Abstract
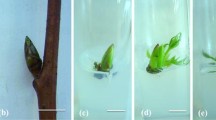
In vitro clonal propagation of Capparis decidua was achieved using nodal explants from mature trees, and cotyledonary node, cotyledon and hypocotyl explants taken from the seedlings. Explants cultured on MS medium supplemented with BAP showed differentiation of multiple shoots and shoot buds in 4–5 weeks in the primary cultures. The medium with BAP (5 mg/l) was the best for shoot bud proliferation from the nodal as well as seedling explant. Shoot multiplication was best on cotyledonary node. In the nodal explants shoot multiplication was best on medium supplemented with 5 mg/l BAP and after second subculturing further multiplication of shoot buds was highest on the medium containing 3 mg/l BAP. Shoots were separated from mother cultures in each subculturing for rooting. Rooting was best achieved using 1 mg/l IBA in the medium. Rooted plantlets were transferred td earthen pots with garden soil and peat moss mixture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
6 — benzylaminopurine
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- IBA:
-
Indole-3-butyric acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog (1962) medium
References
Rodriguez R, Rey M, Cuozzol L & Ancora G, In vitro Dev Biol, 6 (1990) 531.
Bhandari MM, Flora of the Indian desert, MPS Repros, Jodhpur (1995).
Khoshoo TN, Curr Sci, 70 (1996) 205.
Murashige T & Skoog F, Physiol Plant, 15 (1962) 473.
Fijorino P & Lorenti F, Hort Science, 22 (1987) 353.
Mittal A, Agarwal R & Gupta SC, Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult, 19 (1989) 65.
Dhawan V, In Plant biotechnology: Commercial prospects and problems (J Prakash, RLM Pierik, Editors) Oxford & IBH Publishers, New Delhi (1993) p 43.
Rahman SM, Hossain M, Biswas BK, Joarder OI & Islam R, Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult, 32 (1993) 363.
Barve DM & Mehta AR, Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult, 35 (1993) 237.
Kothari SL & Chandra N, Hort Science, 19 (1984) 703.
Sivadas P, Kothari SL & Chandra N, Plant Cell Rep, 9 (1990) 93.
Oinam GS & Kothari SL, Plant Cell Rep, 14 (1995) 245.
Sharma VK, Rao A, Varshney A & Kothari SL, Plant Cell Rep, 15 (1995) 227.
Jaiwal PK & Gulati A, Plant Cell Rep, 10 (1991) 569.
Khalekuzzaman M, Islam R, Reza MA & Joarder OI, Phytomorphology, 45 (1995) 107.
Dwari M & Chand PK, Phytomorphology, 46 (1996) 123.
Detrez C, Nediaye S & Dreyfus B, Plant Cell Rep, 14 (1994) 87.
Nandwani D & Ramawat KG, Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult, 29 (1992) 173.
Amin MN & Jaiswal VS, Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult, 9 (1987) 235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tyagi, P., Kothari, S.L. Micropropagation of Capparis decidua through In Vitro Shoot Proliferation on Nodal Explants of Mature Tree and Seedling Explants. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 6, 19–23 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03263003
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03263003