Abstract
The field of human body composition research is reaching a mature stage in its development. Quantifying the main body components is integral to the study of growth, as the assessment of human physical characteristics is important both in anthropological and medical fields. This article will focus on body composition methodology. Specifically, our attention is aimed at estimates of body fatness. An overview is first provided of the five-level model of body composition as it relates to measures of fatness. We then provide general concepts related to techniques for estimating body composition. Finally, we briefly discuss the measurement of adipose tissue distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray G.A. Contemporary Diagnosis and Management of Obesity. H.H.C. Newton, Pennsylvania, 1998.
Heymsfield S.B., Allison D.B., Heshka S., Pierson R.N. Jr. Assessment of human body composition. In Allison D.B. (Ed.), Handbook of assessment methods for eating behaviors and weight-related problems. SAGE Publications, Thousand Oaks, California, 1995, p. 515.
National Institute of Health. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: the Evidence Report. Department of Health and Human Services, Bethesda, 1998.
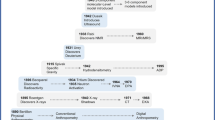
Wang Z.M., Pierson R.N. Jr., Heymsfield S.B. The five level model: a new approach to organizing body composition research. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 56: 19–28.
Yasumura S., Wang J., Pierson R.N. Jr. (Eds). In vivo body composition studies. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., vol. 904, 2000.
Roche A.F., Heymsfield S.B., Lohman T.G. (Eds.), Human body composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1996.
Heymsfield S.B., Wang Z.M., Baumgartner R.N., Ross R. Human body composition: advances in models and methods. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997; 17: 527–558.
Ellis K.J. Human body composition: in vivo methods. Physiol. Rev. 2000; 80: 649–680.
Pietrobelli A., Heymsfield S.B., Wang Z.M., Gallagher D. Multi-component body composition models: recent advances and future directions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 55: 69–75.
Heymsfield S.B., Wang Z.M., Gallagher D., Pietrobelli A. Multicomponent models of body composition: an overview. In: Pierson R.N. Jr. (Ed.), Quality of the cell body mass. Serono Symposia USA. Springer-Verlag, New York, 2000, p. 33.
Pietrobelli A., Heo M., Faith M.S. Assessment of childhood and adolescents body composition: a practical guide. In Dasgupta P., Hauspie R. (Eds.), Perspectives in human growth, development and maturation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands, 2001, p. 67.
Pietrobelli A., Wang Z.M., Heymsfield S.B. Techniques used in measuring human body composition. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 1998, 1: 439–448.
Pierson R.N. Jr. (Ed.), Quality of the cell body mass. Serono Symposia USA. Springer-Verlag, New York, 2000.
Pierson R.N. Jr., Wang J., Heymsfield S.B., Dilmanian F.D., Weber D.A. High precision in vivo neutron activation analysis: a new era for compartmental analysis on body composition. In: Yasumura S., Harrison J., McNeil G.G., Woodhead A.D., Dilmanian F.D. (Eds.), In vivo body composition studies. Plenum Press, New York, 1990, p. 317.
Heymsfield S.B., Waki M., Kehayias J.J. et al. Chemical and elemental analysis of humans in vivo using improved body composition models. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261: E190–E198.
Kehayias J.J., Heymsfield S.B., LoMonte A.F., Wang J., Pierson R.N. Jr. In vivo determination of body fat by measuring total body carbon. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53: 1339–1344.
Snyder W.M., Cook M.J., Nasset E.S., Karhausen L.R., Howells G.P., Tipton I.H. Report of the task group on reference man. Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1975.
Comizio R., Pietrobelli A., Tan Y.X. et al. Total body lipid and triglyceride response to energy deficit: relevance to body composition models. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274: E860–E866.
Behnke A.R., Feen B.G., Welham W.C. The specific gravity of healthy men. JAMA 1942, 118: 495–498.
Moore F.D., Oleson K.H., McMurray J.D., Parker H.V., Ball M.R. The body cell mass and its supporting environment. Saunders Publishing, Philadelphia, 1963.
Hoffman J.G., Hempelmann L.H. Estimation of whole-body radiation doses in accidental fission bursts. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1957, 77: 144–160.
Anderson J., Osborn S.B., Tomlinson R.W.S. et al. Neutronactivation analysis in man in vivo. A new technique in medical analysis. Lancet 1964, 2: 1201–1205.
Ryde S.J.S. In vivo neutron activation analysis. In Pierson RN Jr. (Ed.), Quality of the cell body mass. Serono Symposia USA. Springer-Verlag, New York, 2000, p. 103.
Ellis K.J. Whole body counting and neutron activation analysis. In: Roche A.F., Heymsfield S.B., Lohman T.G. (Eds.), Human body composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1996, p. 45.
Forbes G.B. Human body composition. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1987.
Schoeller D.A., van Santen E., Peterson D.W., Diets W., Jaspan J., Klein P.D. Total body water measurement in humans with 18O and 2H labeled water. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1980, 33: 2686–2693.
Schoeller D.A.. Hydrometry. In: Roche A.F., Heymsfield S.B., Lohman T.G. (Eds.), Human body composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1996, p. 25.
Yanovski S.Z., Heymsfield S.B., Lukaski H.C., Bioelectrical impedance analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64 (S3): 387–532.
Baumgartner R.N. Electrical impedance and total body electrical conductivity. In: Roche A.F., Heymsfield S.B., Lohman T.G. (Eds.), Human body composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1996, p. 79.
Pietrobelli A., Morini P., Battistini N.C., Chiumello G., Nunez C., Heymsfield S.B. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass: prediction from multiple frequency segmental bioimpedance analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 52: 507–511.
Pietrobelli A., Formica C., Wang Z.M., Heymsfield S.B. Dual energy X-ray Absorptiometry body composition model: review of physical concepts. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271: E941–E951.
Lohman T.G. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. In: Roche A.F., Heymsfield S.B., Lohman T.G. (Eds.), Human body composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1996, p. 63.
Pietrobelli A., Wang Z.M., Formica C., Heymsfield S.B. Dual energy X-ray Absorptiometry: fat estimation errors due to variation in soft tissue hydration. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274: E860–E866.
Despres J.P., Ross R., Lemieux S. Imaging techniques applied to the measurement of human body composition. In: Roche A.F., Heymsfield S.B., Lohman T.G. (Eds.), Human body composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1996, p. 149.
Roche A.F. Anthropometry and ultrasound. In: Roche A.F., Heymsfield S.B., Lohman T.G. (Eds.), Human body composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1996, p. 167.
Pi-Sunyer X.P. Obesity: criteria and classification. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2000 59: 505–509.
Allison D.B., Zhu S.K., Plankey M., Faith M.S., Heo M. Differential association of body mass index and adiposity with all-cause mortality among men in the first and second National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES I and NHANES II) follow-up studies. Int. J. Obes. 2002, 26: 410–416.
Calle E.E., Thun M.J., Petrelli J.M., Rodriguez A., Heath C.W. Jr. Body mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of U.S. adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341: 1097–1105.
Cole T.J., Bellizzi M.C., Flegal K.M., Dietz W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 2000, 320: 1240–1243.
Ellis K.J., Abrams S.A., Wong W.W. Monitoring childhood obesity: assessment of the weight/height2 index. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 150: 939–946.
Pietrobelli A., Faith M.S., Allison D.B., Gallagher D., Chiumello G., Heymsfield S.B. Body mass index as a measure of adiposity among children and adolescent: a validation study. J. Pediatr. 1998, 132: 204–210.
Horswill C.A., Geesman R., Boileau R.A., Williams B.T., Layman D.K., Massey B.H. Total body electrical conductivity (TOBEC): relationship to estimates of muscle mass, fat-free weight, and lean body mass. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 49: 593–598.
Fogelholm M., van Marken Lichtenbelt W. Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 51: 495–503.
Going S.B. Densitometry. In: Roche A.F., Heymsfield S.B., Lohman T.G. (Eds.), Human body composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1996, p. 3.
Nunez C., Kovera A., Pietrobelli A. et al. Body composition in children and adults by air displacement plethysmography. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53: 382–387.
Deurenberg P. Methods for determining fat mass and fat distribution. Acta Pediatr. Suppl. 1992, 383: 53–57.
Durning J.V.G.A., Womersley J. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 17 to 72 years. Br. J. Nutr. 1974, 32: 77–97.
Poliot M.C., Despres J.P., Lemieux S., Moorjani S., Bouchard C., Tremblay A. Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women. Am. J. Cardiol. 1994, 73: 460–468.
Chan J.M., Rimm E.B., Colditz G.A., Stampfer M.J., Willett W.C. Obesity, fat distribution, and weight gain as risk factors for clinical diabetes in men. Diabetes Care 1994, 17: 961–969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pietrobelli, A., Heymsfield, S.B. Establishing body composition in obesity. J Endocrinol Invest 25, 884–892 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03344052
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03344052