mature adipocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2001, 189: 72–78.
Kruszynska Y.T., Yu J.G., Olefsky J.M., Sobel B.E. Effects of troglitazone on blood concentrations of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 in patients with type 2 diabetes and in lean and obese normal subjects. Diabetes 2000, 49: 633–639.
Nordt T.K., Bode C., Sobel B.E. Stimulation in vivo of expression of intra-abdominal adipose tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor type I by proinsulin. Diabetologia 2001, 44: 1121–1124.
Samad F., Pandey M., Bell P.A., Loskutoff D.J. Insulin continues to induce plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 gene expression in insulin-resistant mice and adipocytes. Mol. Med. 2000, 6: 680–692.
Yudkin J.S. Abnormalities of coagulation and fibrinolysis in insulin resistance. Evidence for a common antecedent? Diabetes Care 1999, 22: C25–C30.
Westerbacka J., Yki-Järvinen H., Turpeinen A. et al. Inhibition of platelet-collagen interaction: an in vivo action of insulin abolished by insulin resistance in obesity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22: 167–172.
Chan P., Huang T.Y., Shieh S.M., Lin T.S., Tsai C.W. Thrombophilia in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 1997, 4: 425–429.
He G., Pedersen S.B., Bruun J.M., Richelsen B. Regulation of plasminogen activitor inhibitor-1 in human adipose tissue: interaction between cytokines, cortisol and estrogen. Horm. Metab. Res. 2000, 32: 515–520.
Skurk T., Lee Y.M., Hauner H. Angiotensin II and its metabolites stimulate PAI-1 protein release from human adipocytes in primary culture. Hypertension 2001, 37: 1336–1340.
Halleux C.M., Declerck P.J., Tran S.L., Detry R., Brichard S.M. Hormonal control of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene expression and production in human adipose tissue: stimulation by glucocorticoids and inhibition by catecholamines. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84: 4097–4105.
De Pergola G., De Mitrio V., Perricci A. et al. Influence of free testosterone on antigen levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in premenopausal women with central obesity. Metabolism 1992, 41: 131–134.
Kostantinides S., Schafer K., Loskutoff D.J. The prothrombotic effects of leptin possible implications for the risk of cardiovascular disease in obesity. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 947: 134–141.
Maruyama I., Nakata M., Yamaji K. Effect of leptin. Obesity and arterial thrombosis. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 902: 315–319.
Ozata M., Avcu F., Durmus O., Yilmaz I., Ozdemir I.C., Yalcin A. Leptin does not play a major role in platelet aggregation in obesity and leptin deficiency. Obes. Res. 2001, 9: 627–630.
De Mitrio V., De Pergola G., Vettor R. et al. Plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-I is associated with plasma leptin irrespective of body mass index, body fat mass, and plasma insulin and metabolic parameters in premenopausal women. Metabolism 1999, 48: 960–964.
Morange P.E., Lijnen H.R., Alessi M.C., Kopp F., Collen D., Juhan-Vague I. Influence of PAI-1 on adipose tissue growth and metabolic parameters in a murine model of diet-induced obesity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20: 1150–1154.
Morange P.E., Bastelica D., Bonzi M.F. et al. Influence of t- PA and u-PA on adipose tissue development in a murine model of diet-induced obesity. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 87: 306–310.
Gallistl S., Sudi K.M., Cvirn G., Muntean W., Borkenstein M. Effects of short-term energy restriction and physical training on haemostatic risk factors for coronary heart disease in obese children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25: 529–532.
Bastard J.P., Vidal H., Jardel C. et al. Subcutaneous adipose tissue expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor- 1 gene during very low calorie diet in obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24: 70–74.
Marckmann P. Dietary treatment of thrombogenic disorders related to the metabolic syndrome. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 83 (Suppl.): S121–S126.
Yosefy C., Viskoper J.R., Laszt A. et al. The effect of fish oil on hypertension, plasma lipids, and hemostasis in hypertensive, obese, dyslipidemic patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 1999, 61: 83–87.
Charles M.A., Morange P., Eschwege E., Andre P., Vague P., Juhan-Vague I. Effect of weight change and metformin on fibrinolysis and the von Willebrand factor in obese nondiabetic subjects: the BIGPRO1 Study. Biguanides and the prevention of the risk of obesity. Diabetes Care 1998, 21: 1967–1972.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Pergola, G., Pannacciulli, N. Coagulation and fibrinolysis abnormalities in obesity. J Endocrinol Invest 25, 899–904 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03344054
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03344054