Abstract
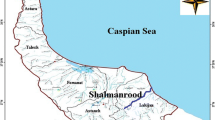
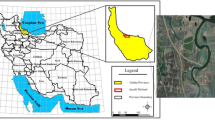
During estuarine mixing, dissolved metals come into the particulate phase due to the flocculation processes. Such processes are biologically vital. In the present study, controlling mechanisms of elemental flocculation during estuarine mixing in northern and southern estuaries of Iran in relation to the various physical and chemical parameters of waters have been compared. Except for zinc and lead, for other studied elements in Minab River, water flocculate at higher rates in comparison with the rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea. Redox potential might have negative effect on flocculation process in Minab Estuary. Contrary to rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea, in Minab River elemental flocculation is governed by dissolved organic carbon and it shows a non-liner and conservative behavior during estuarine mixing which implies that dissolved organic carbon originates from terrigenous source. The results also shows that maximum removal of elements occurs in lower salinities (1.5 to 5.8 ‰) for the rivers in North of Iran and 3.3 to 11.4 ‰ for Minab River in South of Iran. Flocculation of studied metal in different rivers results in reduction of overall metal pollution load by various percentages. The initial metal contents on river water and mean discharge of river might lead to higher flocculation rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achterberg, E. P.; Herzl, V. M. C.; Braungardt, C.B.; Millward, G. E.; (2003). Metal behaviour in an estuary polluted by acid mine drainage: The role of particulate matter. Environ. Pollut., 121(2), 283–292 (10 pages).
Anderson, A. J. B. (1971). Numerical examination of multivariate soil samples. Math. Geol. 3(1), 1–14 (14 pages).
Anikiev, V. V.; Goryachev, N. A. (1991). Heavy metals behavior at mixing between marine and riverine waters. Geokhimiya, 11, 6–42 (37 pages).
Bewers, J. M.; Mac, A. I. D.; Sundby, B., (1974). Trace metals in the waters of Gulf of St. Lawrence. Can. J. Earth Sci., 11, 939–950 (12 pages).
Biati. A.; Moattar, F.; Karbassi, A. R.; Hassani, A. H., (2010a). Role of saline water in removal of heavy elements from industrial wastewaters. Int. J. Environ. Res., 4(1), 169–176 (8 pages).
Biati. A.; Karbassi, A. R.; Hassani, A. H.; Monavari, S. M.; Moattar, F., (2010b). Role of metal species in flocculation rate during estuarine mixing. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(2), 327–336 (10 pages).
Boyle, E.A.; Edmond, J. M.; Sholkovitz, E. R., (1977). The mechanism of Fe removal in estuaries. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 41(9), 1313–1324 (12 pages).
Davis, J. B., (1973). Statistic and data analysis in geology. Wiley, New York, 456–473 (18 pages).
Deck, B. L., (1981). Nutrient-element distribution in Hudson estuary. Ph.D. thesis. Columbia University, New York.
Duinker, J.C.; Nolthing, R. F., (1978). Mixing, removal and mobilization of trace metals in the Rhine estuary. Neth. J. Sea Res., 12, 205–223 (19 pages).
Duinker, J. C.; Nolting, R. F.; Michel, D., (1983). Effects of salinity, pH and redox conditions on the behavior of Cd, Zn, Ni and Mn in the Scheldt estuary. Thalassia Jugosl., 18, 191–201 (11 pages).
Eckert, J. M.; Sholkovitz, E. R., (1976). The flocculation of Fe, Al and humates from river water by electrolytes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 40(7), 847–848 (2 pages).
Featherstone, A. M., O’Grady, B. V., (1997). Removal of dissolved Cu and Fe at the freshwater - seawater interface of an acid mine stream. Mar. Poll., 34(5), 332–337 (6 pages).
Gerringa, L. J. A.; de Baar, H. J. W.; Nolthing, R. F.; Paucot, H., (2001). The influence of salinity on the solubility of Zn and Cd sulfides in the Scheldt estuary. Sea Res., 46,(3–4) 201–211 (11 pages).
Hassani, A. H.; Seif, S.; Javid, A. H.; Borghei, M., (2008) Comparison of Adsorption Process by GAC with Novel Formulation of Coagulation - Flocculation for Color Removal of Textile Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res., 2(3), 239–248 (10 pages).
Hunter, K. A., (1983). On the estuarine mixing of dissolved substances in relation to colloidal stability and surface properties. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 47(3), 467–473 (7 pages).
Karbassi, A. R.; Nadjafpour, S., (1996). Flocculation of dissolved Pb, Cu, Zn, and Mn during estuarine mixing of river water with the Caspian Sea. Environ. Pollut., 93, 257–260 (4 pages).
Karbassi, A. R.; Nouri, J.; Ayaz, G. O., (2007). Flocculation of trace metals during mixing of Talar river water with Caspian seawater. Int. J. Environ. Res. 1(1), 66–73 (8 pages).
Karbassi, A. R.; Nouri, J.; Mehrdadi, N.; Ayaz, G. O., (2008a). Flocculation of heavy metals during mixing of freshwater with Caspian seawater. Environ. Geol., 53(8), 1811–1816 (6 pages).
Karbassi, A. R.; Nouri, J.; Nabi Bidhendi, Gh. R.; Ayaz, G. O., (2008b). Behavior of Cu, Zn, Pb, Ni and Mn during mixing of freshwater with the Caspian seawater. Desalination, 229(1–3), 118–124 (7 pages).
Krachler, R.; Jirsa, F.; Ayromlou, S., (2005). Factors influencing the dissolved iron input by river water to the open ocean. Biogeosciences Discussions., 2, 537–549 (13 pages).
Lance, G. N.; William, W. T., (1966). A Generalized sorting for computer classification. Nature. 212–218 (7 pages).
Mantoura, R. F. C.; Mann, S. V., (1979). Dissolved organic carbon in estuaries. In: Severn, R. T.; Dineley, D., Hawker, L. E. (Ed.) Tidal power and estuary management. Bristol, Scientechnical. 279–286 (8 pages).
Martoura. R. F. C.; Woodward, E. M. S., (1983). Conservative behavior of riverine dissolved organic carbon in the Severn estuary: Chemical and geochemical implications. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 47(7), 1293–1309 (17 pages).
Matagi, S. V.; Swai, D.; Mugabe, R., (1998). A review of heavy metal removal mechanisms in wetlands. Afr. J. Trop. Hydrobiol. Fish., 8(1–2), 23–25 (3 pages).
Meire, P.; Ysebaert, T.; Van Damme, S.; Van den Bergh, E.; Maris, T.; Struyf, E., (2005). The Scheldt estuary: A description of a changing ecosystem. Hydrobiologia, 540(1–3), 1–11 (11 pages).
Meyer, J. L., Tate, C. M., (1983). The effects of watershed disturbance on dissolved organic carbon dynamics of a stream. Ecology., 64(1), 33–44 (12 pages).
Moor. R. M.; Burton, J. D.; Williams, P. J. B.; Young, M. L., (1979). The behavior of dissolved organic material, Fe and Mn in estuarine mixing. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 43(6), 919–926 (8 pages).
Pritchard, D. W. (1967). What is an estuary: Physical viewpoints. Estuaries, G. H. Lauff (Ed.). Publication No. 83, American Association for the Advanced of Science, Washington, D. C., 3–5 (3 pages).
Saeedi, M.; Karbassi, A. R., Mehrdadi, N. (2003). Flocculation of dissolved Mn, Zn, Ni and Cu during the estuarine mixing of Tadjan river water with Caspian seawater. Int. J. Environ. Stud., 60(6), 567–576 (10 pages).
Samarghandi, M. R.; Nouri, J.; Mesdaghinia, A. R.; Mahvi, A. H.; Nasseri, S.; Vaezi, F., (2007). Efficiency removal of phenol, lead and cadmium by means of UV/TiO2/H2O2 processes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(1), 19–25 (7 pages).
Savchenko, A. V., Gramm-Osipov, L. M., Mar’yash, A. A (2009). Physicochemical modeling of the behavior of microelements (As, V, Cr, Co and Hg) under the mixing of riverine and marine waters (the Razdol’naya River-Amur Bay system). Oceanology, 49(1), 39–46 (8 pages).
Shankar, R.; Karbassi, A. R., (1992). Flocculation of Cu, Zn, Ni and Fe during mixing of Mulki river water and Arabian seawater, west of India. Proceedings of 7th international symposium on water rock interaction, Utah, USA, 565–568 (4 pages).
Sharp, J. H., (1991). Review of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus biogeochemistry. Rev. Geophys., 29, 648–657 (10 pages).
Shokovitz, E. R., (1976). Flocculation of dissolved organic and inorganic matter during the mixing river water and seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 40(7), 831–845 (15 pages).
Sholkovitz, E. R.; Boyle, E. A.; Price, N. B., (1977). Removal of dissolved material in the Amazon estuary. Eos. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union., 5, 423–439 (17 pages).
Zhiqing. L. E., Jianhu, Z., Jinsi, C., (1987). Flocculation of dissolved Fe, Al, Mn, Si, Cu, Pb and Zn during estuarine mixing. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 6(44), 567–576 (10 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biati, A., Karbassi, A.R. Comparison of controlling mechanisms of flocculation processes in estuaries. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 731–736 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326182
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326182